A nurse is teaching a client who has chronic kidney failure about planning a low-protein diet. The client states, "Why do I have to be concerned about protein?" Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
"A low-protein diet reduces the risk for edema."
"A low-protein diet will reduce the risk for hyperkalemia
"A low-protein diet will increase the nitrogenous wastes in the blood."
"A low protein diet reduces the risk for uremia."
The Correct Answer is D
A. Edema in chronic kidney failure is more closely associated with sodium and water retention rather than protein intake.
B. Hyperkalemia in chronic kidney failure can be managed by restricting dietary potassium intake, but it is not primarily related to protein intake.
C. A low-protein diet aims to decrease, not increase, nitrogenous wastes in the blood.
D. A low-protein diet reduces the risk for uremia, a condition resulting from chronic kidney failure where urea and other waste products build up in the body due to impaired renal function. A low-protein diet helps decrease the workload on the kidneys by reducing the amount of nitrogenous waste they need to filter and excrete.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
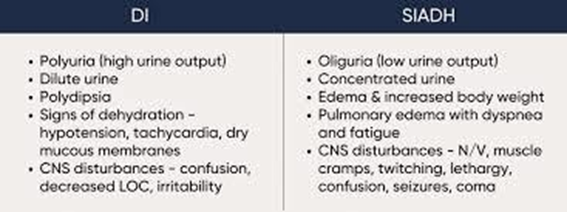
A. Hyperglycemia is associated with diabetes mellitus, not diabetes insipidus. Diabetes insipidus is characterized by excessive thirst and urination due to inadequate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), not hyperglycemia.
B. Dehydration is a hallmark finding in diabetes insipidus due to excessive urination and fluid loss. Clients with diabetes insipidus may exhibit signs of dehydration, such as dry mucous membranes, decreased skin turgor, and hypotension.
C. Bradycardia is not typically associated with diabetes insipidus.
D. Polyphagia, or excessive hunger, is a symptom of diabetes mellitus, not diabetes insipidus.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a nonspecific marker of inflammation and is not used to assess the therapeutic effect of epoetin alfa.
B. The hematocrit (Hct) measures the proportion of red blood cells in the blood. Epoetin alfa stimulates the production of red blood cells, leading to an increase in hematocrit levels, indicating a therapeutic effect of the medication.
C. The leukocyte count measures the number of white blood cells in the blood and is not relevant for assessing the therapeutic effect of epoetin alfa.
D. The platelet count measures the number of platelets in the blood and is not relevant for assessing the therapeutic effect of epoetin alfa.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
