A nurse in a provider's office is preparing to teach a middle adult client who has a new diagnosis of metabolic syndrome and an HbA1c of 6 Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to teach the client about first?
Insulin glargine
Regular insulin
Exenatide
Metformin
The Correct Answer is D
A. Insulin glargine:
Insulin glargine is a long-acting insulin used to control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. However, it is typically not the first-line choice for a client with a new diagnosis of metabolic syndrome and an HbA1c of 6.
B. Regular insulin:
Regular insulin is a short-acting insulin used to control blood sugar levels, but it is not typically the first choice for initial management of metabolic syndrome. It may be considered in certain situations, but other options are often explored first.
C. Exenatide:
Exenatide is a medication that belongs to the class of incretin mimetics and is used to improve blood sugar control. However, it may not be the first choice for initial treatment.
D. Metformin:
This is the correct answer. Metformin is a first-line medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and is commonly used to manage metabolic syndrome. It helps improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production by the liver.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
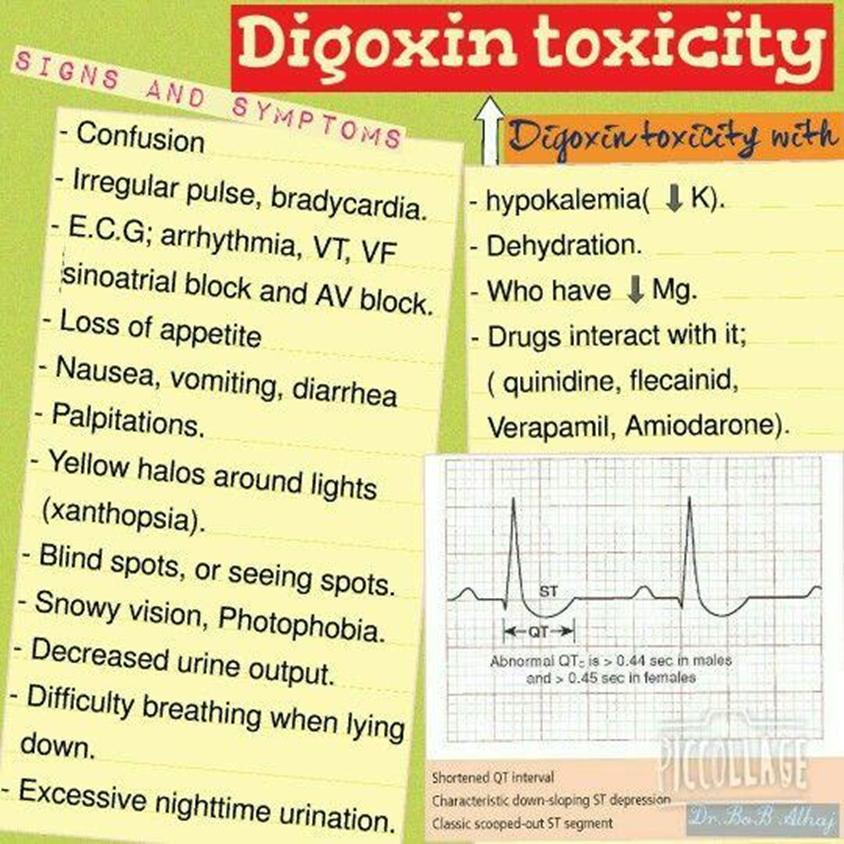
A. Visual disturbances:
Visual disturbances, such as blurred or yellow-tinted vision, are common signs of digoxin toxicity. Clients should report any changes in vision promptly.
B. Potassium 4.4 mEq/L:
While electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium levels, can increase the risk of digoxin toxicity, a potassium level of 4.4 mEq/L is within the normal range and, by itself, does not indicate digoxin toxicity.
C. Insomnia:
Insomnia is not a typical sign of digoxin toxicity. Symptoms of toxicity are more likely to involve the gastrointestinal and visual systems.
D. Sudden weight gain:
Sudden weight gain can be a symptom of heart failure exacerbation but is not a direct indication of digoxin toxicity. Other signs, such as visual disturbances, are more specific to digoxin toxicity.
Correct Answer is ["A","C"]
Explanation
A. Absence of deep-tendon reflexes:
Absence of deep-tendon reflexes is a sign of magnesium toxicity. Magnesium sulfate, when infused in high doses, can lead to neuromuscular blockade and affect reflexes. Discontinuing the infusion and administering calcium gluconate can counteract the effects of magnesium.
B. Urine output 80 mL in 4 hours:
Urine output is not a direct indicator of magnesium toxicity. Monitoring urine output is important for assessing renal function, but it is not a specific sign of magnesium toxicity.
C. Decreased level of consciousness:
Decreased level of consciousness is another sign of magnesium toxicity. Central nervous system depression is a potential adverse effect of elevated magnesium levels. Administering calcium gluconate can help antagonize the effects of magnesium.
D. Report of chills:
Chills are not typically associated with magnesium toxicity. This symptom may indicate other issues, such as infection or discomfort.
E. Systolic blood pressure 130 mm/Hg:
Systolic blood pressure within a normal range is not a sign of magnesium toxicity. Blood pressure changes are not typically the primary indicators of magnesium toxicity.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
