The nurse is reviewing the health problems for a group of assigned patients. Which patient does the nurse recognize as being at increased risk for developing metabolic alkalosis?
Patient with bulimia.
Patient with COPD.
Patient with venous stasis ulcer.
Patient on dialysis.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale: Patients with bulimia are at increased risk for developing metabolic alkalosis due to recurrent vomiting, which leads to loss of hydrochloric acid from the stomach and results in an elevated blood bicarbonate level.
Choice B rationale: Patients with COPD are more likely to develop respiratory acidosis due to retention of carbon dioxide, not metabolic alkalosis.
Choice C rationale: Patients with venous stasis ulcers do not have a direct association with metabolic alkalosis.
Choice D rationale: Patients on dialysis are more likely to experience metabolic acidosis due to impaired kidney function and inability to excrete acid effectively.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Cerebral bleeding. Choice A rationale:
Stress fractures are not directly related to hypernatremia. Hypernatremia is an electrolyte imbalance, and its main effects are related to cellular dehydration and neurological symptoms rather than bone fractures.
Choice B rationale:
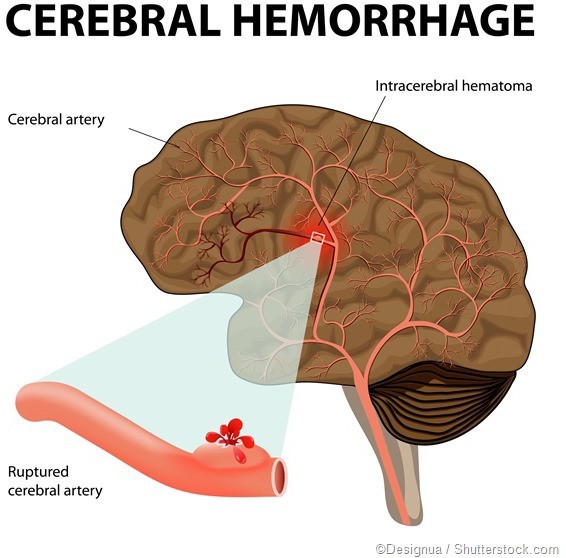
This is the correct answer because hypernatremia can lead to severe dehydration and cause neurological complications, including cerebral bleeding. The brain cells can shrink due to water loss, causing blood vessels to rupture, leading to bleeding in the brain.
Choice C rationale:
Atrial dysrhythmias are not directly associated with hypernatremia. Hypernatremia primarily affects the central nervous system and can lead to neurological symptoms rather than cardiac dysrhythmias.
Choice D rationale:
Pulmonary edema is not a likely consequence of hypernatremia. Pulmonary edema is associated with fluid volume excess, not fluid volume deficit, which is characteristic of hypernatremia.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Hypernatremia.
Choice A rationale:
Hypernatremia is the most likely condition the client is experiencing based on the laboratory result of Sodium 144 mEq/L, which is above the normal range of 136 to 145 mEq/L. Hypernatremia is an elevated sodium level in the blood and can cause various symptoms like extreme thirst, dry mucous membranes, and altered mental status.
Choice B rationale:
To address hypernatremia, the nurse should take two actions. Action 1: Prepare to check a serum albumin level. This is important as hypernatremia can be caused by a relative water deficit due to excess solutes, and measuring serum albumin helps assess the body's water balance. Action 2: Request a STAT ECG. Hypernatremia can lead to cardiac arrhythmias, so an ECG is essential to monitor the patient's heart rhythm. Parameters to Monitor: Parameter 1 - Serum bicarbonate level: Monitoring bicarbonate levels helps evaluate acid-base balance and assess the impact of hypernatremia on the body's buffering systems. Parameter 2 - Intake and Output: Monitoring the patient's fluid intake and output is crucial to ensure proper hydration and track response to treatment.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
