A nurse is preparing to auscultate fetal heart tones for a client who is pregnant. Using Leopold maneuvers, the nurse palpates a round, firm, movable part in the fundal portion of the uterus and a long, smooth surface on the mother's right side. In which of the following maternal quadrants should the nurse auscultate fetal heart tones?
Right upper quadrant
Left lower quadrant
Right lower quadrant
Left upper quadrant
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale: Auscultating fetal heart tones in the right upper quadrant is not appropriate based on the information provided by Leopold maneuvers, which indicates the fetal back is on the right side of the mother's abdomen, and the fetal head is in the fundal portion of the uterus.
Choice B rationale: During Leopold maneuvers, the nurse palpated a round, firm, movable part in the fundal portion of the uterus. This finding corresponds to the fetal head, which is typically located at the top of the uterus (fundus). Additionally, the nurse palpated a long, smooth surface on the mother's right side. This finding indicates the fetal back, which typically lies along the right side of the mother's abdomen, suggesting that the fetus's back is positioned anteriorly (toward the mother's front). The location of the fetal heart is typically best heard over the back of the fetus. Therefore, the nurse should auscultate the fetal heart tones in the maternal quadrant corresponding to the back of the fetus, which is the left lower quadrant.
Choice C rationale: The information from Leopold maneuvers does not indicate the fetal back is in the right lower quadrant. The nurse should not auscultate fetal heart tones in this area.
Choice D rationale: Auscultating fetal heart tones in the left upper quadrant is not appropriate based on the information provided by Leopold maneuvers, which indicates the fetal head is in the fundal portion of the uterus and the fetal back is on the right side of the mother's abdomen. The fetal heart is usually best heard over the back of the fetus, which is not in the left upper quadrant.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Placing the infant in the prone position (face down) after feeding is not recommended for a baby with gastroesophageal reflux. The prone position can increase the risk of aspiration if reflux occurs while the baby is lying down.
Choice B rationale: For an infant with gastroesophageal reflux, placing the baby in an upright position after feeding can help prevent or reduce reflux episodes. Keeping the infant in an upright position allows gravity to assist in keeping stomach contents down and reduces the likelihood of reflux into the esophagus.
Choice C rationale: Placing the infant on the right side after feeding is also not recommended for managing gastroesophageal reflux. The right side position may not be as effective in preventing reflux as the upright position.
Choice D rationale: Placing the baby on either side after feeding is also not recommended for managing gastroesophageal reflux. The upright position is more effective in preventing reflux episodes and promoting digestion. Side-lying positions after feeding may not provide the same benefits and can potentially increase the risk of reflux.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
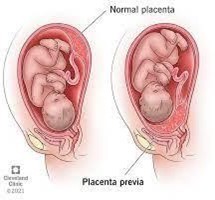
Choice A rationale: Applying ice to the perineal area is not indicated in the case of suspected placenta previa. Placenta previa is related to the location of the placenta in the uterus and is not affected by the perineal area. Ice is commonly used for perineal discomfort after vaginal delivery but is not appropriate for placenta previa.
Choice B rationale: When a client is suspected to have placenta previa, a vaginal exam should be avoided because it can cause trauma to the placenta, leading to significant bleeding. Placenta previa is a condition where the placenta covers part or all of the cervix, and any disruption of the placenta can result in bleeding, which poses a risk to both the mother and the baby. Therefore, a vaginal exam is contraindicated in this situation.
Choice C rationale: Performing a rectal exam is also not appropriate for a client with suspected placenta previa. Rectal exams do not provide any relevant information about the placenta's location, and they can potentially cause discomfort or bleeding in this situation.
Choice D rationale: Applying an external fetal monitor is an appropriate action when caring for a pregnant client, regardless of whether there is a suspected placenta previa. The external fetal monitor is used to assess the baby's heart rate and uterine contractions and is a routine part of prenatal care. However, it does not specifically address the issue of placenta previa. The nurse should be vigilant for any signs of bleeding or changes in fetal heart rate pattern, which may indicate placental issues, and report them promptly for further evaluation and management.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
