A nurse is assessing a client who is 1 hr postpartum. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider?
Lochia rubra with small clots
Minimal perineal edema
Boggy fundus
Temperature 37.7° C (99.9° F)
The Correct Answer is C
. Lochia rubra with small clots:
Lochia rubra is the normal vaginal discharge occurring after childbirth, consisting of blood, mucus, and uterine tissue. It is expected for lochia to be present in the immediate postpartum period, and small clots are also considered normal as long as they are not excessive in size. Therefore, this finding is within the expected range for a client who is 1 hour postpartum and does not require immediate reporting to the provider.
B. Minimal perineal edema:
Perineal edema, or swelling in the perineal area, can be common after childbirth, particularly following vaginal delivery or if there was perineal trauma during labor. Some degree of perineal edema is generally expected in the immediate postpartum period and may resolve with time and appropriate care. As long as the edema is minimal and not causing significant discomfort or obstructing the assessment, it is not typically a cause for immediate concern or reporting to the provider.
C. Boggy fundus:
A boggy fundus refers to a uterus that feels soft and mushy instead of firm and well-contracted. It suggests uterine atony, which is a significant concern in the postpartum period as it can lead to excessive bleeding and postpartum hemorrhage. Therefore, a boggy fundus should be reported promptly to the provider so that interventions can be initiated to address the uterine atony and prevent complications.
D. Temperature 37.7°C (99.9°F):
A temperature of 37.7°C (99.9°F) is slightly elevated but may still fall within the normal range for the immediate postpartum period. While fever can indicate infection, a single temperature reading alone may not be sufficient to confirm an infection. It is important for the nurse to continue monitoring the client's temperature and assess for other signs and symptoms of infection before reporting to the provider. Therefore, this finding does not necessarily warrant immediate reporting unless accompanied by other concerning symptoms suggestive of infection.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Move the client onto their hands and knees.
This action refers to the Gaskin maneuver, which involves changing the maternal position to help alleviate shoulder dystocia during childbirth. By positioning the client on their hands and knees, gravity assists in changing the orientation of the pelvis, potentially allowing more space for the baby to be delivered. While the Gaskin maneuver can be effective in some cases of shoulder dystocia, it is not the McRoberts maneuver.
B. Press firmly on the client's suprapubic area.
This action describes the Rubin maneuver, another technique used to address shoulder dystocia. With the Rubin maneuver, pressure is applied to the anterior shoulder of the fetus, aiming to rotate it into an oblique diameter, which may help dislodge the shoulder from behind the symphysis pubis. While the Rubin maneuver can be helpful in certain cases of shoulder dystocia, it is not the McRoberts maneuver.
C. Apply pressure to the client's fundus.
Applying pressure to the client's fundus is not part of the McRoberts maneuver. In fact, this action is not recommended for managing shoulder dystocia as it could potentially worsen the situation by causing further impaction of the baby's shoulder against the mother's pubic bone.
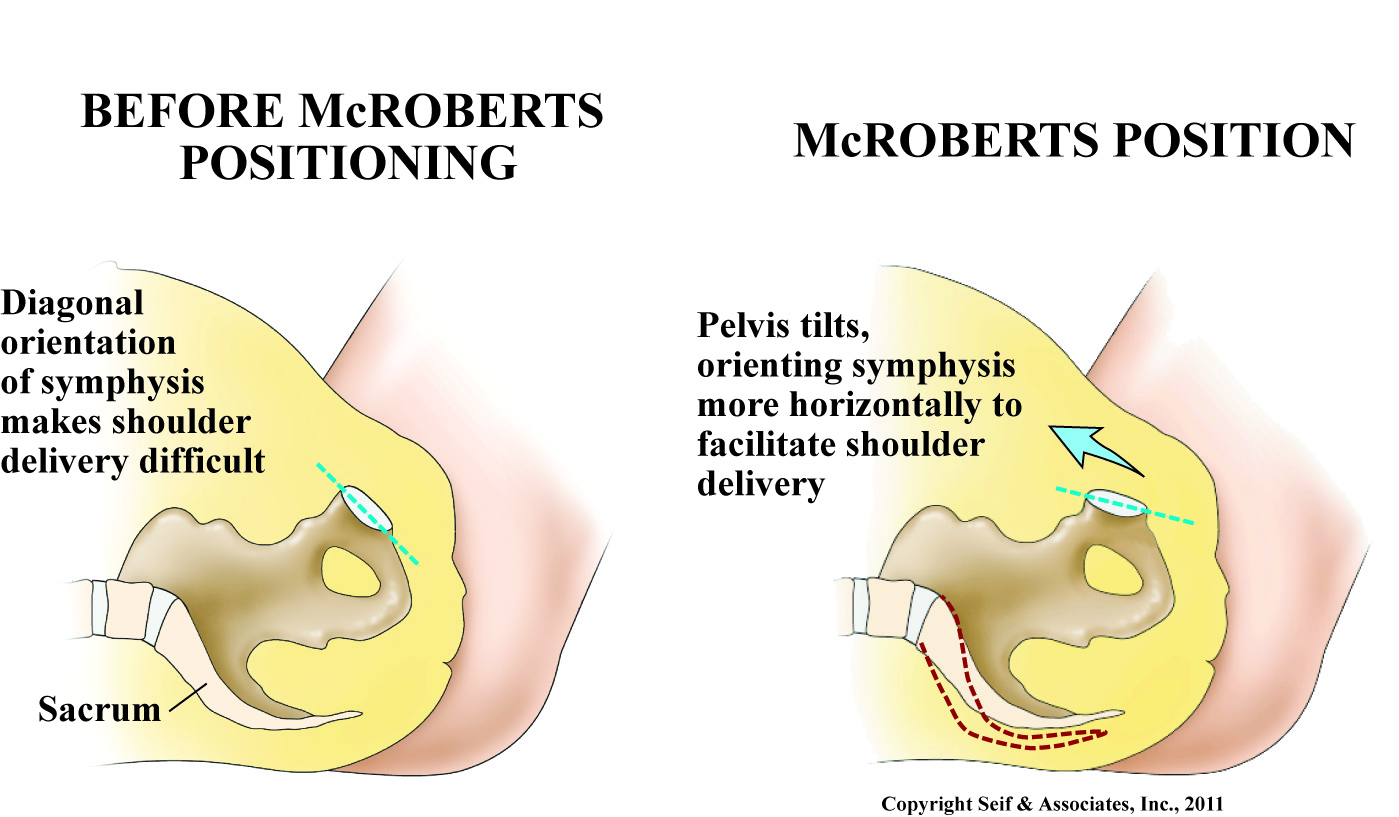
D. Assist the client in pulling their knees toward their abdomen.
This is the correct action corresponding to the McRoberts maneuver. During the McRoberts maneuver, the nurse assists the client in flexing their hips sharply toward their abdomen. This action helps to widen the pelvic outlet and may facilitate the release of the impacted shoulder, allowing for easier delivery of the baby. The McRoberts maneuver is one of the primary maneuvers used to manage shoulder dystocia during childbirth.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Depressed anterior fontanel:
A depressed anterior fontanel is not typically associated with forceps-assisted birth. The fontanelles may become depressed in conditions such as dehydration or if the newborn is in a hypovolemic state, but it is not directly related to forceps use during delivery.
B. Epicanthal folds:
Epicanthal folds are normal anatomical features that are commonly seen in newborns, especially those of certain ethnic backgrounds. They are not indicative of an injury caused by forceps.
C. Facial asymmetry:
Facial asymmetry can occur as a result of forceps application during birth. The forceps' pressure on the baby's face can cause bruising, swelling, or even facial nerve injury, leading to temporary or permanent facial asymmetry.
D. Uneven gluteal skinfolds:
Uneven gluteal skinfolds are not typically associated with forceps-assisted birth. This finding is more commonly seen in conditions such as hip dysplasia or developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), and it is not directly related to forceps use during delivery.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
