The largest artery in the body:
Carotid.
Aorta.
Celiac.
Femoral.
The Correct Answer is B
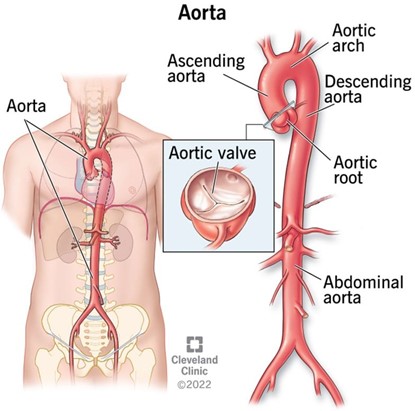
The aorta is the largest artery in the human body, as well as the main artery in the circulatory system.
It originates from the left ventricle of the heart and extends down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries).
The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation.
Choice A. Carotid is wrong because the carotid artery is not the largest artery in the body, but one of the main arteries that pumps blood from the heart to the brain and the rest of the head.
It has a diameter of 4.3 mm-7.7 mm and a blood flow of 350-550 milliliters per minute.
Choice C. Celiac is wrong because the celiac artery is not the largest artery in the body, but a major branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, spleen, pancreas, and duodenum.
Choice D. Femoral is wrong because the femoral artery is not the largest artery in the body, but the largest artery found in the leg region.
It runs down the inner thigh and carries out the important role of supplying blood to the lower body.
It has a diameter of 6.6 mm and a blood flow of 284 milliliters per minute.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Capillary walls consist of a single layer of epithelial cells, and they exchange substances in the blood for substances in the tissue fluid surrounding body cells.
This single layer of cells is called the endothelium and it forms the barrier between the blood and the interstitial fluid.
The endothelium can be either continuous or fenestrated, depending on the tissue type and function.
The capillaries are very thin and allow red blood cells to flow through them single file.
The capillaries also have a layer of a glycoprotein called the glycocalyx that covers their luminal surface.
Choice B. False is wrong because it contradicts the definition and structure of capillaries.
Capillaries are not made of multiple layers of cells, nor do they prevent the exchange of substances between the blood and the tissue fluid.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin by thrombin is the final step in the formation of a blood clot.
Fibrin is a protein that forms a net-like structure that traps platelets and other blood cells, making the clot stronger and more durable.
Choice A is wrong because the formation of a prothrombin activator is the first step in the formation of a blood clot.
A prothrombin activator is a complex of enzymes that converts prothrombin to thrombin.
Choice B is wrong because the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin by the prothrombin activator is the second step in the formation of a blood clot.
Thrombin is an enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
Choice D is wrong because tissue damage is not a step in the formation of a blood clot, but a trigger for the clotting process.
When blood vessels are injured, they release substances that activate platelets and clotting factors.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
