A nurse is caring for a client who states their parent died from complications of a GI bleed. Which of the following statements from the nurse will help the client decrease their risk of developing a peptic ulcer?
“Avoid consuming undercooked foods.”
“Avoid using hormone replacement therapy as this can increase your risk for a peptic ulcer.”
“Avoid foods that have been fried.”
“Avoid using decongestants for seasonal allergies/colds due to their positive link to developing a peptic ulcer.”
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A Reason:
Avoiding undercooked foods is generally good advice for preventing foodborne illnesses, but it is not specifically related to reducing the risk of peptic ulcers. Peptic ulcers are primarily caused by Helicobacter pylori infection and the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Choice B Reason:
There is no established link between hormone replacement therapy and an increased risk of peptic ulcers. The primary risk factors for peptic ulcers include H. pylori infection, NSAID use, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Choice C Reason:
This is the correct answer. Fried foods can irritate the stomach lining and increase the production of stomach acid, which can exacerbate the symptoms of peptic ulcers and potentially contribute to their development. Avoiding fried foods can help reduce irritation and promote healing.
Choice D Reason:
There is no evidence to suggest that decongestants for seasonal allergies or colds are linked to the development of peptic ulcers. The main contributors to peptic ulcers are H. pylori infection and NSAID use.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
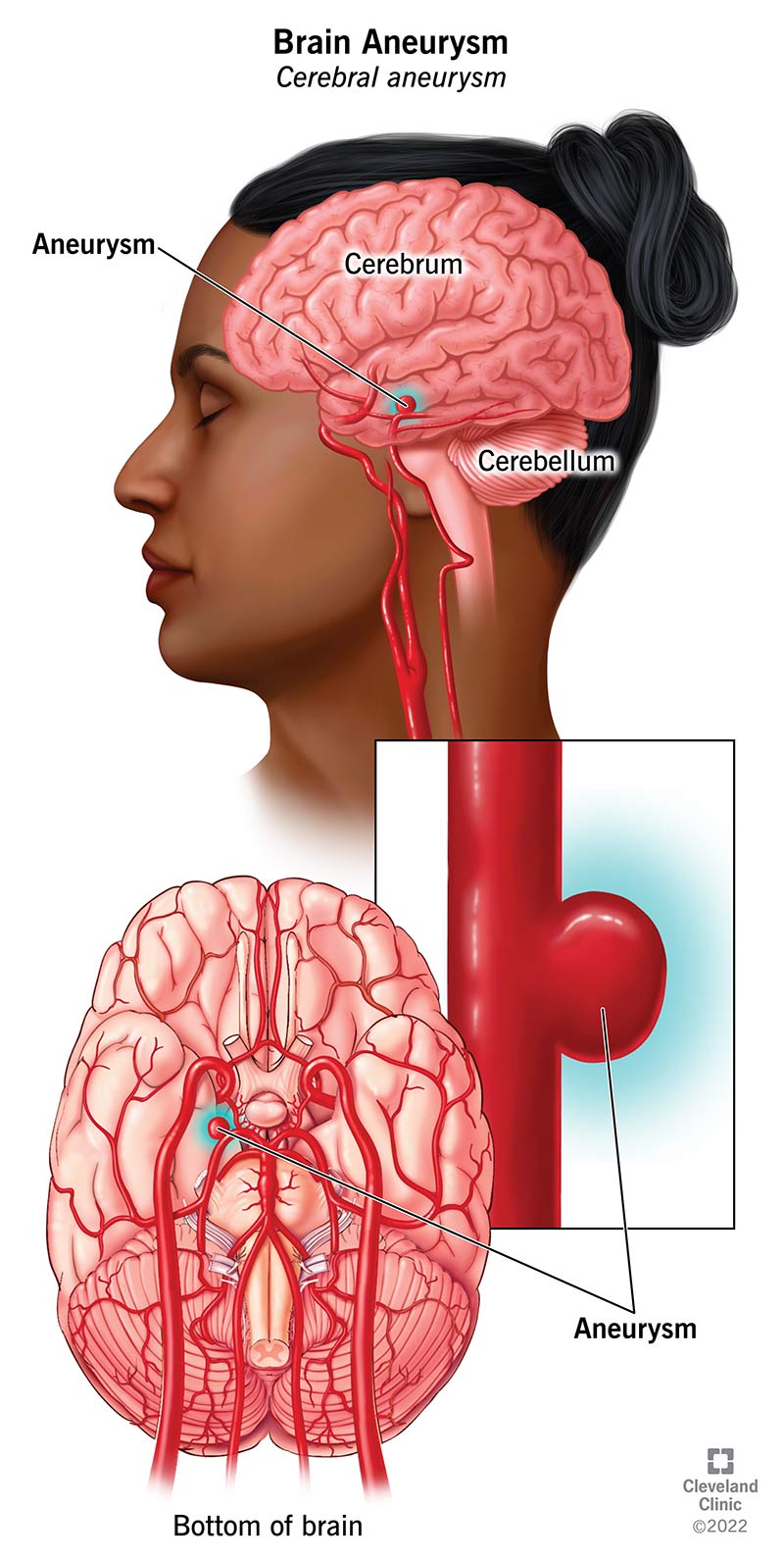
Correct Answer is ["A","B","C","D","E"]
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Light sensitivity
Light sensitivity, also known as photophobia, is a common symptom of a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. When an aneurysm ruptures, it can cause bleeding in the brain, leading to increased intracranial pressure and irritation of the meninges, which can result in sensitivity to light.
Choice B Reason: Loss of consciousness
Loss of consciousness is a critical symptom of a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. The sudden increase in intracranial pressure from the bleeding can lead to a rapid decline in the patient’s level of consciousness. This symptom is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
Choice C Reason: A dilated pupil
A dilated pupil can indicate increased intracranial pressure or direct pressure on the cranial nerves due to the bleeding from a ruptured aneurysm. This symptom is often associated with severe neurological impairment and requires urgent medical intervention.
Choice D Reason: Visual disturbances
Visual disturbances, such as blurred or double vision, can occur due to the pressure exerted by the bleeding on the optic nerves or other parts of the visual pathway. These disturbances are significant indicators of neurological compromise.
Choice E Reason: Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of increased intracranial pressure, which can result from a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. The irritation of the brain’s vomiting center due to the bleeding can lead to these symptoms.
Choice F: Numbness on one side of the face
Numbness on one side of the face is not typically a direct symptom of a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. While neurological deficits can occur, numbness is more commonly associated with other types of strokes or localized nerve damage rather than the acute presentation of a ruptured aneurysm.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Instruct the client to wear a hospital gown every day, even when out of bed
This intervention does not directly address the prevention of complications related to immobility. Wearing a hospital gown may be necessary for medical reasons, but it does not promote mobility or prevent complications such as pressure ulcers, muscle atrophy, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Encouraging the client to wear regular clothes when out of bed might actually promote a sense of normalcy and encourage more movement.
Choice B Reason: Have the client remain in bed for self-care activities
Keeping the client in bed for self-care activities is counterproductive in preventing complications of immobility. Prolonged bed rest can lead to muscle atrophy, decreased joint mobility, and increased risk of pressure ulcers and DVT. Encouraging the client to get out of bed and perform self-care activities while standing or sitting can help maintain muscle strength and joint flexibility.
Choice C Reason: Encourage the client to sit in the chair for all meals
Encouraging the client to sit in a chair for meals is an effective intervention to prevent complications of immobility. Sitting up helps improve digestion and respiratory function and reduces the risk of pressure ulcers by changing the pressure points on the body. It also promotes muscle activity and circulation, which are crucial in preventing DVT and maintaining overall physical health.
Choice D Reason: Elevate the head of the bed to 30° to 45° for medication administration
While elevating the head of the bed can be beneficial for certain medical conditions and for medication administration, it does not significantly contribute to preventing complications of immobility. This position can help with respiratory function and prevent aspiration during medication administration, but it does not promote overall mobility or prevent muscle atrophy and pressure ulcers.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
