A client who underwent cardiac stent placement four days ago arrives to the emergency department reporting a sudden onset of chest pressure and shortness of breath. Which action should the nurse take next?
Evaluate upper and lower extremities for perfusion, pulse volume, and pitting edema.
Listen for extra heart sounds, murmurs, and rhythm with the bell of the stethoscope.
Obtain a 12-lead electrocardiogram and begin continuous cardiac monitoring.
Verify troponin level assessments are scheduled every 3-6 hours for a series of three
The Correct Answer is C
A. Evaluate upper and lower extremities for perfusion, pulse volume, and pitting edema:
This option focuses on assessing perfusion and circulation in the extremities. While it's important in certain situations, in the context of a client who recently underwent cardiac stent placement and is now experiencing chest pressure and shortness of breath, the priority is to assess the cardiac status more directly.
B. Listen for extra heart sounds, murmurs, and rhythm with the bell of the stethoscope:
This option involves auscultating the heart for abnormal sounds or rhythms. While it's a valuable assessment in general, in this particular scenario, obtaining an electrocardiogram (ECG) and initiating continuous cardiac monitoring would provide a more comprehensive and immediate evaluation of the cardiac status.
C. Obtain a 12-lead electrocardiogram and begin continuous cardiac monitoring:
This is the correct choice. Obtaining a 12-lead ECG and initiating continuous cardiac monitoring is crucial in assessing the client's cardiac function. It allows for the detection of any acute changes in the heart's electrical activity or rhythm, which is essential for timely intervention and management.
D. Verify troponin level assessments are scheduled every 3-6 hours for a series of three:
Monitoring troponin levels is important in assessing cardiac damage, but in this acute situation, obtaining an immediate ECG and initiating continuous cardiac monitoring take precedence for a more real-time evaluation of the client's cardiac status. Troponin levels may be monitored subsequently based on the initial findings.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Activity level of bowel sounds:
Bowel sounds are important to assess, but they may not directly influence or be influenced by the abdominal pain associated with chronic pancreatitis.
B. Eating patterns and dietary intake.
Clients with chronic pancreatitis often experience abdominal pain exacerbated by the intake of food, especially fatty meals. Monitoring the client's eating patterns and dietary intake is crucial for identifying triggers that may worsen the abdominal pain. By understanding the relationship between food intake and pain, the nurse can provide guidance on dietary modifications to help manage the symptoms.
C. Level and amount of physical activity:
While physical activity is important for overall health, it may not be the primary factor contributing to or alleviating the abdominal pain in a client with chronic pancreatitis.
D. Color and consistency of feces:
Monitoring the color and consistency of feces is important for assessing pancreatic function, but it may not be the most immediate factor to address in the context of managing abdominal pain. Dietary patterns are more directly related to pain management in this case.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
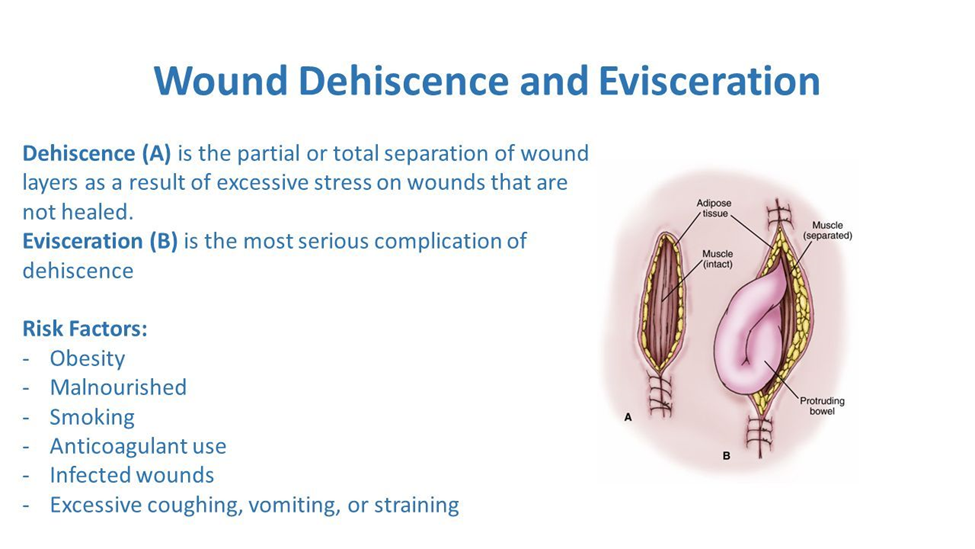
A. Prepare the client to return to the operating room:
This is the correct and immediate priority. Evisceration, where internal organs protrude through the surgical incision, is a surgical emergency. Returning the client to the operating room is necessary to assess the extent of the complication, address the wound dehiscence, and protect the exposed organs. This intervention aims to prevent further complications and provide necessary surgical interventions.
B. Obtain a sample of the drainage to send to the lab:
While obtaining samples for laboratory analysis can be important for infection control, in the context of a client with evisceration, the primary concern is the surgical emergency. The priority is to address the wound complication by returning to the operating room rather than focusing on laboratory analysis at this immediate moment.
C. Bring additional sterile dressing supplies to the room:
While bringing additional supplies may be necessary, the priority in this situation is to prepare for the client's return to the operating room. Once the client is in a controlled surgical environment, additional dressing changes and wound care can be performed as needed.
D. Auscultate the abdomen for bowel sound activity:
While monitoring bowel sounds is a routine nursing assessment, in the context of evisceration, the immediate concern is the exposure of internal organs and the risk of infection. Preparing for the operating room takes precedence over routine assessments.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
