A nurse is caring for a client with a pressure injury. Which of the following should the nurse recognize as a priority in the plan of care?
Keeping the wound clean and non-infected
Application of a negative pressure wound care device
Client education on wound prevention
Promoting a high carbohydrate, low protein diet
The Correct Answer is A
A. Keeping the wound clean and non-infected: When caring for a client with a pressure injury, the priority in the plan of care is to keep the wound clean and prevent infection. This involves regular wound assessment, proper wound cleaning techniques, application of appropriate dressings, and monitoring for signs of infection such as increased redness, swelling, warmth, or drainage. Preventing infection is crucial for promoting healing and preventing complications.
B. Application of a negative pressure wound care device: While negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) can be beneficial in promoting wound healing, it may not be the immediate priority unless specifically indicated by the healthcare provider based on the stage and characteristics of the pressure injury. Keeping the wound clean and preventing infection take precedence over NPWT in the initial plan of care.
C. Client education on wound prevention: While client education is important for preventing future pressure injuries, it is not the immediate priority when caring for an existing pressure injury. The focus initially should be on managing the current wound to promote healing and prevent complications.
D. Promoting a high carbohydrate, low protein diet: Nutritional interventions are important in wound healing, but promoting a specific diet is not the immediate priority in the plan of care for a pressure injury. Providing adequate nutrition and addressing any nutritional deficiencies may be part of the overall plan, but it is secondary to keeping the wound clean and preventing infection.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Loose connective tissue:
Melanocytes are not typically found in loose connective tissue. Their primary location is within the epidermis, specifically in the basal layer, where they interact with keratinocytes to produce melanin and contribute to skin color. Loose connective tissue contains collagen and elastin fibers, as well as fibroblasts, but it does not house melanocytes.
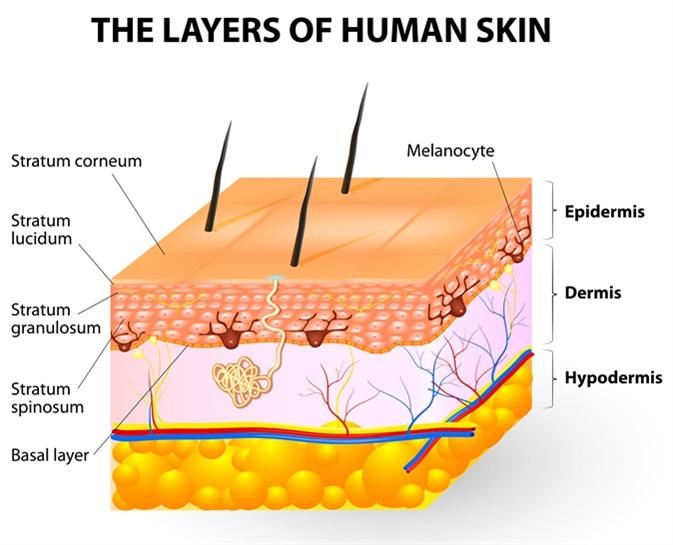
B. Epidermis:
This is the correct answer. Melanocytes are primarily located in the basal layer of the epidermis, which is the deepest layer of the epidermis. These cells produce melanin, a pigment that helps protect the skin from UV radiation and determines skin color. Melanocytes are interspersed among keratinocytes in the epidermis and transfer melanin to keratinocytes to provide skin pigmentation.
C. Dermis:
The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis and consists of connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands. While the dermis plays a crucial role in supporting and nourishing the epidermis, melanocytes are not primarily located in the dermis. They are confined to the basal layer of the epidermis.
D. Superficial fascia:
The superficial fascia, also known as the subcutaneous tissue or hypodermis, lies beneath the dermis and consists of adipose (fat) tissue and connective tissue. It provides insulation, energy storage, and cushioning for underlying structures. However, melanocytes are not typically found in the superficial fascia. They are restricted to the epidermis, specifically the basal layer, where they carry out their function of melanin production.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Increase the effectiveness of the skin graft:
Debridement can indeed increase the effectiveness of a skin graft by preparing a clean, viable wound bed for grafting. Removing dead tissue and debris helps the skin graft adhere to healthy tissue and promotes successful graft take. However, this is not the primary purpose of debridement.
B. Promote movement in the affected area:
While debridement can indirectly contribute to promoting movement by improving wound healing and reducing pain, the primary purpose of debridement is not to promote movement in the affected area.
C. Prevent infection and promote healing:
This statement accurately reflects the primary purpose of debridement. By removing nonviable tissue, debris, and foreign material from the wound, debridement helps prevent infection by reducing the bacterial load and creating an environment conducive to healing. It also promotes granulation tissue formation and wound contraction, which are essential for wound healing.
D. Promote suppuration of the wound:
Suppuration refers to the formation and discharge of pus from a wound, often indicating infection. Debridement aims to remove necrotic tissue and prevent infection, so promoting suppuration is not a desired outcome of debridement.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
