The practical nurse (PN) is auscultating a client's heart sounds. Which abnormal heart sound should the PN report to the charge nurse? (Please listen to the audio file to select the option that applies.)
S4.
S2.
S1.
S3.
Correct Answer : A,D
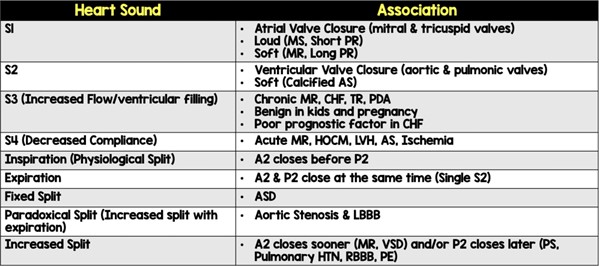
S3 is an extra heart sound that occurs during diastole (the filling phase of the cardiac cycle). It is commonly associated with conditions such as heart failure and volume overload. S3 is often described as a low-frequency, dull, and distant sound heard after S2 (the second heart sound).
B, C- S1, and S2 are the normal heart sounds that are typically heard in all individuals. S1 is the first heart sound, heard as "lub," and is caused by the closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves. S2 is the second heart sound, heard as "dub," and is caused by the closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves. These sounds are normal and expected.
S4 is another abnormal heart sound, which occurs during late diastole and is associated with conditions such as ventricular hypertrophy and reduced ventricular compliance.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Edema, particularly if it is new or worsening, can be an indicator of preeclampsia, a potentially serious condition characterized by high blood pressure and organ dysfunction. Monitoring the client's blood pressure is crucial in assessing for signs of preeclampsia and determining the appropriate course of action.
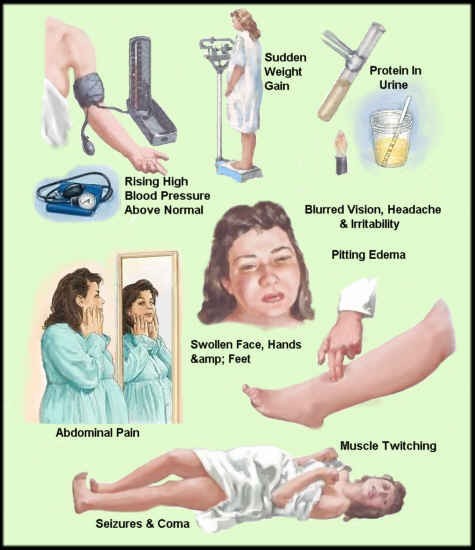
B. Due date: The due date is an important piece of information for monitoring the progress of the pregnancy, but it is not directly relevant to the client's presenting symptom of edema. The focus should be on assessing for potential complications associated with edema, such as preeclampsia.
C. Fundal height: Fundal height is a measurement used to estimate fetal growth and position. While it is an important parameter to monitor during prenatal visits, it is not directly related to the client's edema. The priority in this situation is to assess for signs of preeclampsia or other complications, which may require assessing the blood pressure.
D. Gravida and parity: Gravida refers to the total number of pregnancies a woman has had, while parity refers to the number of pregnancies that have reached viability (20 weeks or more). While these pieces of information provide a background understanding of the client's obstetric history, they do not provide immediate insight into the current issue of edema. Assessing the blood pressure would be more relevant in this situation to identify any potential complications.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Knowing the type of uterine incision from the previous cesarean section is crucial when considering the option of vaginal birth after cesarean (VBAC). The type of incision can provide important insights into the potential risks and complications associated with a trial of labor.
Specifically, a low transverse uterine incision is considered the most favorable for VBAC, as it has a lower risk of uterine rupture compared to other types of incisions, such as a classical or vertical incision.
A. While information about the client's intent regarding breastfeeding of the newborn is important for providing appropriate support and education, it does not have a direct impact on the decision-making process for VBAC.
C. A history of contracting Herpes simplex virus is relevant to the client's overall health and may have implications for the management of the pregnancy, but it is not directly related to the decision regarding VBAC.
D. The religious preference of the client's family, while important for respecting cultural and spiritual beliefs, does not have a direct impact on the decision-making process for VBAC.

Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
