What is the most dangerous effect on the fetus of a mother who smokes cigarettes while pregnant?
Genetic changes and anomalies
Intrauterine growth restriction
Fetal addiction to the substance inhaled
Extensive central nervous system damage
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason: Genetic changes and anomalies are not the most dangerous effect, as they are rare and not directly caused by smoking. Smoking can increase the risk of some birth defects, such as cleft lip and cleft palate, but these are not genetic changes and can be corrected by surgery. Smoking can also cause chromosomal abnormalities in the eggs, but these usually result in miscarriage or stillbirth, not live births.
Choice B reason: Maternal smoking is a significant risk factor for intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). Nicotine and carbon monoxide from cigarettes reduce oxygen supply to the fetus, leading to lower birth weights and smaller body lengths.
Choice C reason: Fetal addiction to the substance inhaled is not the most dangerous effect, as it is not permanent and can be treated by medication and supportive care. Smoking can expose the fetus to nicotine, carbon monoxide, and other harmful chemicals, which can cross the placenta and affect the fetal brain and nervous system. Smoking can also cause withdrawal symptoms in the newborn, such as irritability, tremors, and difficulty feeding.
Choice D reason: Although prenatal exposure to smoking can affect neurodevelopment and is associated with behavioral issues, extensive central nervous system damage is not the most immediate or dangerous effect. The most critical concern remains intrauterine growth restriction.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: A sleepy, sedated affect is not a concerning sign, as it is a common side effect of magnesium sulfate. Magnesium sulfate is a central nervous system depressant that can cause drowsiness, lethargy, and reduced alertness.
Choice B reason: Absent ankle clonus is not a concerning sign, as it indicates a normal neuromuscular response. Ankle clonus is a rhythmic jerking of the foot when the ankle is dorsiflexed. It is a sign of hyperreflexia, which can occur in severe preeclampsia due to increased blood pressure and cerebral edema.
Choice C reason: A respiratory rate of 10 breaths/min is a concerning sign, as it indicates respiratory depression. This is a serious complication of magnesium sulfate toxicity, which can lead to respiratory arrest and death. The nurse should monitor the woman's respiratory rate closely and report any signs of respiratory distress.
Choice D reason: Deep tendon reflexes of 2+ are not a concerning sign, as they indicate a normal neuromuscular response. Deep tendon reflexes are graded from 0 to 4, with 2 being the average. Magnesium sulfate can cause hyporeflexia or areflexia, which are signs of magnesium sulfate toxicity.
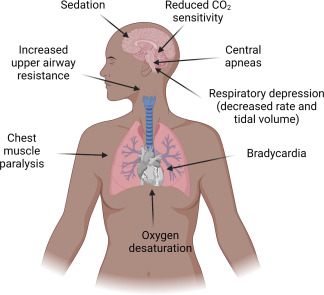
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is incorrect because primary dysmenorrhea is menstrual pain that is not associated with any underlying condition. It usually begins with the onset of menstruation and lasts for a few days. It does not cause pain during intercourse or infertility.
Choice B reason: This is correct because endometriosis is a condition where the endometrial tissue that normally lines the uterus grows outside the uterus, such as on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or pelvic organs. It causes chronic inflammation, scarring, and adhesions that can result in severe pain during menstruation and intercourse, as well as infertility.
Choice C reason: This is incorrect because secondary dysmenorrhea is menstrual pain that is caused by an underlying condition, such as fibroids, pelvic inflammatory disease, or adenomyosis. It usually develops later in life and lasts longer than primary dysmenorrhea. It may or may not cause pain during intercourse or infertility, depending on the condition.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because PMS stands for premenstrual syndrome, which is a group of physical and emotional symptoms that occur before menstruation. It may include mood swings, irritability, bloating, headaches, or breast tenderness. It does not cause severe pain during menstruation or intercourse, or infertility.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
