After administering furosemide 20 mg PO to a client diagnosed with hypertension and peripheral edema, which finding would best indicate that the therapeutic effect of the medication has been achieved?
Blood pressure remains stable at 130/86 mmHg.
Lungs are clear to auscultation.
Serum potassium has decreased from 4.0 to 3.5 mEq/L.
Urine output increases from 30 mL per hour to 100 mL per hour.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A Reason
While maintaining a stable blood pressure is important for a client with hypertension, furosemide is primarily a diuretic, and its therapeutic effect is to reduce fluid overload, not directly to stabilize blood pressure. Therefore, this finding alone does not best indicate the therapeutic effect of furosemide.
Choice B Reason
Clear lungs upon auscultation suggest an improvement in pulmonary edema, which can be associated with fluid overload in conditions such as heart failure. However, for a client with peripheral edema, the primary therapeutic goal of furosemide is to reduce the excess fluid in the extremities, not just the lungs.
Choice C Reason
A decrease in serum potassium is a known side effect of furosemide due to its action on the kidneys, leading to increased excretion of potassium. While it's important to monitor for hypokalemia, a decrease in potassium does not directly indicate the therapeutic effect of reducing edema.
Choice D Reason
An increase in urine output from 30 mL per hour to 100 mL per hour is a direct indication that furosemide is achieving its therapeutic effect. Furosemide is a loop diuretic that increases urine production to help the body eliminate excess fluid, thereby reducing edema associated with conditions like hypertension.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Using bronchodilators every 2 hours as needed may not be appropriate for all clients. Bronchodilators are typically used on a schedule or as needed based on symptoms, but overuse can lead to tolerance and decreased effectiveness. The nurse should provide education on the proper use and timing of bronchodilators.
Choice B reason:
Pursed-lip breathing is a technique that helps control shortness of breath and improve ventilation. It can slow down the client's breathing, promote relaxation, and ensure more effective lung function. This technique is particularly beneficial during an acute exacerbation of COPD and should be included in the discharge teaching plan.
Choice C reason:
Increasing home oxygen without proper assessment can be dangerous. Oxygen therapy should be titrated based on the client's oxygen saturation and clinical status. Clients with COPD are at risk of CO2 retention, and too much oxygen can suppress their drive to breathe. The nurse should educate the client on monitoring their SpO2 and when to adjust oxygen levels, typically under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Choice D reason:
Huff coughing is a technique used to clear mucus from the airways. While it can be effective, it should be taught by a respiratory therapist or nurse who can assess the client's ability to perform the technique correctly. It is not the first-line teaching for a client being discharged with an acute exacerbation of COPD.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice a reason:
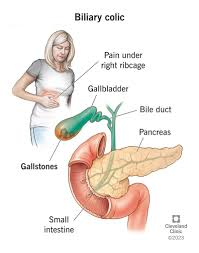
A cream to soothe itching may be used if the client is experiencing pruritus, which can sometimes accompany biliary issues due to bile salts in the skin. However, pruritus is not a direct symptom of biliary colic, which is characterized primarily by pain.
Choice b reason:
Pain medication is the appropriate treatment for biliary colic. Biliary colic is caused by the temporary blockage of the bile duct by a gallstone, leading to intense pain in the upper right abdomen or the center of the abdomen. Pain relief is typically achieved with anti-inflammatory drugs or antispasmodics, and in some cases, opioids may be necessary.
Choice c reason:
An antibiotic would be prescribed if there was an infection, such as cholecystitis or cholangitis. Biliary colic itself does not necessarily indicate an infection unless accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or elevated white blood cell count.
Choice d reason:
A laxative is not typically used to treat biliary colic. While laxatives can help relieve constipation, biliary colic is a result of gallstones obstructing the bile duct, not bowel movement issues.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
