A nurse is planning care for a client who has diverticulitis. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following complications of diverticulitis?
Ulcerative colitis
Dysphagia
Peritonitis
Crohn's disease
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason: Ulcerative colitis is not a complication of diverticulitis. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes ulcers and inflammation in the colon and rectum. Diverticulitis is an acute condition that occurs when small pouches called diverticula in the colon become infected or inflamed.
Choice B reason: Dysphagia is not a complication of diverticulitis. Dysphagia is a term for difficulty swallowing, which can have many causes, such as stroke, nerve damage, or esophageal cancer. Diverticulitis affects the lower part of the digestive tract, not the upper part.
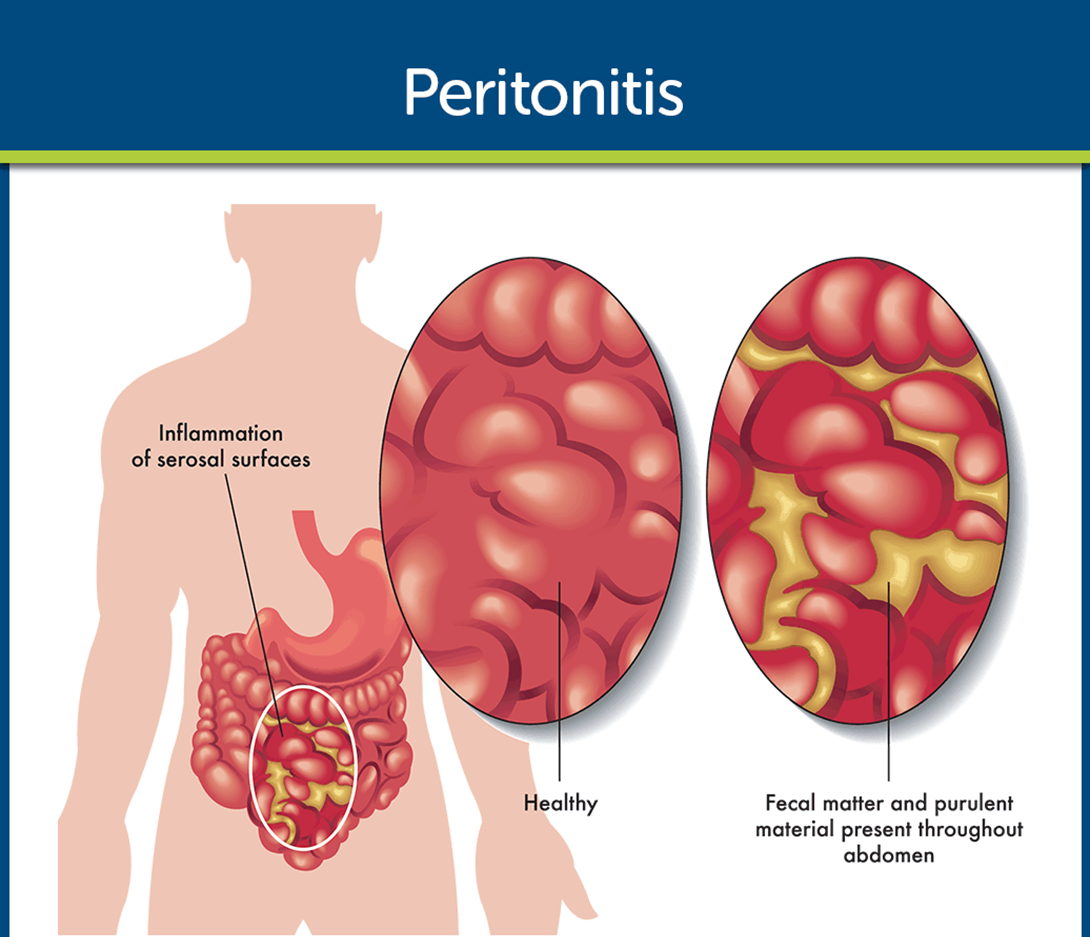
Choice C reason: Peritonitis is a complication of diverticulitis. Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It can be caused by a perforation or rupture of a diverticulum, which allows bacteria and fecal matter to enter the peritoneal space. Peritonitis is a serious and life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Choice D reason: Crohn's disease is not a complication of diverticulitis. Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that can affect any part of the digestive tract, causing ulcers, fistulas, and strictures. Diverticulitis is an acute condition that affects only the colon, not the entire digestive tract.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: Monitoring respiratory status for signs and symptoms of pulmonary complications is a priority nursing intervention for a client with hypervolemia. Hypervolemia is a condition where there is excess fluid in the blood vessels, which can cause fluid to leak into the lungs and impair gas exchange. The nurse should assess the client for signs of pulmonary edema, such as dyspnea, crackles, cough, and pink-tinged sputum.
Choice B reason: Encouraging the client to consume sodium-free fluids is not a priority nursing intervention for a client with hypervolemia. Sodium-free fluids may still contribute to fluid overload, especially if the client has impaired renal function or heart failure. The nurse should limit the client's fluid intake and administer diuretics as prescribed to reduce the fluid volume.
Choice C reason: Weighing dressings with a large-bore catheter is not a priority nursing intervention for a client with hypervolemia. This may be a relevant intervention for a client with hemorrhage, who may lose blood through a large-bore catheter or dressing. The nurse should monitor the client's blood pressure, pulse, and hemoglobin levels for signs of blood loss.
Choice D reason: Drawing a blood sample for typing and cross-matching is not a priority nursing intervention for a client with hypervolemia. This may be a relevant intervention for a client who needs a blood transfusion, which may be indicated for a client with anemia, trauma, or surgery. The nurse should check the client's blood type and compatibility before administering any blood products.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: Pyuria, or pus in the urine, is not a direct sign of fluid volume overload. It may indicate a urinary tract infection, kidney stones, or other renal problems.
Choice B reason: Weight loss is not a typical finding of fluid volume overload. In fact, weight gain is a common symptom of fluid retention, as the body holds more fluid than it excretes.
Choice C reason: Jugular vein distention, or the bulging of the neck veins, is a serious indicator of fluid volume overload. It reflects increased pressure in the right side of the heart and the systemic circulation. It may also signal heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, or pericardial tamponade.
Choice D reason: Muscle contractions are not directly related to fluid volume overload. They may be caused by electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, muscle fatigue, or nerve disorders.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
