A patient is admitted with hypernatremia caused by being stranded on a boat in the Atlantic Ocean for five days without a fresh water source. What is this patient at risk for developing?
Stress fractures.
Cerebral bleeding.
Atrial dysrhythmias.
Pulmonary edema.
The Correct Answer is B
Cerebral bleeding. Choice A rationale:
Stress fractures are not directly related to hypernatremia. Hypernatremia is an electrolyte imbalance, and its main effects are related to cellular dehydration and neurological symptoms rather than bone fractures.
Choice B rationale:
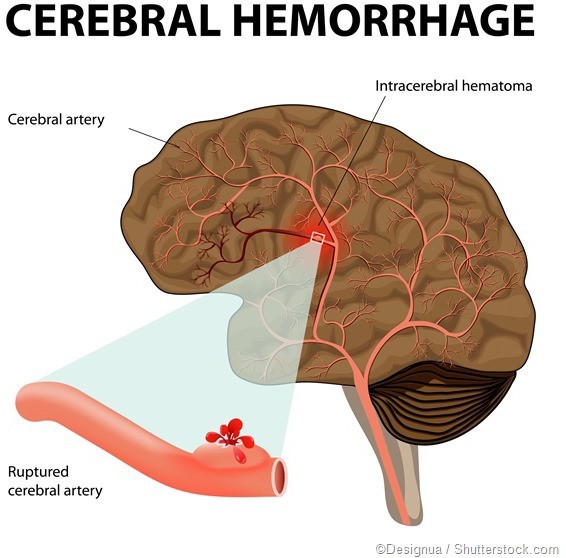
This is the correct answer because hypernatremia can lead to severe dehydration and cause neurological complications, including cerebral bleeding. The brain cells can shrink due to water loss, causing blood vessels to rupture, leading to bleeding in the brain.
Choice C rationale:
Atrial dysrhythmias are not directly associated with hypernatremia. Hypernatremia primarily affects the central nervous system and can lead to neurological symptoms rather than cardiac dysrhythmias.
Choice D rationale:
Pulmonary edema is not a likely consequence of hypernatremia. Pulmonary edema is associated with fluid volume excess, not fluid volume deficit, which is characteristic of hypernatremia.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","B","C"]
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
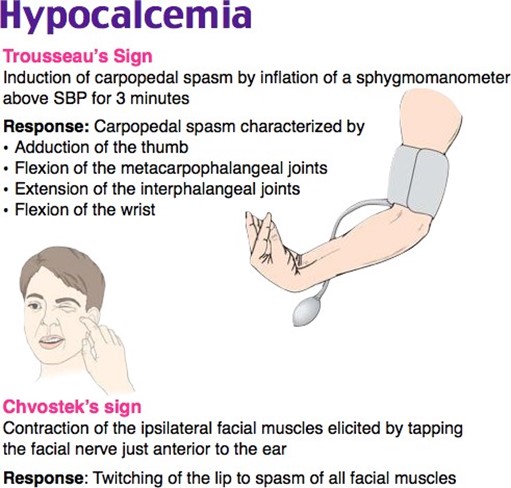
The nurse considered contraction of facial muscles as a finding of hypocalcemia because it is associated with Chvostek's sign, which indicates neuromuscular irritability due to low calcium levels.
Choice B rationale:
Complaints of fingers tingling are indicative of hypocalcemia since tingling sensations (paresthesias) in the extremities can result from decreased calcium levels affecting nerve function.
Choice C rationale:
Carpal spasm with blood pressure measurement is known as Trousseau's sign and is associated with hypocalcemia. When the blood pressure cuff is inflated above systolic pressure, it can cause tetany in the hand if the calcium levels are low.
Choice D rationale:
Asking when foot numbness would go away does not directly relate to hypocalcemia or its symptoms. It is not a finding used to come to the conclusion of hypocalcemia in this scenario.
Choice E rationale:
The heart rate being 88 and regular does not directly indicate hypocalcemia. While hypocalcemia can lead to cardiac arrhythmias, a heart rate of 88 and regular is within the normal range and not a specific finding for hypocalcemia.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Increased urine ketones are not indicative of fluid volume deficit. Instead, they may suggest diabetic ketoacidosis or starvation ketosis.
Choice B rationale:
Decreased Hgb (hemoglobin) is not specific to fluid volume deficit and can be seen in various conditions such as anemia or bleeding.
Choice C rationale:
Decreased urine specific gravity is not consistent with fluid volume deficit, as it usually results in concentrated urine with increased specific gravity.
Choice D rationale:
An increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level is expected in fluid volume deficit due to reduced kidney perfusion and function. BUN is a marker of kidney function and is elevated when fluid volume is low.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
