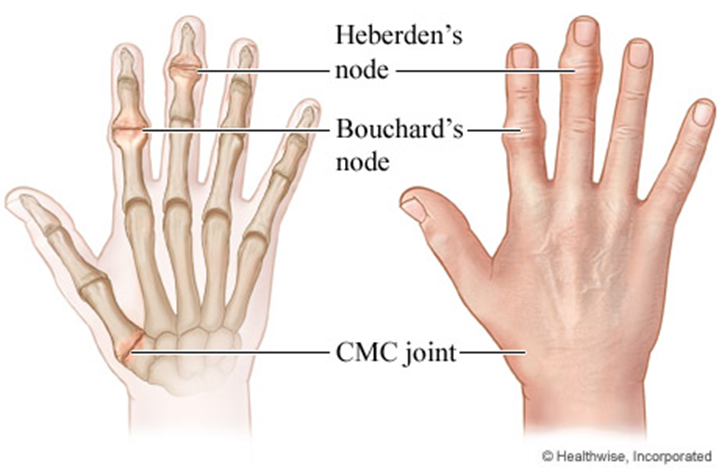
While assessing a client with degenerative joint disease, the nurse observes Heberden's nodes, large prominences on the client's fingers that are reddened. The client reports that the nodes are painful. Which action should the nurse take?
Discuss approaches to chronic pain control with the client.
Review the client's dietary intake of high-protein foods.
Notify the healthcare provider of the finding immediately.
Assess the client's radial pulses and capillary refill time.
The Correct Answer is A
A. Discuss approaches to chronic pain control with the client:
This is the correct answer. Heberden's nodes are bony enlargements that can occur in osteoarthritis, particularly in the joints of the fingers. These nodes can be associated with pain. Discussing approaches to chronic pain control with the client is an appropriate nursing intervention to address the client's pain and improve quality of life.
B. Review the client's dietary intake of high-protein foods:
Dietary intake of high-protein foods is not directly related to the management of Heberden's nodes in degenerative joint disease. Pain control and joint protection measures are more relevant.
C. Notify the healthcare provider of the finding immediately:
While it's important to communicate significant findings to the healthcare provider, the presence of Heberden's nodes in degenerative joint disease may not require immediate notification unless there are other concerning symptoms or complications.
D. Assess the client's radial pulses and capillary refill time:
Assessing radial pulses and capillary refill time is not directly related to managing Heberden's nodes in degenerative joint disease. These nodes are primarily a result of joint changes in osteoarthritis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Increased temperature to the lower extremity:
While increased temperature could indicate inflammation or infection, it is not as immediately concerning as impaired circulation.
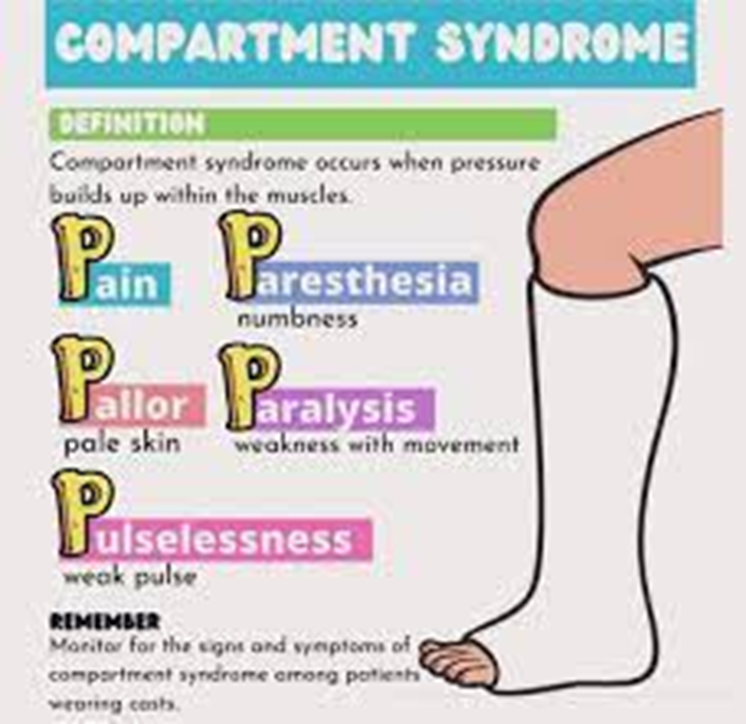
B. Right foot pale with sluggish capillary refill.
This finding suggests a potential impairment in blood flow to the right foot, which could be due to complications such as compartment syndrome or impaired circulation. Compartment syndrome is a serious condition that occurs when there is increased pressure within a muscle compartment, leading to reduced blood flow. Pale color and sluggish capillary refill indicate compromised circulation and require prompt intervention to prevent further damage.
C. Circumferential edema of the right foot:
Edema is a common finding after a fracture and cast application. However, in the context of pale color and sluggish capillary refill, it may indicate increased pressure within the compartment, requiring immediate attention.
D. Complaint of throbbing right leg pain:
Pain is a common complaint after a fracture, and throbbing pain may be expected. However, the priority is to address the potential compromise in circulation indicated by the pale color and sluggish capillary refill.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Encourage regular turning:
While turning is important for preventing complications like pressure ulcers, in this acute situation, addressing fluid imbalance and potential sepsis take precedence.
B. Monitor skin for breakdown:
Monitoring for skin breakdown is essential but is not the most critical intervention at this moment.
C. Assess wound drainage daily:
Daily assessment of wound drainage is important for evaluating the status of the surgical site. However, in this situation of potential anastomosis leakage with signs of systemic infection and hypotension, immediate interventions to stabilize the client's condition are of higher priority.
D. Strict IV fluid replacement:
This is the correct answer. The client is displaying signs of systemic infection (fever) and possible sepsis (tachycardia, hypotension), which might be due to an anastomosis leakage following gastric bypass surgery. Ensuring adequate IV fluid replacement is crucial to address hypotension, maintain perfusion, and support hemodynamic stability in this critical situation.

Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
