A nurse evaluates the following arterial blood gas values in a patient: pH 7.48, PaO 98 mm Hg, PaCO 28 mm Hg, and HCO - 22 mEq/L (22 mmol/L). Which patient condition does the nurse correlate with these results?
Diarrhea and vomiting for 36 hours
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Anxiety-induced hyperventilation
Diabetic ketoacidosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
The Correct Answer is C
A. Diarrhea and vomiting for 36 hours:
Diarrhea and vomiting can lead to metabolic acidosis due to loss of bicarbonate and increased hydrogen ion concentration in the blood. However, the ABG values provided indicate respiratory alkalosis (high pH and low PaCO2), which is not consistent with metabolic acidosis caused by diarrhea and vomiting. Therefore, this choice does not correlate with the ABG values.
B. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD):
COPD is a respiratory condition characterized by airflow limitation and increased airway resistance. It can lead to respiratory acidosis due to retention of carbon dioxide (PaCO2 levels would be elevated). The ABG values in the scenario show respiratory alkalosis (low PaCO2), which is the opposite of what would be expected in COPD. Therefore, this choice does not correlate with the ABG values provided.
C. Anxiety-induced hyperventilation:
Anxiety-induced hyperventilation is a common cause of respiratory alkalosis. During hyperventilation, there is excessive elimination of carbon dioxide (PaCO2 levels decrease), leading to an increase in pH (alkalosis). The ABG values in the scenario show a high pH (7.48) and low PaCO2 (28 mm Hg), consistent with respiratory alkalosis seen in hyperventilation due to anxiety.
D. Diabetic ketoacidosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD):
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a metabolic condition characterized by hyperglycemia, ketosis, and metabolic acidosis (low pH and low bicarbonate levels). COPD, as mentioned earlier, can lead to respiratory acidosis due to retained carbon dioxide. Neither of these conditions correlates with the ABG values provided, which show respiratory alkalosis (high pH and low PaCO2). Therefore, this choice does not correlate with the ABG values.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Diarrhea and vomiting for 36 hours:
Diarrhea and vomiting can lead to metabolic acidosis due to loss of bicarbonate and increased hydrogen ion concentration in the blood. However, the ABG values provided indicate respiratory alkalosis (high pH and low PaCO2), which is not consistent with metabolic acidosis caused by diarrhea and vomiting. Therefore, this choice does not correlate with the ABG values.
B. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD):
COPD is a respiratory condition characterized by airflow limitation and increased airway resistance. It can lead to respiratory acidosis due to retention of carbon dioxide (PaCO2 levels would be elevated). The ABG values in the scenario show respiratory alkalosis (low PaCO2), which is the opposite of what would be expected in COPD. Therefore, this choice does not correlate with the ABG values provided.
C. Anxiety-induced hyperventilation:
Anxiety-induced hyperventilation is a common cause of respiratory alkalosis. During hyperventilation, there is excessive elimination of carbon dioxide (PaCO2 levels decrease), leading to an increase in pH (alkalosis). The ABG values in the scenario show a high pH (7.48) and low PaCO2 (28 mm Hg), consistent with respiratory alkalosis seen in hyperventilation due to anxiety.
D. Diabetic ketoacidosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD):
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a metabolic condition characterized by hyperglycemia, ketosis, and metabolic acidosis (low pH and low bicarbonate levels). COPD, as mentioned earlier, can lead to respiratory acidosis due to retained carbon dioxide. Neither of these conditions correlates with the ABG values provided, which show respiratory alkalosis (high pH and low PaCO2). Therefore, this choice does not correlate with the ABG values.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
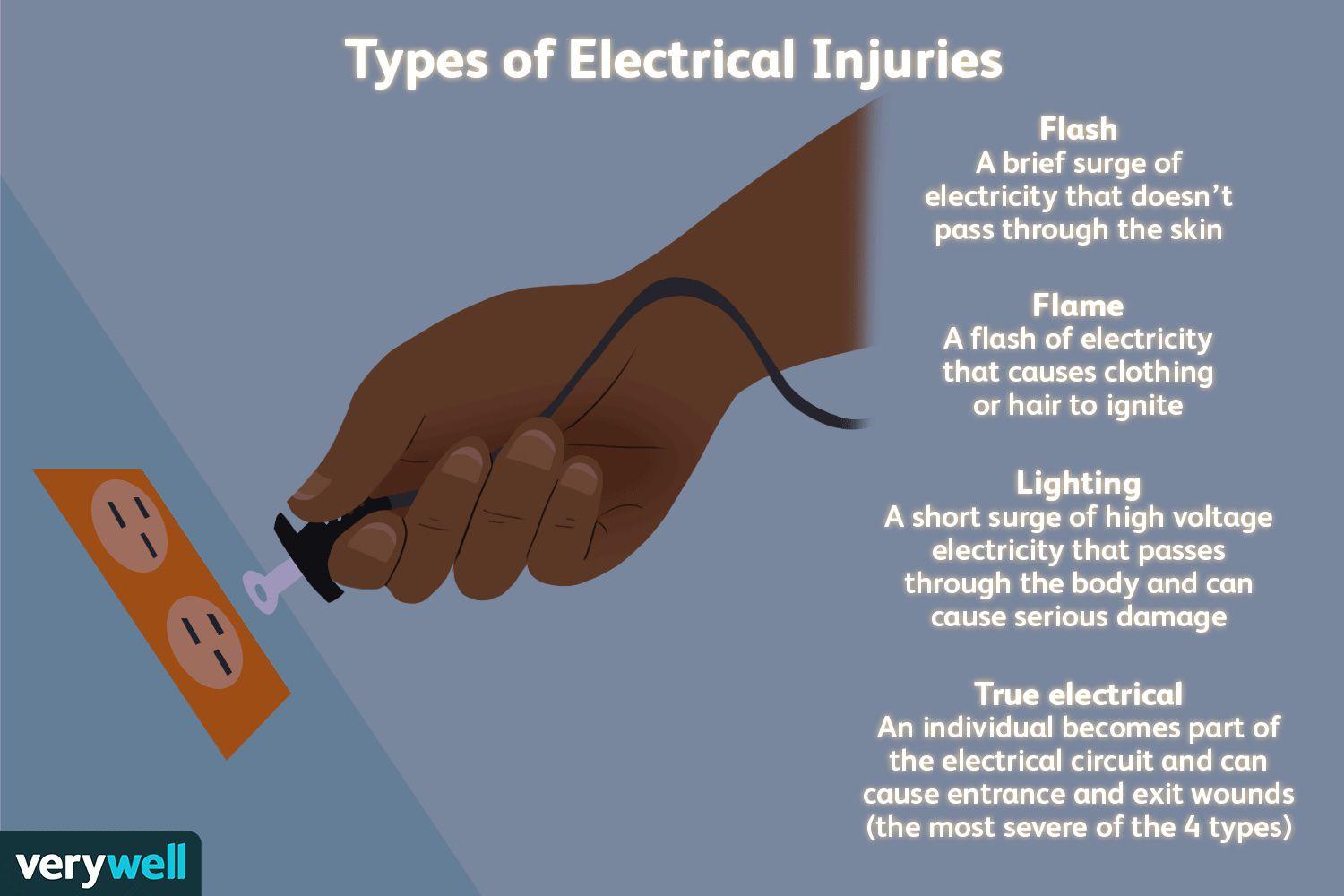
A. Electrical burns can have small amounts of skin damage, but more extensive damage beneath the skin.
This response is the best choice because it educates the client about the potential for deeper tissue damage associated with electrical burns. It acknowledges that while the burn on the skin may appear small, the damage underneath could be more extensive, affecting muscles, nerves, and blood vessels.
B. Electrical burns commonly cause reddened/purplish skin without blistering.
This statement is not the best response because it focuses solely on the appearance of the skin without addressing the potential for deeper tissue damage. While it is true that electrical burns can present with reddened or purplish skin without blistering, this response does not provide comprehensive information about the nature and severity of electrical burns.
C. Electrical burns typically are minor.
This response is incorrect because it downplays the seriousness of electrical burns. While some electrical burns may indeed be minor, others can cause significant tissue damage and complications. It's important for the nurse to educate the client about the range of severity that electrical burns can present.
D. Electrical burns usually cause much more skin damage than what can be seen on your skin.
This statement is partially accurate but does not provide as much information as choice A. While it acknowledges that electrical burns can cause more damage than what is visible on the skin's surface, it doesn't emphasize the potential for deeper tissue damage as effectively as choice A does.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
