Blood Compatibility and Crossmatching
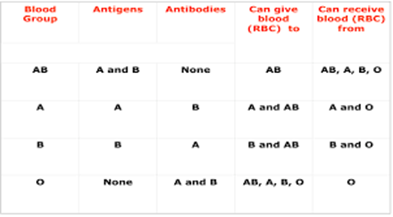
- Blood compatibility is determined by the presence or absence of antigens on the surface of RBCs and antibodies in the plasma
- The most important antigens are the ABO group (A, B, AB, or O) and the Rh factor (positive or negative)
- The most common antibodies are antiA, anti-B, anti-D (Rh), and irregular antibodies that react with other antigens
- Blood compatibility is based on the principle of avoiding agglutination (clumping) or hemolysis (destruction) of RBCs due to antigen-antibody reactions
- The ideal blood transfusion is autologous (from the client's own blood), followed by allogeneic (from a compatible donor)
- The universal donor is O negative, meaning that it can be given to any recipient regardless of their blood type
- The universal recipient is AB positive, meaning that it can receive any blood type without adverse reactions
- Crossmatching is a laboratory test that confirms the compatibility of the donor's blood with the recipient's blood
- Crossmatching involves mixing a sample of the donor's RBCs with a sample of the recipient's plasma and observing for agglutination or hemolysis
- A compatible crossmatch indicates that there is no reaction between the donor's RBCs and the recipient's plasma
- An incompatible crossmatch indicates that there is a reaction between the donor's RBCs and the recipient's plasma; this can lead to a transfusion reaction if transfused
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Questions on Blood Compatibility and Crossmatching
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is ["A","B","D"]
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Search Here
Related Topics
- Enteral nutrition (EN) - Blood and Cardiovascular Disorders
- Mobility devices: crutches, canes, continuous passive ROM machine. - Blood and Cardiovascular Disorders
- Bandaging - Blood and Cardiovascular Disorders
- IV insertion - Blood and Cardiovascular Disorders
- Immunodefeciency disorders - Blood and Cardiovascular Disorders
More on Nursing
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
