What maternal condition always requires delivery by cesarean section?
Partial abruptio placentae
Ectopic pregnancy
Eclampsia
Total placenta previa
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A reason: Partial abruptio placentae is not the correct answer, as it does not always require delivery by cesarean section. Partial abruptio placentae is a condition where the placenta partially separates from the uterine wall before the baby is born. This can cause bleeding, pain, and fetal distress. Depending on the severity of the condition, the gestational age, and the fetal status, the delivery may be vaginal or cesarean.
Choice B reason: Ectopic pregnancy is not the correct answer, as it does not require delivery by cesarean section. Ectopic pregnancy is a condition where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. This can cause bleeding, pain, and rupture of the tube. Ectopic pregnancy is not viable and needs to be removed surgically or treated with medication. It cannot result in a live birth².
Choice C reason: Eclampsia is not the correct answer, as it does not always require delivery by cesarean section. Eclampsia is a severe complication of preeclampsia, a condition where the pregnant woman develops high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Eclampsia can cause seizures, coma, and death for the mother and the baby. The only cure for eclampsia is delivery of the baby, which may be vaginal or cesarean depending on the maternal and fetal condition.
Choice D reason: Total placenta previa is the correct answer, as it always requires delivery by cesarean section. Total placenta previa is a condition where the placenta completely covers the cervix, the opening of the uterus. This can cause painless bleeding, preterm labor, and fetal distress. Vaginal delivery is impossible and dangerous, as it can cause severe bleeding and damage to the placenta and the baby. Cesarean section is the only safe way to deliver the baby.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: A sleepy, sedated affect is not a concerning sign, as it is a common side effect of magnesium sulfate. Magnesium sulfate is a central nervous system depressant that can cause drowsiness, lethargy, and reduced alertness.
Choice B reason: Absent ankle clonus is not a concerning sign, as it indicates a normal neuromuscular response. Ankle clonus is a rhythmic jerking of the foot when the ankle is dorsiflexed. It is a sign of hyperreflexia, which can occur in severe preeclampsia due to increased blood pressure and cerebral edema.
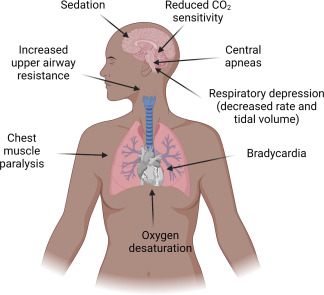
Choice C reason: A respiratory rate of 10 breaths/min is a concerning sign, as it indicates respiratory depression. This is a serious complication of magnesium sulfate toxicity, which can lead to respiratory arrest and death. The nurse should monitor the woman's respiratory rate closely and report any signs of respiratory distress.
Choice D reason: Deep tendon reflexes of 2+ are not a concerning sign, as they indicate a normal neuromuscular response. Deep tendon reflexes are graded from 0 to 4, with 2 being the average. Magnesium sulfate can cause hyporeflexia or areflexia, which are signs of magnesium sulfate toxicity.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Partial abruptio placentae is not the correct answer, as it does not always require delivery by cesarean section. Partial abruptio placentae is a condition where the placenta partially separates from the uterine wall before the baby is born. This can cause bleeding, pain, and fetal distress. Depending on the severity of the condition, the gestational age, and the fetal status, the delivery may be vaginal or cesarean.
Choice B reason: Ectopic pregnancy is not the correct answer, as it does not require delivery by cesarean section. Ectopic pregnancy is a condition where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. This can cause bleeding, pain, and rupture of the tube. Ectopic pregnancy is not viable and needs to be removed surgically or treated with medication. It cannot result in a live birth².
Choice C reason: Eclampsia is not the correct answer, as it does not always require delivery by cesarean section. Eclampsia is a severe complication of preeclampsia, a condition where the pregnant woman develops high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Eclampsia can cause seizures, coma, and death for the mother and the baby. The only cure for eclampsia is delivery of the baby, which may be vaginal or cesarean depending on the maternal and fetal condition.
Choice D reason: Total placenta previa is the correct answer, as it always requires delivery by cesarean section. Total placenta previa is a condition where the placenta completely covers the cervix, the opening of the uterus. This can cause painless bleeding, preterm labor, and fetal distress. Vaginal delivery is impossible and dangerous, as it can cause severe bleeding and damage to the placenta and the baby. Cesarean section is the only safe way to deliver the baby.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
