When admitting a patient with a stroke who is unconscious and unresponsive to stimuli. The nurse learns from the patient’s family that the patient has a history of GERD, the nurse will plan to do frequent assessment of the patient’s:
Breath sounds.
abdominal girth.
Bowel sounds.
Apical pulse.
The Correct Answer is A
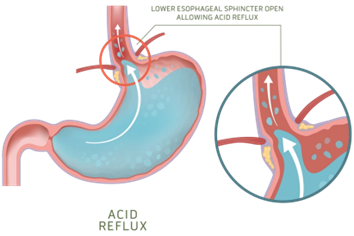
GERD can increase the risk of aspiration (inhalation of stomach contents into the lungs), which can cause respiratory issues, including abnormal breath sounds. In these cases, monitoring of breath sounds may be more appropriate than monitoring of bowel sounds.
Bowel sounds are not typically monitored for GERD patients as GERD is a condition that affects the esophagus and the stomach, not the intestines. GERD is caused by the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, which can cause symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation.
Abdominal girth is not routinely monitored for GERD patients as it is not typically related to the condition. GERD is a disorder that affects the esophagus and stomach and does not typically cause significant changes in abdominal size or girth. In rare cases, GERD can be complicated by a condition known as a para oesophageal hernia, which can cause a visible bulge in the abdomen. In these cases, monitoring of abdominal size and shape may be necessary.
The apical pulse is not routinely monitored for GERD patients as it is not directly related to the condition. GERD is a disorder that affects the digestive system, specifically the esophagus and stomach and does not typically have an impact on heart rate or rhythm.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The nurse will include the instruction "Offer the client the commode or urinal every 2 hours" in the teaching plan for the client's family. This approach is known as timed voiding and can help the client re-establish a regular pattern of urination. Option "a" promotes frequent voiding, which helps
prevent accidents and promotes bladder health. Option "b" is not a recommended approach and can lead to dehydration, urinary tract infections, and other complications. Option "c" is also not recommended since holding urine for extended periods can lead to bladder distention and increase the risk of urinary tract infections. Option "d" is also not recommended since catheterization should only be considered in specific cases where other options have failed or are not feasible.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
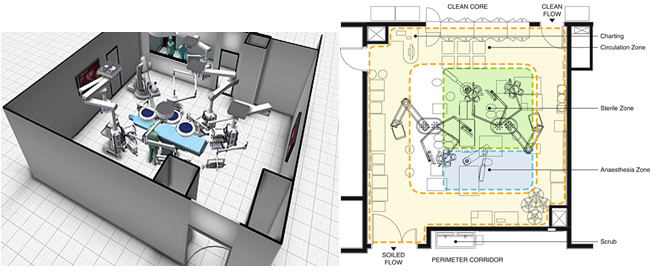
The operating room is a sterile environment, and it is critical to maintain a clean and controlled environment to reduce the risk of infection to the patient. The measures taken include maintaining positive air pressure, controlling temperature and humidity, filtering the air, using sterile surgical instruments, and limiting traffic in and out of the operating room. These measures help to prevent the spread of infectious agents that may be present in the operating room. While the other options (a, b, and d) may also be important considerations in the design of the operating room, preventing transmission of infection is the primary goal.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.