A nurse is assessing a client's peripheral circulation. In which of the following locations should the nurse palpate to assess the posterior tibial pulse? (Selectable areas, or "Hot Spots," are outlined in the artwork below. Select only the outlined area that corresponds to your answer.)
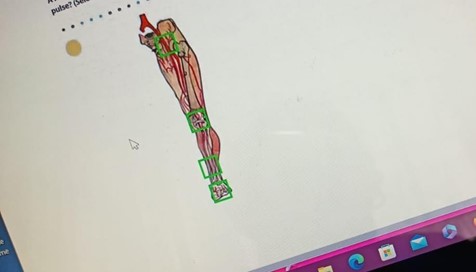
inguinal canal
knee
lower third of the tibia
dorsal aspect of the foot
The Correct Answer is C
A. Inguinal canal is not the correct location for assessing the posterior tibial pulse. This area is associated with the femoral pulse.
B. The knee is not the correct location for assessing the posterior tibial pulse. This area is not directly related to the posterior tibial pulse.
C. The lower third of the tibia, anterior aspect is the correct location for palpating the posterior tibial pulse. This pulse can be found on the inside of the ankle, slightly below and behind the medial malleolus.
D. Dorsal aspect of the foot is where the dorsalis pedis pulse is located, not the posterior tibial pulse.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Requesting a prescription for an indwelling urinary catheter should be considered a last resort. Catheters come with risks of infection and other complications, so they should only be used when other interventions have failed.
B. Taking the client to the bathroom every 2 hours is a proactive approach to managing urinary incontinence in older adults with dementia. This helps ensure that the client has regular opportunities to empty their bladder, reducing the likelihood of accidents.
C. Reminding the client to tell the nurse when he has to urinate may not be effective in clients with dementia, as they may have difficulty recognizing or communicating their need to urinate.
D. Using adult diapers should also be considered a last resort and should not be the primary intervention. While they can provide a temporary solution, they do not address the underlying issue and can contribute to skin problems if not changed frequently.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. The reported tympanic temperature of 37.1°C (98.8°F) is within normal range.
B. The blood pressure (BP) reading of 98/58 mm Hg indicates a relatively low diastolic pressure. Diastolic pressure is an important indicator of perfusion to vital organs, especially the coronary arteries and the brain. It's crucial to ensure that this reading is accurate.
C. The reported pulse rate of 92/min falls within the normal range for an adult at rest.
D. The reported respiratory rate of 18/min is within the normal range for an adult at rest.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
