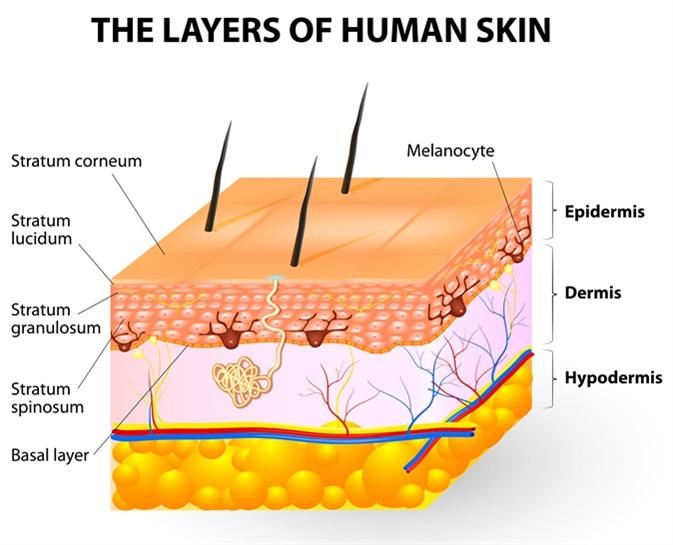
Melanocytes give rise to the pigment melanin, which is responsible for skin color. Where can the melanocytes be found?
Loose connective tissue
Epidermis
Dermis
Superficial fascia
The Correct Answer is B
A. Loose connective tissue:
Melanocytes are not typically found in loose connective tissue. Their primary location is within the epidermis, specifically in the basal layer, where they interact with keratinocytes to produce melanin and contribute to skin color. Loose connective tissue contains collagen and elastin fibers, as well as fibroblasts, but it does not house melanocytes.
B. Epidermis:
This is the correct answer. Melanocytes are primarily located in the basal layer of the epidermis, which is the deepest layer of the epidermis. These cells produce melanin, a pigment that helps protect the skin from UV radiation and determines skin color. Melanocytes are interspersed among keratinocytes in the epidermis and transfer melanin to keratinocytes to provide skin pigmentation.
C. Dermis:
The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis and consists of connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands. While the dermis plays a crucial role in supporting and nourishing the epidermis, melanocytes are not primarily located in the dermis. They are confined to the basal layer of the epidermis.
D. Superficial fascia:
The superficial fascia, also known as the subcutaneous tissue or hypodermis, lies beneath the dermis and consists of adipose (fat) tissue and connective tissue. It provides insulation, energy storage, and cushioning for underlying structures. However, melanocytes are not typically found in the superficial fascia. They are restricted to the epidermis, specifically the basal layer, where they carry out their function of melanin production.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Body mass index (BMI) of 19:
A BMI of 19 falls within the normal weight range. While obesity (high BMI) is a known risk factor for surgical complications, including SSIs, having a lower BMI (underweight) like 19 may not directly increase the risk of SSIs. However, extreme malnutrition or low BMI due to underlying health conditions could potentially impact wound healing and immune function, indirectly contributing to infection risk.
B. History of deep vein thrombosis (DVT):
A history of deep vein thrombosis is a risk factor for surgical complications, including SSIs. Patients with a history of DVT may have impaired circulation or underlying vascular issues, which can affect tissue perfusion, wound healing, and increase the risk of infections.
C. Aged 55 years old:
Age is a risk factor for surgical complications, including SSIs. Older adults, typically defined as those aged 65 and above, may have reduced immune function, slower wound healing, and underlying health conditions that contribute to infection risk. While 55 years old is not considered advanced age in terms of surgical risk, older age in general is associated with a higher risk of complications.
D. Type 2 diabetes mellitus:
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a significant risk factor for SSIs. Diabetes can impair immune function, delay wound healing, and increase susceptibility to infections. Poorly controlled blood sugar levels in diabetic patients can further exacerbate the risk of SSIs post-surgery.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. A 60-year-old client with gastritis:
Gastritis is inflammation of the stomach lining and typically does not directly increase the risk of skin infections. However, if the gastritis is due to an underlying condition that affects the immune system, such as an autoimmune disorder, the client may have a slightly higher risk of infections, including skin infections, compared to a healthy individual of the same age. Overall, gastritis alone is not a significant risk factor for skin infections compared to the other options.
B. A 20-year-old client with a closed tibia fracture:
A closed tibia fracture refers to a broken shinbone that does not break the skin. While fractures themselves do not necessarily increase the risk of skin infections, they can indirectly contribute to infection risk if there are complications such as open wounds, surgical procedures, or prolonged immobilization. In this case, because the fracture is closed and presumably not complicated by open wounds or surgery, this client is not significantly prone to skin infections compared to the other options.
C. A 55-year-old client taking an ACE inhibitor:
ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors are medications commonly used to treat conditions like high blood pressure and heart failure. While these medications can cause side effects like a dry cough or skin rash in some individuals, they do not directly increase the risk of skin infections. Unless the client experiences a severe allergic reaction or develops a rash that becomes infected, the use of ACE inhibitors alone is not a major risk factor for skin infections compared to the other options.
D. A 35-year-old client receiving chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy is a treatment for cancer that works by targeting rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells but also affecting some healthy cells like those in the bone marrow responsible for producing white blood cells. As a result, chemotherapy can significantly weaken the immune system, leading to a higher risk of infections, including skin infections. Patients undergoing chemotherapy are particularly susceptible to bacterial, fungal, and viral infections due to their compromised immune response. Therefore, the 35-year-old client receiving chemotherapy is the most prone to skin infections among the options given due to their weakened immune system.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
