A nurse is administering an enteral feeding through a client's NG tube. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Cleanse the top of the can of formula with an alcohol wipe.
Keep the formula cold until instillation.
Withhold the feeding if the residual volume is 150 mL.
Flush the tube with 30 mL of sterile water before the feeding.
None
None
The Correct Answer is A
Correct answer: D
A. Wiping the top of the can before opening prevents contamination and reduces the risk of introducing pathogens into the feeding system.
B. Cold formula can cause gastric discomfort or cramping. It's recommended to bring the formula to room temperature before administration to avoid gastric irritation and enhance comfort during feeding.
C. The action of withholding the feeding depends on the institution's protocol and the specific clinical condition of the client. Typically, residuals greater than 200 mL might indicate delayed gastric emptying, but the threshold can vary. A residual volume of 150 mL may not necessarily require withholding the feeding, though it may warrant further assessment.
D. In most cases, flushing is done with tap water (if safe for drinking) or sterile water in immunocompromised clients. The key step is to flush before and after feedings, but the standard practice is not automatically sterile water for all patients.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
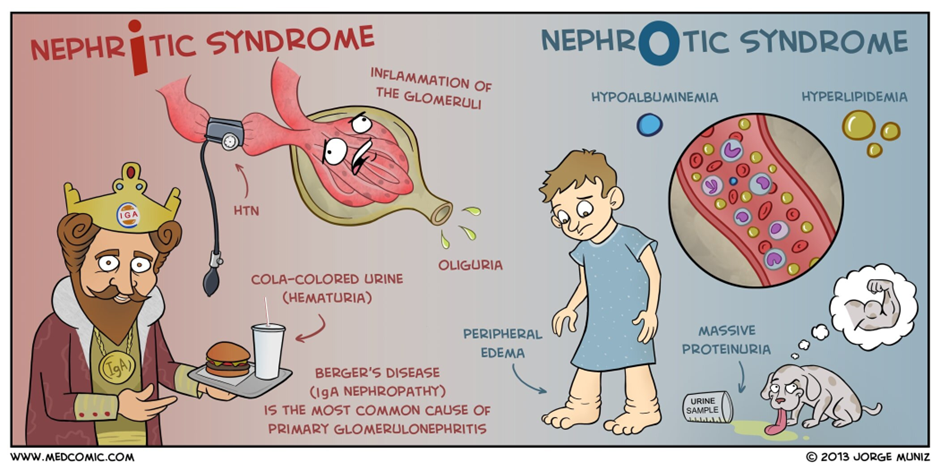
A. Proteinuria:
Minimal change nephrotic syndrome is characterized by increased permeability of the glomerular filtration barrier, leading to proteinuria. The loss of proteins, especially albumin, in the urine is a key feature.
B. Hypocalcemia:
Hypocalcemia is not typically associated with MCNS. In fact, the loss of proteins, including albumin, in the urine can lead to decreased oncotic pressure in the blood vessels, resulting in edema. However, calcium levels are usually within the normal range.
C. Hyperalbuminemia:
This is not a characteristic finding in minimal change nephrotic syndrome. In fact, the condition is associated with hypoalbuminemia due to the loss of albumin in the urine.
D. Positive for Ketones:
Ketones are not typically associated with minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Ketones in the urine are more commonly associated with conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis or starvation.
Correct Answer is A
No explanation
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
