A nurse is reinforcing teaching about immunizations with a woman in her first trimester of pregnancy whose diagnostic testing indicates she does not have immunity to rubella. The nurse should recommend that the client receive a measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine at which of the following times?
When she does not desire future pregnancies
Prior to discharge from the hospital after giving birth
Two weeks before attempting pregnancy again
Prior to giving birth
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A rationale: If the woman does not desire future pregnancies, she may not need the MMR vaccine, but the timing of vaccine administration is not appropriate for the current situation.
Choice B rationale: Administering the MMR vaccine prior to discharge from the hospital after giving birth is recommended during the postpartum period, especially if the woman is planning to have more children in the future.
Choice C rationale: The MMR vaccine contains live attenuated viruses and is contraindicated during pregnancy. If a woman is planning to become pregnant and is not immune to rubella, she should receive the MMR vaccine at least one month before attempting pregnancy. This allows time for her body to develop immunity before conception occurs.
Choice D rationale: The current guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advise that the measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine should not be administered during pregnancy due to possible effects on the uterus.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
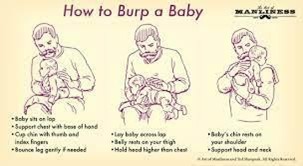
Choice A rationale: This statement is correct. Burping the baby halfway through each feeding can help release air and prevent discomfort from gas build-up.
Choice B rationale: This statement is correct. It is essential to watch for signs of satiety in the baby, such as slowing down sucking, turning away from the bottle, or becoming relaxed.
Stopping the feeding when the baby is full helps prevent overfeeding.
Choice C rationale: This statement indicates a need for further teaching. The duration of feeding can vary for different babies, and it is not advisable to limit the feeding time to a specific duration like 10 to 15 minutes. Babies have different feeding patterns and may take longer or shorter periods to finish a feeding. It is essential to allow the baby to feed until they are full and satisfied.
Choice D rationale: This statement is correct. It is safe and appropriate to give formula to the baby at room temperature, or it can be warmed if the baby prefers it that way. However, never heat the formula in the microwave as it can create hot spots that may burn the baby's mouth. Instead, warm the formula by placing the bottle in a bowl of warm water. Always test the temperature on the inside of your wrist before feeding the baby to ensure it's not too hot.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Turning the client onto her left side is a common measure to improve fetal oxygenation and is often used during labor. However, in this scenario, the nurse needs to address the absence of fetal movement during the nonstress test.
Choice B rationale:
Encouraging the client to walk around and then resume monitoring is not appropriate when there is a concern about the absence of fetal movement during the nonstress test.
Choice C rationale:
Vibroacoustic stimulation involves using sound stimulation to elicit fetal movement. If there has been no fetal movement during the nonstress test, this intervention can be used to assess fetal well-being and provoke a response from the fetus.
Choice D rationale:
Preparing the client for induction of labor is not indicated based solely on the absence of fetal movement during a nonstress test. Further assessment and interventions are needed before considering induction.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
