A nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing postoperative nausea and vomiting. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following complications of vomiting?
Diarrhea
Dehydration
Urinary frequency
Peripheral edema
The Correct Answer is B
A. Diarrhea:
Explanation: Vomiting is more likely to be associated with dehydration than diarrhea. While vomiting and diarrhea can both lead to fluid loss, dehydration is a more immediate concern.
B. Dehydration:
Explanation: This is correct. Vomiting can lead to a significant loss of fluids, and dehydration is a potential complication. It's important to monitor the client's fluid balance, provide oral rehydration solutions or intravenous fluids as needed, and address the underlying cause of vomiting.
C. Urinary frequency:
Explanation: While dehydration can lead to decreased urine output, urinary frequency is not a typical complication of vomiting. Dehydration often results in decreased urine production.
D. Peripheral edema:
Explanation: Peripheral edema is not a direct complication of vomiting. It is more commonly associated with conditions such as heart failure or renal issues.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
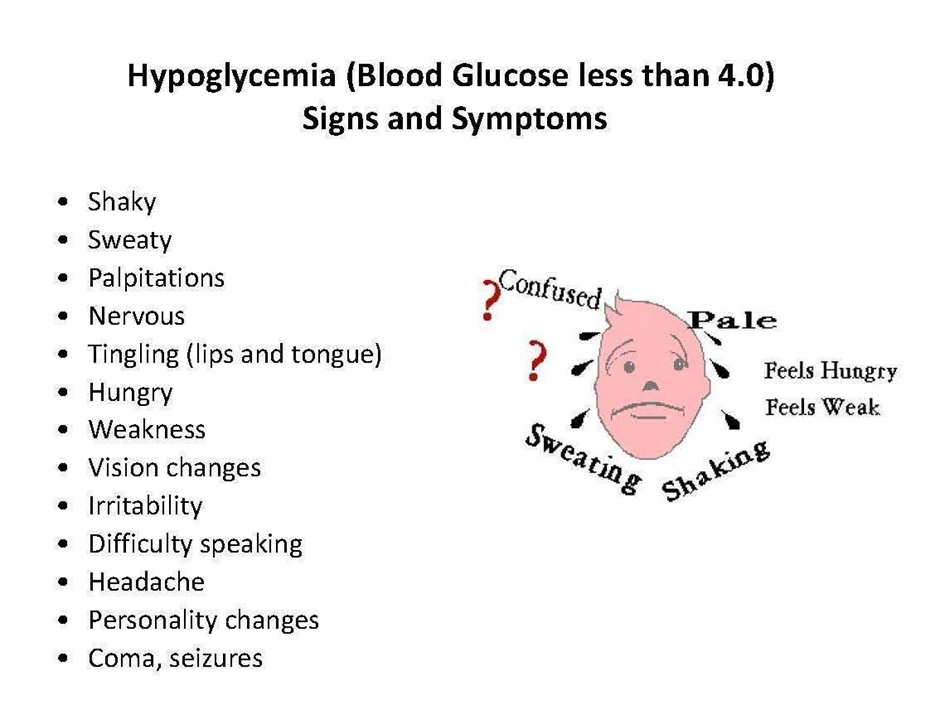
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Dry mucous membranes:
Explanation: Dry mucous membranes are not typically associated with hypoglycemia. Instead, they might be seen in conditions such as dehydration.
B. Fruity breath odor:
Explanation: Fruity breath odor is more commonly associated with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which is a complication of hyperglycemia, not hypoglycemia.
C. Diaphoresis:
Explanation: Diaphoresis, or excessive sweating, is a common manifestation of hypoglycemia. It results from the activation of the sympathetic nervous system in response to low blood sugar levels.
D. Polyuria:
Explanation: Polyuria, or increased urination, is not a typical manifestation of hypoglycemia. It is more commonly associated with hyperglycemia and diabetes.
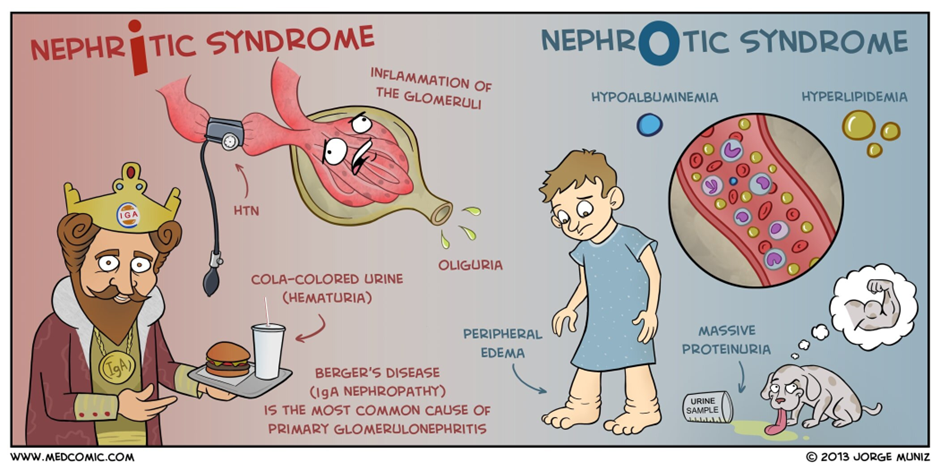
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Proteinuria:
Minimal change nephrotic syndrome is characterized by increased permeability of the glomerular filtration barrier, leading to proteinuria. The loss of proteins, especially albumin, in the urine is a key feature.
B. Hypocalcemia:
Hypocalcemia is not typically associated with MCNS. In fact, the loss of proteins, including albumin, in the urine can lead to decreased oncotic pressure in the blood vessels, resulting in edema. However, calcium levels are usually within the normal range.
C. Hyperalbuminemia:
This is not a characteristic finding in minimal change nephrotic syndrome. In fact, the condition is associated with hypoalbuminemia due to the loss of albumin in the urine.
D. Positive for Ketones:
Ketones are not typically associated with minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Ketones in the urine are more commonly associated with conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis or starvation.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
