A nurse is caring for a client with a chronic wound and is discussing smoking cessation. The client does not understand how smoking may impact wound healing. Which of the following would be the best nurse response?
Smoking causes you to cough frequently and the wound might get infected by sputum.
Nicotine causes vasoconstriction so your wound might not get enough blood flow to heal.
Nicotine causes tar to build up in the wound and it will impair healing.
Smoking is bad and you should stop right away.
The Correct Answer is B
A. Smoking causes you to cough frequently, and the wound might get infected by sputum.
While smoking can indeed contribute to respiratory issues like coughing, linking this directly to wound infection by sputum is not the most accurate explanation of how smoking affects wound healing. The primary concern with smoking and wound healing lies in its effects on circulation and tissue oxygenation rather than the risk of infection due to coughing.
B. Nicotine causes vasoconstriction, so your wound might not get enough blood flow to heal.
This is the best response among the options provided. Nicotine, a major component of cigarette smoke, is known to constrict blood vessels (vasoconstriction). This constriction reduces blood flow to the wound site, leading to decreased delivery of oxygen and nutrients necessary for proper wound healing. It addresses the direct physiological impact of smoking on wound healing and provides a clear explanation for the client.
C. Nicotine causes tar to build up in the wound, and it will impair healing.
While nicotine and other components of tobacco smoke can have detrimental effects on healing, particularly through vasoconstriction, the explanation about tar building up in the wound is not entirely accurate. Tar is more associated with lung damage from smoking rather than direct buildup in external wounds. Therefore, this response is less specific and may confuse the client about the actual mechanism of how smoking affects wound healing.
D. Smoking is bad, and you should stop right away.
While this response emphasizes the importance of smoking cessation, it lacks specificity in explaining how smoking impacts wound healing. Providing specific information about vasoconstriction due to nicotine, as mentioned in option B, would be more helpful in helping the client understand the direct effects of smoking on their chronic wound and why cessation is crucial.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
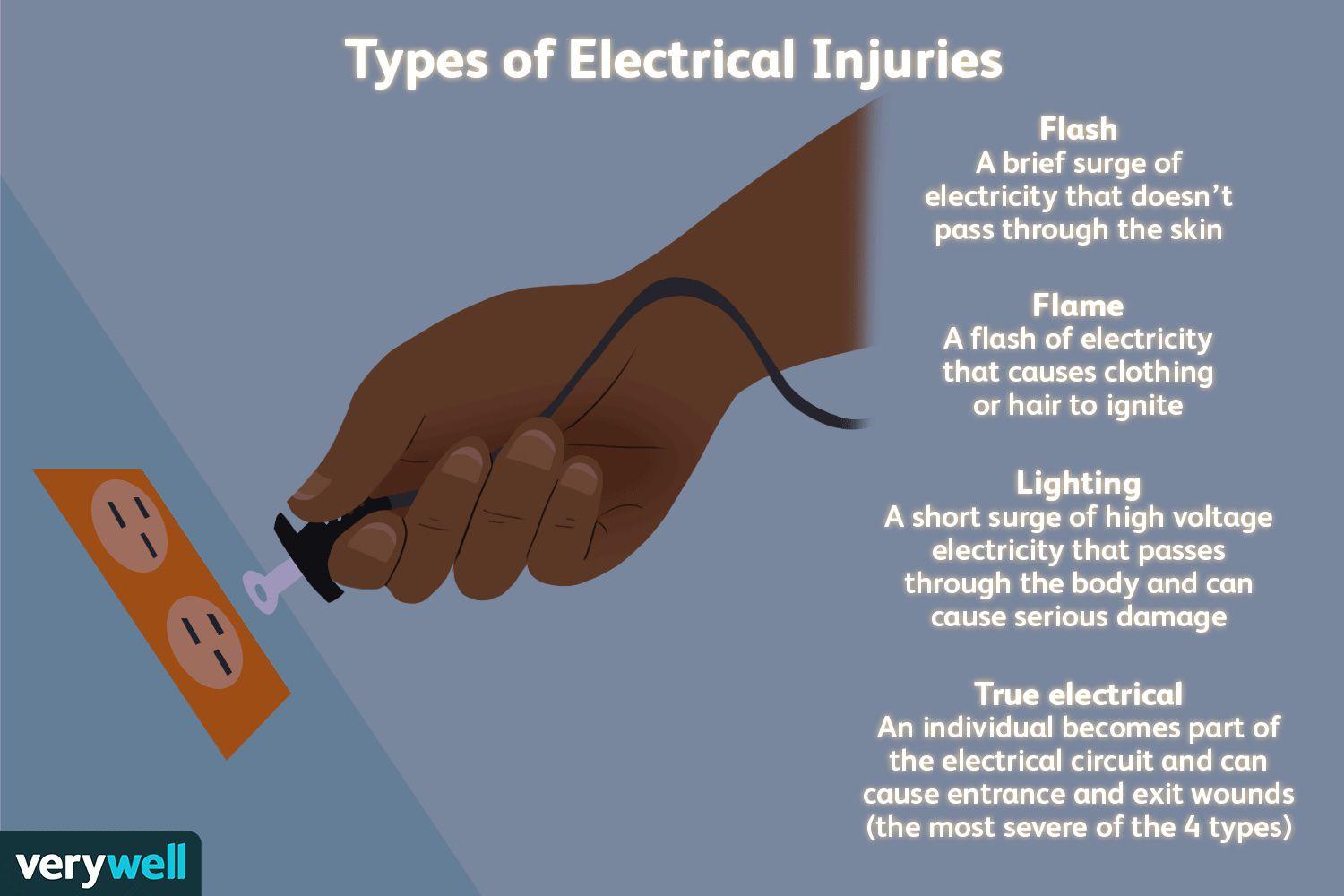
A. Electrical burns can have small amounts of skin damage, but more extensive damage beneath the skin.
This response is the best choice because it educates the client about the potential for deeper tissue damage associated with electrical burns. It acknowledges that while the burn on the skin may appear small, the damage underneath could be more extensive, affecting muscles, nerves, and blood vessels.
B. Electrical burns commonly cause reddened/purplish skin without blistering.
This statement is not the best response because it focuses solely on the appearance of the skin without addressing the potential for deeper tissue damage. While it is true that electrical burns can present with reddened or purplish skin without blistering, this response does not provide comprehensive information about the nature and severity of electrical burns.
C. Electrical burns typically are minor.
This response is incorrect because it downplays the seriousness of electrical burns. While some electrical burns may indeed be minor, others can cause significant tissue damage and complications. It's important for the nurse to educate the client about the range of severity that electrical burns can present.
D. Electrical burns usually cause much more skin damage than what can be seen on your skin.
This statement is partially accurate but does not provide as much information as choice A. While it acknowledges that electrical burns can cause more damage than what is visible on the skin's surface, it doesn't emphasize the potential for deeper tissue damage as effectively as choice A does.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
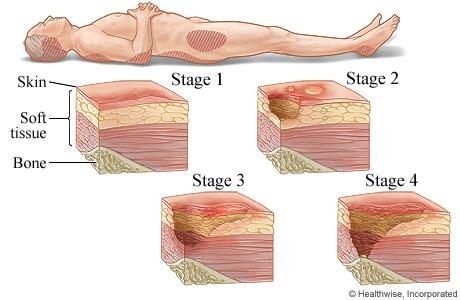
A. Stage III pressure injury
Stage III pressure injuries involve full-thickness skin loss, extending into the subcutaneous tissue but not through the fascia. These wounds typically present as deep craters and may involve undermining or tunneling. Non-blanchable erythema alone without visible skin loss is not characteristic of a Stage III pressure injury.
B. Stage IV pressure injury
Stage IV pressure injuries are the most severe and involve full-thickness tissue loss with exposed bone, tendon, or muscle. These wounds often have extensive tissue damage and can be difficult to manage. Again, non-blanchable erythema without visible skin loss is not indicative of a Stage IV pressure injury.
C. Stage II pressure injury
Stage II pressure injuries involve partial-thickness skin loss with damage to the epidermis and possibly the dermis. These wounds often present as shallow open ulcers or blisters and may have characteristics such as intact or ruptured blisters. While Stage II injuries can present with erythema, non-blanchable erythema specifically indicates a Stage I injury.
D. Stage I pressure injury
Stage I pressure injuries are the earliest stage and involve non-blanchable erythema of intact skin. The skin may be warmer or cooler than surrounding tissue and may have changes in sensation. There is no visible skin loss at this stage, but the area is at risk for further injury if pressure is not relieved. Therefore, non-blanchable erythema on the heels most likely indicates a Stage I pressure injury.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
