A nurse is teaching a client who takes acetaminophen daily to manage mild knee pain. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse reactions to this medication?
Tinnitus
Hyperglycemia
Jaundice
Muscle pain
The Correct Answer is C
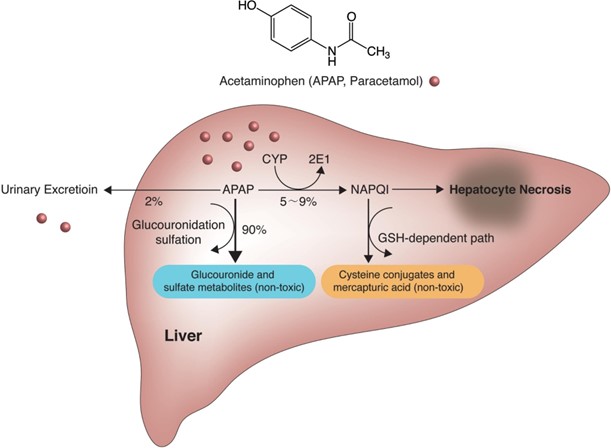
Acetaminophen is a commonly used over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer. One of the potential adverse reactions to acetaminophen is liver toxicity, which can present with symptoms such as jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, and pale stools. It is important for the client to be aware of these signs and symptoms and report them to their healthcare provider if they occur. Monitoring for jaundice can help identify any potential liver-related complications associated with acetaminophen use.
The other options provided in the question are not typically associated with acetaminophen use:
- Tinnitus: Tinnitus refers to a perception of ringing or buzzing in the ears. It is not a commonly reported adverse reaction to acetaminophen.
- Hyperglycemia: Hyperglycemia refers to high blood sugar levels. Acetaminophen does not typically cause hyperglycemia as a side effect.
- Muscle pain: Acetaminophen is used to relieve mild to moderate pain, including muscle pain. It is not an adverse reaction to the medication.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Robitussin A-C contains codeine, which is an opioid antitussive that can have sedating effects. One of the major disadvantages of using this medication is the potential for drowsiness as a side effect. This can impair the client's ability to perform tasks that require alertness and can interfere with daily activities.
The other options listed are not the major disadvantage of antitussive therapy with Robitussin A-C:
The medication is irritating to the bronchial tree: Robitussin A-C is primarily used as an antitussive (cough suppressant) rather than for its effects on the bronchial tree. While it may have some mild irritant properties due to certain ingredients, it is not considered a major disadvantage of this medication.
The client may use the medication for 14 days: The duration of use for Robitussin A-C is typically determined by the healthcare provider based on the client's condition. While prolonged use of antitussives is generally not recommended without medical supervision, the duration of use is not considered the major disadvantage of this medication.
The medication is very expensive: The cost of medication can vary, and while cost may be a consideration for some individuals, it is not considered the major disadvantage of Robitussin
A-C specifically. The major disadvantage relates more to the potential for drowsiness caused by the medication.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Expectorants are medications that help thin and loosen mucus in the respiratory tract, making it easier to cough up and clear from the airways. Increasing fluid intake, particularly water helps to keep the mucus thin and less sticky, facilitating its removal. Adequate hydration can help promote effective expectoration and relieve congestion.
The other options are incorrect because:
B. Taking the medication once a day only, usually at bedtime: The dosing frequency and timing of expectorants can vary depending on the specific medication prescribed. It is important to follow the healthcare provider's instructions regarding the dosing schedule.
C. Increase fiber and fluid intake to prevent constipation: This instruction is unrelated to expectorant use. Increasing fiber and fluid intake is commonly recommended to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation, but it is not directly related to expectorant therapy.
D. Restrict fluids to decrease mucus production: Restricting fluids can lead to dehydration and thickening of mucus secretions. It is important to stay adequately hydrated to maintain thin and easily expectorated mucus. Restricting fluids is not recommended for managing mucus production.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
