The nurse observes the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) obtain vital signs on four adult clients.
For which client should the nurse intervene to redirect to use of proper method?
Using automatic BP cuff with shivering client with history of an irregular heart rate.
Pulling the client’s ear pinna backward, up and out to obtain a tympanic membrane temperature.
Counting the client’s radial pulse who is supine with the forearm straight alongside the body.
Counting the respirations for one full minute for a client with tachypnea.
The Correct Answer is A
Using an automatic BP cuff with a shivering client with a history of an irregular heart rate can result in inaccurate and low readings.
This is because shivering can interfere with the cuff inflation and deflation, and an irregular heart rate can affect the accuracy of the device.
The nurse should intervene and use a manual BP cuff with a stethoscope instead.
Choice B is wrong because pulling the client’s ear pinna backward, up and out to obtain a tympanic membrane temperature is the correct technique for adults and older children. This helps to straighten the ear canal and allow the light to reflect on the tympanic membrane, which shares the same vascular artery as the hypothalamus.
Choice C is wrong because counting the client’s radial pulse who is supine with the forearm straight alongside the body is an appropriate method.
The radial pulse can be easily palpated at the wrist, and the supine position and straight forearm do not affect the pulse rate.
Choice D is wrong because counting the respirations for one full minute for a client with tachypnea is a recommended practice.
Tachypnea means rapid breathing, and counting for one full minute can ensure accuracy and detect any variations in the respiratory pattern.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
This needle size is appropriate for an intramuscular injection into the deltoid of a 175-pound adult male with a viscous fluid.
The needle length should be long enough to reach the muscle through the subcutaneous tissue, and the needle gauge should be suitable for the viscosity of the fluid. A 23-gauge needle is a common choice for intramuscular injections.
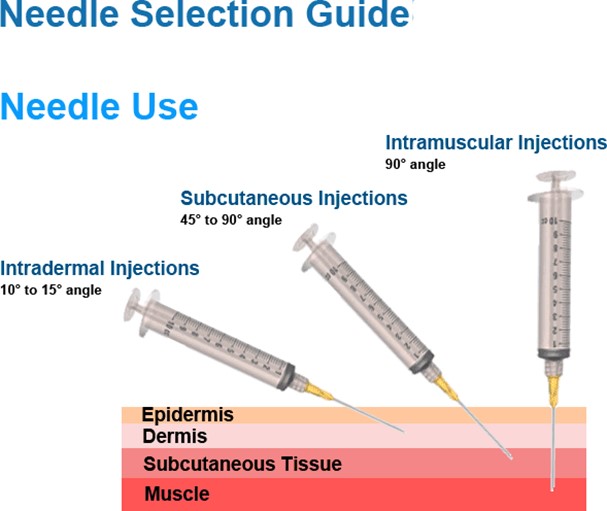
Choice A is wrong because a 1/2 inch needle is too short to reach the deltoid muscle in an adult male.
Choice C is wrong because a 1-1/2 inch needle is too long and may cause injury to the underlying nerves or blood vessels.
Choice D is wrong because a 16-gauge needle is too large and may cause excessive tissue trauma and pain.
Correct Answer is ["A","E"]
Explanation
Olanzapine is an antipsychotic drug that can cause weight gain and increased blood sugar as common side effects.
Therefore, the nurse should monitor the client’s weight and blood sugar regularly to prevent complications such as obesity and diabetes.
Choice B is wrong because olanzapine does not affect skin turgor, which is a measure of hydration status.
Choice C is wrong because olanzapine does not cause falls, although it may cause dizziness or unsteadiness as side effect.
Choice D is wrong because olanzapine does not cause significant changes in blood pressure, although it may cause orthostatic hypotension (a drop in blood pressure when standing up) as a side effect.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
