A nurse is monitoring an infant who is 6 months old and has sneezing, coughing, nasal congestion, intermittent fever, and apneic spells. The nurse should recognize these findings are consistent with which of the following diagnoses?
Epiglottitis
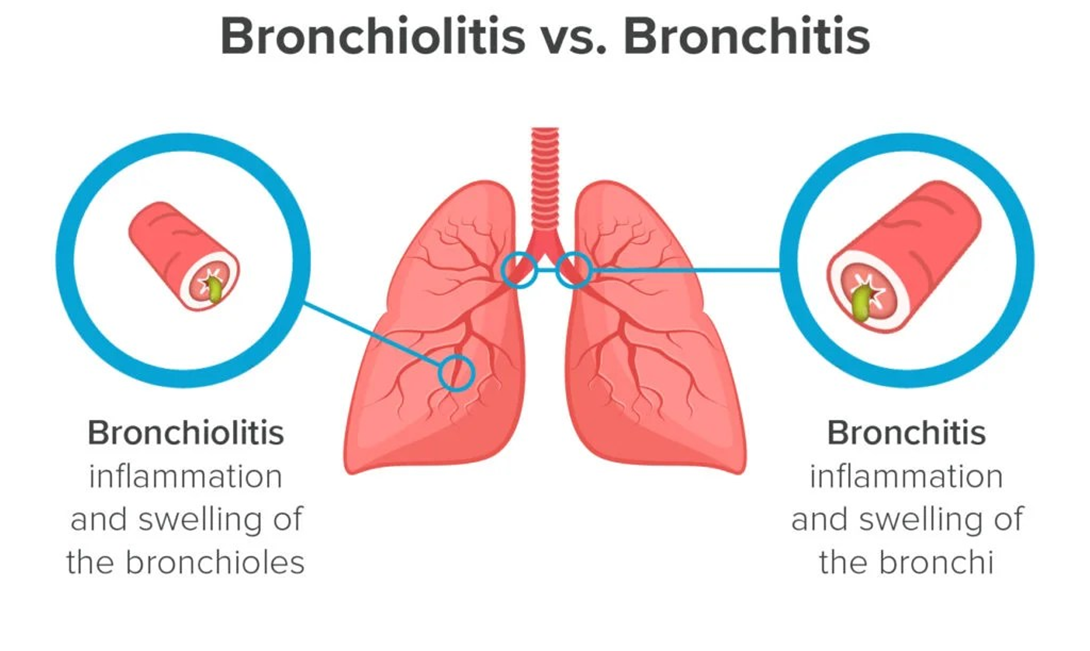
Bronchiolitis
Influenza
Croup
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason: Epiglottitis is a life-threatening condition that causes inflammation and swelling of the epiglottis, the flap of tissue that covers the entrance to the trachea. It can block the airway and cause respiratory distress. The signs and symptoms of epiglottitis include drooling, dysphagia, dysphonia, high fever, and tripod position. Epiglottitis is rare in infants and more common in children aged 2-6 years.
Choice B reason: Bronchiolitis is a viral infection that causes inflammation and mucus production in the bronchioles, the smallest airways in the lungs. It can impair gas exchange and cause respiratory distress. The signs and symptoms of bronchiolitis include sneezing, coughing, nasal congestion, wheezing, tachypnea, retractions, and apneic spells. Bronchiolitis is common in infants and children under 2 years of age, especially during the winter months.
Choice C reason: Influenza is a viral infection that affects the respiratory system. It can cause fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, sore throat, cough, and nasal congestion. Influenza can also lead to complications such as pneumonia, otitis media, and sinusitis. Influenza is common in children and adults of all ages, especially during the flu season.
Choice D reason: Croup is a viral infection that causes inflammation and narrowing of the larynx and trachea. It can cause a characteristic barking cough, hoarseness, stridor, and respiratory distress. Croup is common in children aged 6 months to 3 years, especially during the fall and winter months.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is the best option to prevent reflux, as it allows gravity to help keep the stomach contents down. The nurse should advise the parent to keep the baby upright for at least 30 minutes after each feeding.
Choice B reason: Positioning the baby side lying during sleep is not recommended, as it can increase the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). The nurse should instruct the parent to place the baby on the back for sleep, and elevate the head of the crib slightly.
Choice C reason: Thickening the baby's formula with oatmeal may help reduce reflux, but it is not the first choice, as it can cause overfeeding, constipation, or allergic reactions. The nurse should suggest this option only if prescribed by the provider.
Choice D reason: Feeding the baby formula rather than breast milk is not a good option, as breast milk is easier to digest and has many benefits for the baby's health and development. The nurse should encourage the parent to continue breastfeeding, and offer smaller and more frequent feedings.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Drooling is not a sign of hemorrhage, but rather a sign of difficulty swallowing or breathing. Drooling may occur after a tonsillectomy due to throat pain or swelling, but it does not indicate bleeding.
Choice B reason: Poor fluid intake is not a sign of hemorrhage, but rather a sign of dehydration or nausea. Poor fluid intake may occur after a tonsillectomy due to throat pain or fear of swallowing, but it does not indicate bleeding.
Choice C reason: Increased pain is not a sign of hemorrhage, but rather a sign of inflammation or infection. Increased pain may occur after a tonsillectomy due to tissue damage or healing, but it does not indicate bleeding.
Choice D reason: Frequent swallowing is a sign of hemorrhage, as it indicates that the child is trying to clear blood from the throat. Frequent swallowing may occur after a tonsillectomy due to bleeding from the surgical site or a ruptured blood vessel.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
