The nurse is concerned that a patient recovering from a thyroidectomy is developing hypocalcemia. What findings did the nurse use to come to this conclusion? Select all that apply.
Contraction of the facial muscles.
Complaints of fingers tingling.
Carpal spasm with blood pressure measurement.
Asked when the foot numbness would go away.
Correct Answer : A,B,C
Choice A rationale:
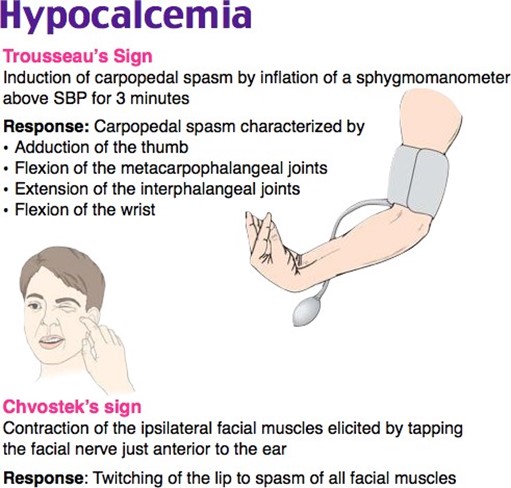
The nurse considered contraction of facial muscles as a finding of hypocalcemia because it is associated with Chvostek's sign, which indicates neuromuscular irritability due to low calcium levels.
Choice B rationale:
Complaints of fingers tingling are indicative of hypocalcemia since tingling sensations (paresthesias) in the extremities can result from decreased calcium levels affecting nerve function.
Choice C rationale:
Carpal spasm with blood pressure measurement is known as Trousseau's sign and is associated with hypocalcemia. When the blood pressure cuff is inflated above systolic pressure, it can cause tetany in the hand if the calcium levels are low.
Choice D rationale:
Asking when foot numbness would go away does not directly relate to hypocalcemia or its symptoms. It is not a finding used to come to the conclusion of hypocalcemia in this scenario.
Choice E rationale:
The heart rate being 88 and regular does not directly indicate hypocalcemia. While hypocalcemia can lead to cardiac arrhythmias, a heart rate of 88 and regular is within the normal range and not a specific finding for hypocalcemia.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The client with a phosphate level of 5.7 mg/dL likely has a manifestation of hypoparathyroidism. Hypoparathyroidism leads to decreased parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion, which causes increased renal phosphate reabsorption, leading to elevated phosphate levels in the blood.
Choice B rationale:
A calcium level of 9.8 mg/dL is within the normal range (8.5-10.2 mg/dL) and does not indicate hypoparathyroidism.
Choice C rationale:
A vitamin D level of 25 ng/mL is within the normal range (30-100 ng/mL) and does not suggest hypoparathyroidism.
Choice D rationale:
A magnesium level of 1.8 mEq/L is within the normal range (1.7-2.2 mEq/L) and does not directly indicate hypoparathyroidism.
Correct Answer is ["B","C","E"]
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Dysrhythmias are not a direct consequence of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or the acid-base imbalance indicated by the patient's pH of 7.2 and bicarbonate level of 20 mEq/L. DKA primarily affects the respiratory system, leading to Kussmaul respirations, not dysrhythmias.
Choice B rationale:
Kussmaul respirations are an expected finding in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and metabolic acidosis. These deep, rapid breaths are the body's attempt to compensate for the acidosis by eliminating excess CO2.
Choice C rationale:
Weakness is a common symptom of DKA. The hyperglycemia and acidosis result in intracellular dehydration and impaired cellular function, leading to weakness and fatigue.
Choice D rationale:
Cold, clammy skin is not typically associated with DKA. Instead, patients with DKA may have warm, dry skin due to dehydration and impaired thermoregulation.
Choice E rationale:
Tachycardia is an expected finding in a patient with DKA. The metabolic acidosis and dehydration lead to an increase in heart rate as the body attempts to maintain perfusion.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
