A client is diagnosed with an enterocele. The nurse interprets this condition as:
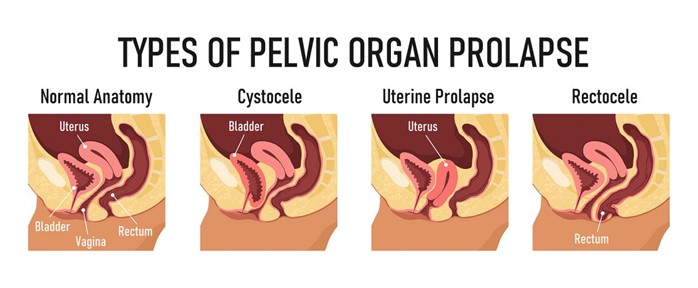
Protrusion of the posterior bladder wall downward through the anterior vaginal wall
Bulging of the small intestine through the posterior vaginal wall
Descent of the uterus through the pelvic floor into the vagina
Sagging of the rectum with pressure exerted against the posterior vaginal wall
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A: Protrusion of the posterior bladder wall downward through the anterior vaginal wall is not the correct answer because it describes a different condition called cystocele. A cystocele occurs when the bladder pushes into the vagina due to weakened pelvic support structures.
Choice B: Bulging of the small intestine through the posterior vaginal wall is the correct answer because it describes an enterocele. Enterocele occurs when the small intestine slides into a pouch between the rectum and vagina due to weakened pelvic support structures.
Choice C: Descent of the uterus through the pelvic floor into the vagina is not the correct answer because it describes a different condition called uterine prolapse. Uterine prolapse occurs when the uterus drops down into or out of the vagina due to weakened pelvic support structures.
Choice D: Sagging of the rectum with the pressure exerted against the posterior vaginal wall is not the correct answer because it describes a different condition called rectocele. Rectocele occurs when the rectum bulges into or out of the vagina due to weakened pelvic support structures.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","C","D","E"]
Explanation
Choice A: Fecal incontinence is not the correct answer because it is not a disorder of pelvic organ prolapse. Fecal incontinence is a condition that causes the loss of bowel control, resulting in involuntary leakage of stool or gas. It can be caused by various factors such as nerve damage, muscle weakness, or diarrhea. It is not related to the displacement or descent of pelvic organs.
Choice B: Rectocele is the correct answer because it is a disorder of pelvic organ prolapse. Rectocele is a condition that occurs when the rectum bulges or sags into the vagina, creating a pouch or hernia. It can cause symptoms such as constipation, difficulty with bowel movements, or a feeling of pressure or fullness in the vagina. It is caused by the weakening or stretching of the pelvic floor muscles and connective tissue that support the rectum and vagina.
Choice C: Urinary incontinence is the correct answer because it is a disorder of pelvic organ prolapse. Urinary incontinence is a condition that causes the loss of bladder control, resulting in involuntary leakage of urine or urge to urinate. It can be caused by various factors such as stress, infection, or medication. It is also related to the displacement or descent of pelvic organs, such as the bladder or urethra, which can affect the function and closure of the urinary sphincter.
Choice D: Cystocele is the correct answer because it is a disorder of pelvic organ prolapse. Cystocele is a condition that occurs when the bladder protrudes or drops into the vagina, creating a pouch or hernia. It can cause symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency, or retention, or a feeling of pressure or fullness in the vagina. It is caused by the weakening or stretching of the pelvic floor muscles and connective tissue that support the bladder and vagina.
Choice E: Enterocele is the correct answer because it is a disorder of pelvic organ prolapse. Enterocele is a condition that occurs when the small intestine bulges or descends into the vagina, creating a pouch or hernia. It can cause symptoms such as lower back pain, pelvic pressure, or difficulty with bowel movements. It is caused by the weakening or stretching of the pelvic floor muscles and connective tissue that support the small intestine and vagina.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
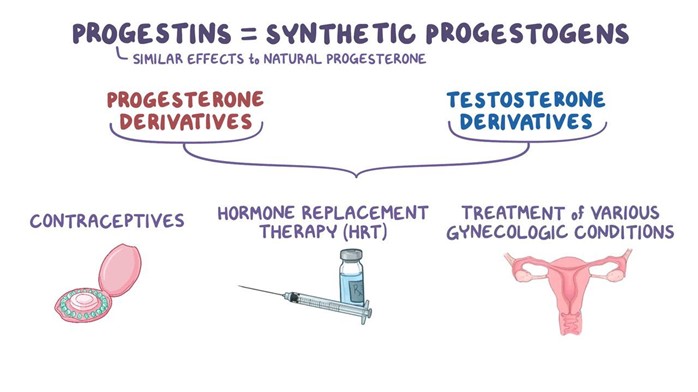
Choice A reason: Antiestrogens are not a first-line treatment for endometriosis, as they can cause severe side effects such as bone loss, hot flashes, and vaginal dryness.
Choice B reason: Progestins are a first-line treatment for endometriosis, as they can suppress the growth of endometrial tissue and reduce pain and bleeding.
Choice C reason: Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues are a second-line treatment for endometriosis, as they can induce temporary menopause and cause bone loss, hot flashes, and mood changes.
Choice D reason: NSAIDs are not a treatment for endometriosis, as they can only provide symptomatic relief for pain and inflammation.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
