A nurse is providing education to a community group about burn prevention. Which of the following is an example of a first-degree burn?
Excessive scarring
Blistering from flames
Blackened dead skin
A sunburn
The Correct Answer is D
A. Excessive scarring:
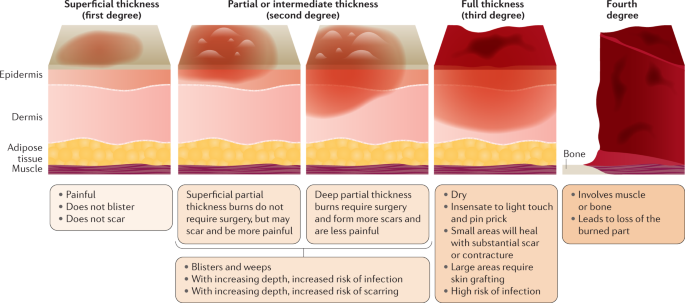
Excessive scarring is not an example of a first-degree burn. It typically occurs in more severe burns that affect deeper layers of the skin, such as second-degree or third-degree burns. Second-degree burns extend into the dermis, while third-degree burns damage all layers of the skin and can lead to significant scarring. First-degree burns, on the other hand, only affect the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) and usually do not result in excessive scarring.
B. Blistering from flames:
Blistering from flames is more characteristic of a second-degree burn rather than a first-degree burn. Second-degree burns involve damage to both the epidermis and part of the dermis, which can result in blister formation. These burns are often caused by direct contact with flames, hot liquids, or steam.
C. Blackened dead skin:
Blackened dead skin is indicative of a third-degree burn, which is the most severe type of burn. Third-degree burns damage all layers of the skin, including the epidermis, dermis, and sometimes underlying tissues. The skin may appear charred or blackened, and these burns often require medical intervention, such as skin grafting, due to the extent of tissue damage.
D. A sunburn:
A sunburn is an example of a first-degree burn. It occurs due to overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, leading to redness, pain, and mild swelling of the skin. First-degree burns affect only the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) and typically heal within a few days without significant scarring or blistering. Applying soothing lotions, staying hydrated, and avoiding further sun exposure can help manage sunburns.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Prevents complications, such as meningitis or pneumonitis
While oral acyclovir can be effective in managing HSV infections and reducing the severity of symptoms, it is not primarily used to prevent complications such as meningitis or pneumonitis. These complications may occur in severe cases of HSV infections, but oral acyclovir's main goal is to manage outbreaks and reduce symptoms.
B. Decreases the probability of recurrent outbreaks
Oral acyclovir can help reduce the frequency of recurrent outbreaks in individuals with HSV infections. However, it does not completely eliminate the probability of recurrent outbreaks. Some individuals may still experience occasional outbreaks even with regular use of oral acyclovir. The medication is more focused on managing outbreaks when they occur rather than preventing them entirely.
C. Shortens the outbreak and lessens the severity of symptoms
This option is the correct choice. Oral acyclovir is effective in shortening the duration of HSV outbreaks and reducing the severity of symptoms such as pain, itching, and lesions. It works by inhibiting the replication of the virus, which helps in faster healing and symptom relief. However, it does not cure the infection or eliminate the virus from the body.
D. Eliminates the likelihood of spreading the infection to others
While oral acyclovir can help manage outbreaks and reduce viral shedding, it does not completely eliminate the risk of spreading the infection to others. It can reduce the likelihood of transmission during active outbreaks, but individuals with HSV can still shed the virus and be contagious even when they are not experiencing visible symptoms. Therefore, other precautions such as practicing safe sex and avoiding close contact during outbreaks are also important for preventing transmission.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. “Call your surgeon if you have any questions at home.”
This instruction is important as it encourages the patient to seek help and clarification if they have any concerns or questions about their postoperative care at home. However, while communication with the surgeon is essential, it is not as immediately critical as ensuring proper hand hygiene when dealing with wound care and drain management.
B. ”Eat a diet high in protein, iron, zinc, and vitamin C.”
Nutritional advice is crucial for postoperative recovery, as a balanced diet high in protein, iron, zinc, and vitamin C can promote wound healing and overall recovery. However, while important for long-term recovery and healing, dietary recommendations do not directly address the immediate risk of infection or complications associated with wound care and drain management.
C. “Wash your hands before touching the drain or dressing."
This instruction is the most important in this context because proper hand hygiene is crucial for preventing infections during wound care and drain management. Clean hands significantly reduce the risk of introducing harmful bacteria or contaminants to the surgical site, which can lead to infections and other complications. Ensuring that the patient washes their hands before touching the drain or dressing is a fundamental measure for promoting wound healing and preventing postoperative complications.
D. “Be sure you keep all your postoperative appointments.”
Keeping postoperative appointments is important for ongoing assessment, monitoring, and follow-up care. However, while essential for overall recovery and management of postoperative issues, it is not as immediate or directly related to the patient's ability to manage their dressing and drain at home.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
