A client with lung cancer who wears a subcutaneous morphine sulfate patch for pain is short of breath and is difficult to arouse. When performing a head to toe assessment, the nurse discovers four analgesic patches on the client's body. Which intervention should the nurse implement first?
Measure the client's blood pressure.
Remove all of the morphine patches.
Apply oxygen per face mask.
Administer a narcotic antagonist.
The Correct Answer is D
A. Measure the client's blood pressure:
While monitoring blood pressure is an important aspect of assessing a client's overall condition, it is not the immediate priority in a suspected opioid overdose. Respiratory depression and difficulty in arousing are more critical concerns that warrant prompt intervention with naloxone.
B. Remove all of the morphine patches:
While eventually, the nurse will need to address the presence of multiple morphine patches, removing them is not the first action. Administering naloxone to reverse the opioid effects takes precedence over patch removal.
C. Apply oxygen per face mask:
While providing oxygen may be necessary to support respiratory function, it doesn't address the underlying cause of the respiratory distress, which is likely opioid toxicity. Administering naloxone is the more direct and immediate intervention to counteract the effects of the opioids.
D. Administer a narcotic antagonist:
This is the correct and immediate priority. If the client is difficult to arouse and has multiple morphine patches, it raises concerns about opioid toxicity. Naloxone is a narcotic antagonist that can reverse the effects of opioid overdose, particularly respiratory depression, and is crucial in this scenario to restore normal respiratory function.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Initiate cardiac telemetry:
Cardiac telemetry is not the immediate priority in this case. Kidney stones are more likely to cause severe localized pain rather than cardiac-related symptoms.
B. Administer a PRN dose of a laxative:
Laxatives are not indicated for the management of kidney stones or the associated flank pain. The priority is to address the specific needs related to the possible passage of kidney stones.
C. Implement seizure precautions:
Seizure precautions are not relevant to the sudden onset of severe flank pain in the context of hyperparathyroidism. The focus should be on managing pain, assessing for kidney stone passage, and addressing the underlying cause.
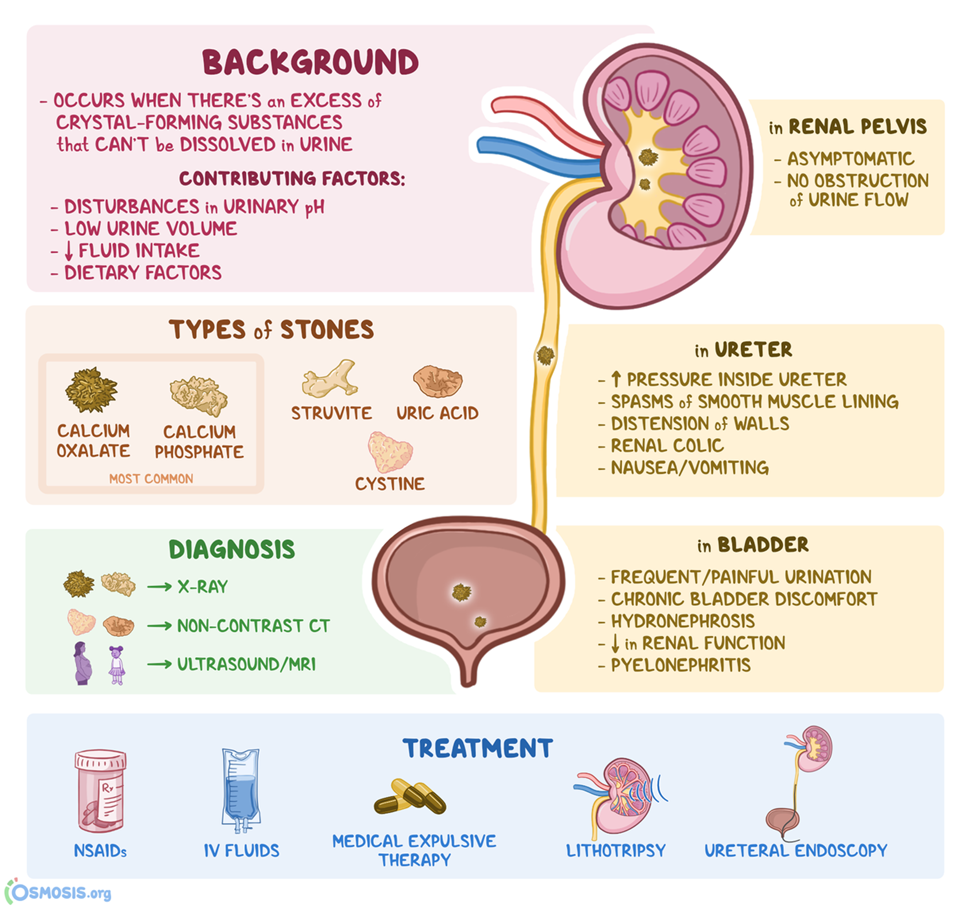
D. Begin straining all urine.
Straining all urine allows for the collection and examination of any passed stones. This information is important for identifying the composition of the stones and guiding further management.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Remind the client to practice pelvic floor (Kegel) exercises regularly.
Pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegel exercises, are typically recommended for conditions involving weakened pelvic floor muscles. However, in the context of urinary retention related to sensorimotor deficits in multiple sclerosis, the issue is more neurological in nature. Therefore, pelvic floor exercises may not address the underlying problem effectively.
B. Provide a bedside commode for immediate use in the client's room.
While a bedside commode may be beneficial for individuals with mobility issues, it doesn't directly address the problem of urinary retention. It focuses on providing a convenient means for the client to void when needed, but it doesn't address the inability to empty the bladder spontaneously.
C. Explain the need to limit intake of oral fluids to reduce client discomfort.
Limiting oral fluids is not an appropriate intervention for urinary retention. In fact, it could lead to dehydration, which is not a recommended approach. The focus should be on addressing the difficulty in voiding through appropriate techniques.
D. Teach the client techniques for performing intermittent catheterization.
This is the correct choice. Intermittent catheterization is a direct and effective method to manage urinary retention in clients with sensorimotor deficits. Teaching the client how to perform intermittent catheterization empowers them to maintain regular bladder emptying and prevent complications associated with urinary retention.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
