Which laboratory results should the nurse closely monitor in a client who has end-stage renal disease (ESRD.?
Serum potassium, calcium, and phosphorus
Erythrocytes, hemoglobin, and hematocrit
Leukocytes, neutrophils, and thyroxine
Blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature
The Correct Answer is A
Choice B reason: Erythrocytes, hemoglobin, and hematocrit are laboratory results that are not as critical as serum potassium, calcium, and phosphorus in a client who has end-stage renal disease (ESRD.. Erythrocytes are red blood cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Hemoglobin is a protein in erythrocytes that binds oxygen. Hematocrit is the percentage of blood volume that is occupied by erythrocytes. ESRD can cause anemia (low erythrocyte, hemoglobin, and hematocrit levels) due to reduced production of erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates erythrocyte formation, by the kidneys. Anemia can cause fatigue, pallor, or shortness of breath.
Choice C reason: Leukocytes, neutrophils, and thyroxine are laboratory results that are not as relevant as serum potassium, calcium, and phosphorus in a client who has end-stage renal disease (ESRD.. Leukocytes are white blood cells that fight infection and inflammation. Neutrophils are a type of leukocyte that respond to bacterial infection. Thyroxine is a hormone that regulates metabolism and growth. ESRD can cause leukopenia (low leukocyte levels) and neutropenia (low neutrophil levels) due to impaired immune function and increased susceptibility to infection. ESRD can also cause hypothyroidism (low thyroxine levels) due to reduced clearance of thyroid hormones by the kidneys. Hypothyroidism can cause weight gain, cold intolerance, or depression.
Choice D reason: Blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature are not laboratory results, but vital signs that should be monitored in a client who has end-stage renal disease (ESRD.. Blood pressure is the force of blood against the walls of the arteries. Heart rate is the number of times the heart beats per minute. Temperature is the measure of body heat. ESRD can cause hypertension (high blood pressurE. due to fluid overload and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, a hormonal pathway that regulates blood pressure and fluid balance. Hypertension can cause headache, chest pain, or stroke. ESRD can also cause tachycardia (high heart ratE. due to anemia, fluid overload, or electrolyte imbalance. Tachycardia can cause palpitations, dizziness, or heart failure. ESRD can also cause fever (high temperaturE. due to infection or inflammation. Fever can cause chills, sweating, or delirium.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
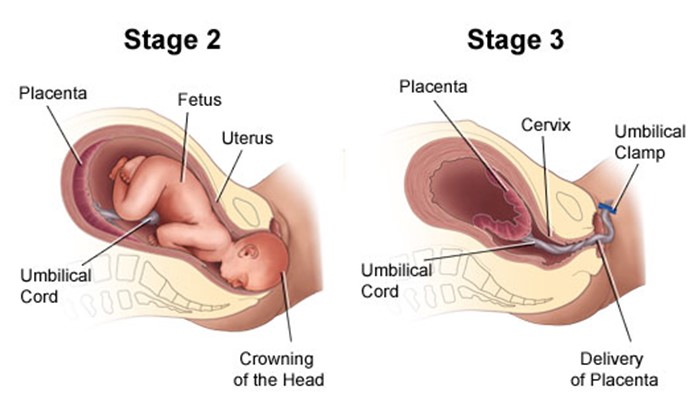
Choice A reason: Providing pain medication to increase the client's tolerance of labor pains is not a specific intervention for the second stage of labor. Pain medication is a drug that relieves pain by blocking pain signals or reducing inflammation. Pain medication can be given during any stage of labor, depending on the client's preference and condition. However, pain medication may have side effects such as sedation, nausea, or respiratory depression, and may affect the fetal heart rate or the progress of labor.
Choice B reason: Assessing the fetal heart rate and pattern for signs of fetal distress is not a particular intervention for the second stage of labor. Fetal heart rate and pattern are indicators of fetal well-being and oxygenation. Fetal heart rate and pattern should be monitored throughout labor, especially during contractions, to detect any abnormalities or complications such as bradycardia, tachycardia, or decelerations.
Choice D reason: Monitoring effects of oxytocin administration to help achieve cervical dilation is not a relevant intervention for the second stage of labor. Oxytocin is a hormone that stimulates uterine contractions and cervical dilation. Oxytocin can be administered during labor to augment or induce labor, especially if there is prolonged or dysfunctional labor. However, oxytocin is not needed in the second stage of labor, when the cervix is already fully dilated and the focus is on pushing and delivering the baby.
Correct Answer is ["A","C","D"]
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is a correct answer because continuing to monitor the client for signs of an infection is important to detect any recurrence or complication of MRSA infection. MRSA is a type of bacteria that is resistant to many antibiotics and can cause serious skin, soft tissue, bone, joint, or bloodstream infections. The nurse should assess the client's vital signs, wound appearance, pain level, and laboratory results.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct answer because calling the healthcare provider for a prescription for linezolid is not necessary unless the client has an active MRSA infection that requires treatment. Linezolid is an antibiotic that can be used to treat MRSA infections, but it has potential side effects and interactions that need to be considered. The nurse should not prescribe or administer antibiotics without a valid order.
Choice C reason: This is a correct answer because collecting multiple sets of blood cultures for MRSA screening is important to identify any asymptomatic bacteremia or sepsis that could result from MRSA infection. MRSA can enter the bloodstream through wounds, catheters, or surgical sites and cause life-threatening complications such as endocarditis, osteomyelitis, or pneumonia. The nurse should obtain blood samples from different sites and times and send them to the laboratory for analysis.
Choice D reason: This is a correct answer because placing the client on contact transmission precautions is important to prevent the spread of MRSA to other clients, staff, or visitors. Contact transmission precautions include wearing gloves and gowns when entering the client's room, using dedicated or disposable equipment, and performing hand hygiene before and after contact with the client or their environment.
Choice E reason: This is not a correct answer because obtaining a sputum specimen for culture and sensitivity is not relevant to the client's history of MRSA wound infection. Sputum culture and sensitivity is a test that can be used to diagnose respiratory infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses. The nurse should only obtain a sputum specimen if the client has signs or symptoms of a respiratory infection, such as cough, fever, chest pain, or dyspnea.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
