The public health nurse is assigned to the population of clients in an inner city community. The nurse identifies which of the following as a priority intervention.
Develop a survey on teen pregnancies
Hold a focus group to discuss immunizations
Interview the elderly at the senior center
Perform a windshield survey
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A reason: Developing a survey on teen pregnancies is not a priority intervention for a public health nurse who is assigned to a new community. This is a specific topic that may not be relevant or important for the whole population. A survey also requires time and resources to design, distribute, and analyze.
Choice B reason: Holding a focus group to discuss immunizations is not a priority intervention for a public health nurse who is assigned to a new community. This is a specific topic that may not be representative of the community's health needs and concerns. A focus group also requires recruitment, facilitation, and interpretation of the participants' views.
Choice C reason: Interviewing the elderly at the senior center is not a priority intervention for a public health nurse who is assigned to a new community. This is a specific group that may not reflect the diversity and characteristics of the whole population. An interview also requires consent, rapport, and recording of the responses.
Choice D reason: Performing a windshield survey is a priority intervention for a public health nurse who is assigned to a new community. This is a general method that allows the nurse to observe and assess various aspects of the environment that affect the health and well-being of the population. A windshield survey also requires minimal resources and can be done quickly and easily. A windshield survey is a method of assessing the health needs and resources of a community by driving or walking around and observing various aspects of the environment, such as housing, transportation, services, and safety. This is a priority intervention for a public health nurse who wants to get a comprehensive overview of the community and identify its strengths and weaknesses.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: A public health nurse is a nurse who works to improve the health and well-being of populations and communities, not specific workplaces. A public health nurse may focus on disease prevention, health promotion, environmental health, or emergency preparedness.
Choice B reason: A community nurse specialist is a nurse who has advanced education and training in a specific area of nursing practice, such as gerontology, oncology, or mental health. A community nurse specialist may work in various settings, such as hospitals, clinics, or schools, to provide specialized care and education to clients and families.
Choice C reason: A nurse clinician is a nurse who has expertise in clinical practice, research, and education. A nurse clinician may work in academic or clinical settings, such as universities, hospitals, or research centers, to develop and implement evidence-based practices and policies.
Choice D reason: An occupational health nurse is a nurse who works to protect and promote the health and safety of workers in various industries, such as manufacturing, mining, or construction. An occupational health nurse may provide services such as health assessment, injury prevention, emergency response, or wellness programs.
Correct Answer is ["B","C"]
Explanation
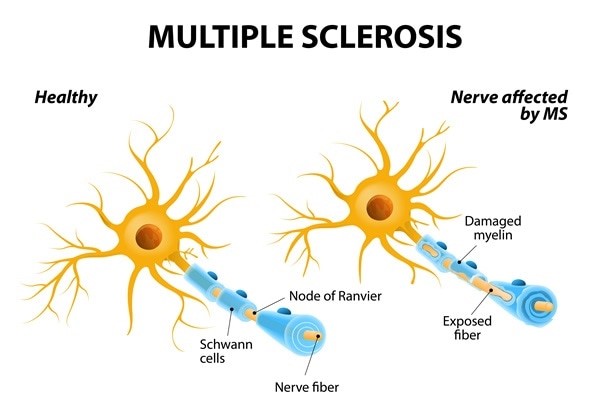
Choice A reason: "I may experience urinary incontinence." This statement does not indicate the need for additional teaching. It is a correct statement that reflects an understanding of one of the possible symptoms of MS. Urinary incontinence is caused by nerve damage that affects bladder control.
Choice B reason: "I should not exercise because this may trigger an exacerbation." This statement indicates the need for additional teaching. It is an incorrect statement that reflects a misconception about exercise and MS. Exercise does not cause or worsen MS relapses but rather has many benefits for people with MS, such as improving muscle strength, balance, mobility, mood, and quality of life.
Choice C reason: "I should alternate the eye patch every other day to help with the double vision." This statement indicates the need for additional teaching. It is an incorrect statement that reflects a misunderstanding of how to manage double vision, which is another possible symptom of MS. Alternating the eye patch every other day does not help with double vision, but rather may cause eye fatigue or confusion. The correct way to use an eye patch is to wear it on one eye only when needed, such as when reading or driving.
Choice D reason: "I may experience visual disturbances." This statement does not indicate the need for additional teaching. It is a correct statement that reflects an awareness of another possible symptom of MS. Visual disturbances may include blurred vision, loss of color vision, pain in one eye, or partial or complete blindness.
Choice E reason: "I need to check the water temperature before I take a bath." This statement does not indicate the need for additional teaching. It is a correct statement that reflects a precaution that people with MS should take. Checking the water temperature before taking a bath can prevent burns or scalds, as some people with MS may have reduced sensation or numbness in their skin.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
