The nurse assesses a client with cirrhosis and finds 4+ pitting edema of the feet and legs, and massive ascites. Which mechanism contributes to edema and ascites in clients with cirrhosis?
Hyperaldosteronism causing an increased sodium reabsorption in renal tubules.
Decreased renin-angiotensin response related to an increase in renal blood flow.
Decreased portacaval pressure with greater collateral circulation.
Hypoalbuminemia that results in a decreased colloidal oncotic pressure
The Correct Answer is D
A. Hyperaldosteronism causing an increased sodium reabsorption in renal tubules.
Hyperaldosteronism is characterized by an excess of aldosterone, a hormone that regulates sodium and water balance. In cirrhosis, however, sodium retention is often related to other mechanisms such as portal hypertension and hypoalbuminemia, rather than hyperaldosteronism.
B. Decreased renin-angiotensin response related to an increase in renal blood flow.
Cirrhosis is more commonly associated with an activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, leading to increased sodium and water retention. The increased renin-angiotensin response is a compensatory mechanism to maintain perfusion in the setting of cirrhosis and does not contribute to decreased renal blood flow.
C. Decreased portacaval pressure with greater collateral circulation.
This statement is not accurate. In cirrhosis, there is typically increased portacaval pressure due to portal hypertension, which can lead to the development of collateral circulation. However, this does not explain the edema and ascites seen in cirrhosis.
D. Hypoalbuminemia that results in a decreased colloidal oncotic pressure.
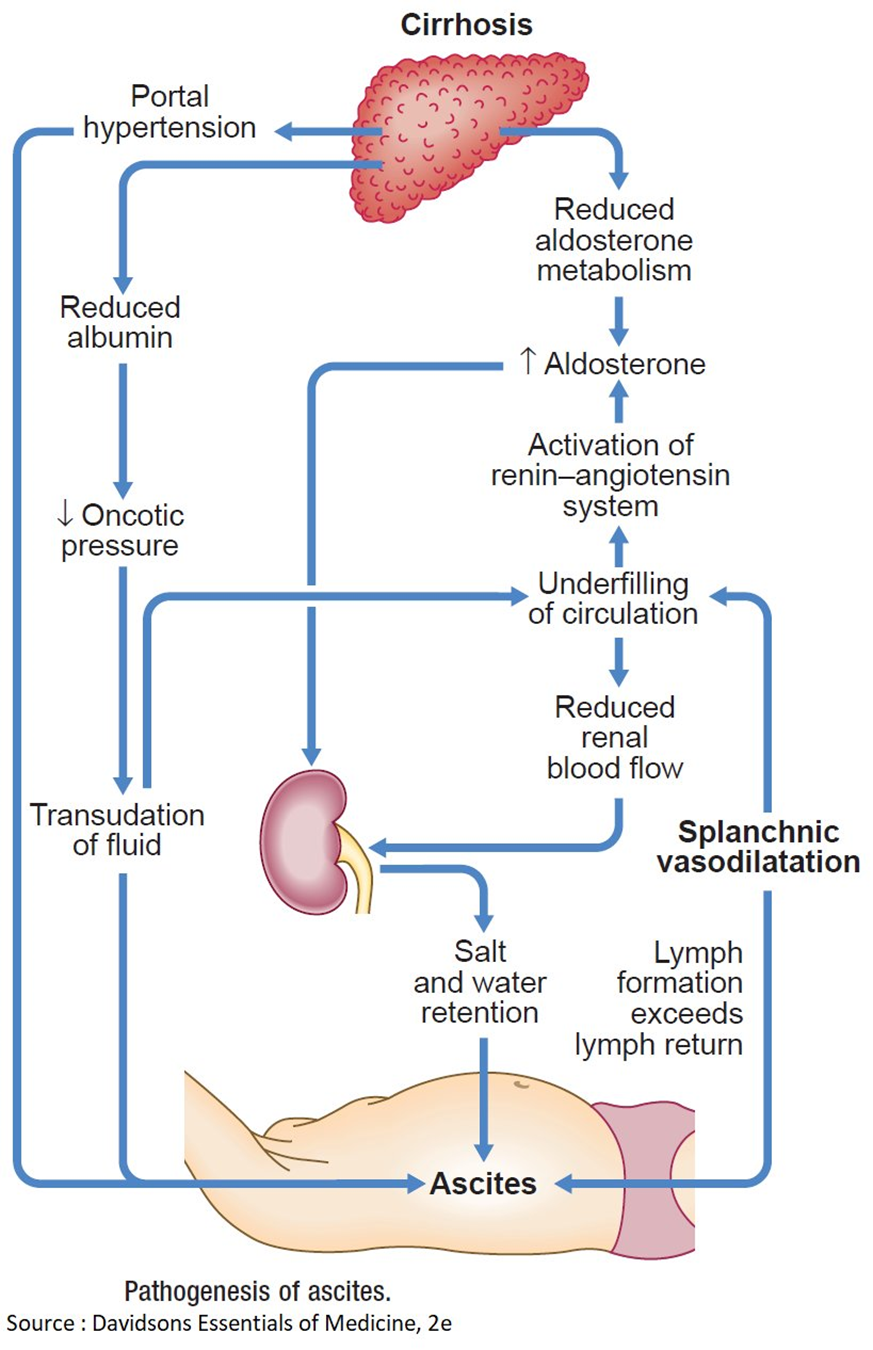
This is the correct choice. In cirrhosis, liver damage leads to decreased synthesis of albumin. Albumin plays a crucial role in maintaining colloidal oncotic pressure, and when it is decreased (hypoalbuminemia), fluid is more likely to leak out of blood vessels, resulting in edema. The same mechanism contributes to the development of ascites in the abdominal cavity.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Assess client for signs and symptoms of upper airway infection:
While upper airway infections can contribute to respiratory symptoms, the client's history of asthma and the exacerbation of symptoms during exercise suggest that asthma management should be a priority.
B. Determine if the client is using an inhaler before exercising:
This is a relevant consideration, and ensuring proper pre-exercise use of bronchodilators (such as an inhaler) is an important aspect of asthma management. However, the question is broader and involves a review of the client's overall asthma management.
C. Teach client to use pursed lip breathing when episodes occur:
Pursed lip breathing is a technique that can help manage symptoms, especially during episodes of bronchoconstriction. However, the focus here is on a more comprehensive assessment and review of the client's routine asthma management.
D. Review the client's routine asthma management prescriptions:
This is the correct answer. The client's reported symptoms during exercise suggest a potential need for adjustments to the routine asthma management plan. Reviewing the client's prescriptions, including the type and timing of medications, can help ensure optimal control of symptoms, especially during physical activity.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Platelet count 40,000 x10/μL (40.000 x109/L):
This is the correct answer. A platelet count of 40,000 x10/μL is significantly below the normal range (usually around 150,000 to 450,000/μL). Low platelet count (thrombocytopenia) can increase the risk of bleeding during and after a surgical procedure. The healthcare provider should be alerted to assess the risk and determine the appropriate management.
B. White blood cells 9,000/μL (9x109/L):
The white blood cell count is within the normal range, and it is not a significant concern for a vertebroplasty procedure.
C. Hematocrit 38% (0.38):
The hematocrit level is within the normal range and is not a significant concern for a vertebroplasty procedure.
D. Hemoglobin 12 g/dL (120 g/L):
The hemoglobin level is within the normal range and is not a significant concern for a vertebroplasty procedure.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
