Eight hours postoperative following a total knee replacement, which intervention should the nurse implement for the client?
Apply cool compresses to the affected limb every six hours.
Place a soft pillow under the affected knee.
Promote bedrest for 24 hours.
Encourage increased fluid intake.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A Reason
Applying cool compresses to the affected limb can help reduce swelling and provide pain relief. However, it's important to follow the surgeon's specific postoperative orders, as the application of cold can vary depending on the surgical technique and patient's condition.
Choice B Reason
Placing a soft pillow under the knee is not recommended after total knee replacement surgery. This position can lead to decreased range of motion and contractures. The knee should be kept in a more extended position to promote healing and mobility.
Choice C Reason
Promoting bedrest for an extended period is not typically advised following knee replacement surgery. Early mobilization is important to prevent complications such as deep vein thrombosis and to encourage circulation and healing. The duration of bedrest should be as per the surgeon's protocol.
Choice D Reason
Encouraging increased fluid intake is important after surgery to prevent dehydration, promote kidney function, and ensure adequate blood volume and circulation. Proper hydration is essential for healing and can help with the metabolism of medications used during and after surgery.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason:
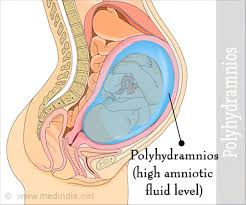
While polyhydramnios can be associated with congenital anomalies or fetal distress, it is not a direct indication of these conditions. Polyhydramnios refers specifically to the excessive accumulation of amniotic fluid. Congenital anomalies may lead to polyhydramnios if they affect the fetus's ability to swallow and process amniotic fluid normally, but the presence of polyhydramnios alone does not confirm these conditions.
Choice B reason:
Elevated levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the amniotic fluid can be indicative of neural tube defects or other fetal abnormalities, but they are not a defining characteristic of polyhydramnios. Normal AFP levels in amniotic fluid at 15 to 21 weeks' gestation range from 10 to 150 ng/ml. Polyhydramnios is diagnosed based on the volume of amniotic fluid, not the AFP levels.
Choice C reason:
Carrying more than one fetus can lead to an increased amount of amniotic fluid, potentially resulting in polyhydramnios. However, the diagnosis of polyhydramnios itself does not imply a multiple gestation pregnancy. It simply indicates that there is more amniotic fluid than usual.
Choice D reason:
Polyhydramnios is defined as an excessive amount of amniotic fluid. It is typically diagnosed when the amniotic fluid index (AFI) exceeds 24 cm or the single deepest pocket (SDP) measures more than 8 cm. This condition can occur due to various reasons, including fetal anomalies, maternal diabetes, and other medical conditions.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason
While hypertension can contribute to the development of PAD, it does not directly cause fats to deposit in the arteries. Hypertension can damage the arterial walls, making them more susceptible to atherosclerosis, but it is not the primary mechanism of PAD development.
Choice B Reason
Excess fats in the diet can contribute to atherosclerosis, which is the accumulation of plaques in the arterial walls. However, the fats do not simply get stored; they combine with other substances, including calcium and inflammatory cells, to form plaques that can restrict blood flow.
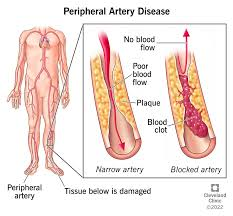
Choice C Reason
This statement is the most accurate. PAD is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaques formed by fats, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances in the blood. These plaques can harden and narrow the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the extremities. The process can be exacerbated by factors such as smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Arterial spasms can occur, but they are not the typical cause of chronic PAD. Spasms are more often associated with conditions like Raynaud's phenomenon or can be a response to stress or cold temperatures. PAD is usually a result of progressive atherosclerosis rather than intermittent spasms.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
