Patient wants to know what causes atherosclerosis. How should the nurse respond? In general, atherosclerosis is caused by
High serum cholesterol levels
Endothelial injury and inflammation
An increase in antithrombotic substances
Congenital heart disease
The Correct Answer is B
Atherosclerosis is a complex disease process that involves the gradual buildup of plaques (fatty deposits) in the walls of arteries, leading to narrowing and reduced blood flow. The exact cause of atherosclerosis is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors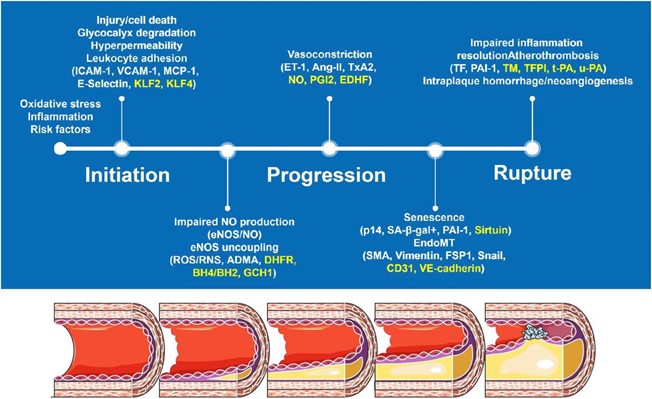
One of the key contributing factors to atherosclerosis is damage to the endothelial cells that line the walls of arteries. This damage can be caused by a variety of factors, including high blood pressure, smoking, high levels of lowdensity lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and other inflammatory factors. When the endothelial cells are damaged, they release chemicals that attract white blood cells to the area. These white blood cells then migrate into the arterial wall, where they begin to accumulate and form fatty deposits called plaques.
Over time, these plaques can grow and calcify, leading to further narrowing of the artery and reducing blood flow to the affected tissue. In addition, plaques can rupture and form blood clots, which can completely block blood flow to the affected area and cause a heart attack or stroke.
While high serum cholesterol levels are a risk factor for atherosclerosis, they are not the sole cause. Similarly, an increase in antithrombotic substances (substances that prevent blood clots) and congenital heart disease are not primary causes of atherosclerosis, although they may contribute to the disease process in some cases.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Elevated pulmonary valvular resistance refers to a condition where there is increased resistance to blood flow through the pulmonary valve and into the lungs. This can lead to an increase in pressure within the right ventricle of the heart, which can eventually lead to right heart failure.
Right heart failure occurs when the right ventricle of the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, which can result in symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention in the legs and abdomen. Causes of right heart failure include pulmonary hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary embolism, and other conditions that increase pressure within the pulmonary circulation.
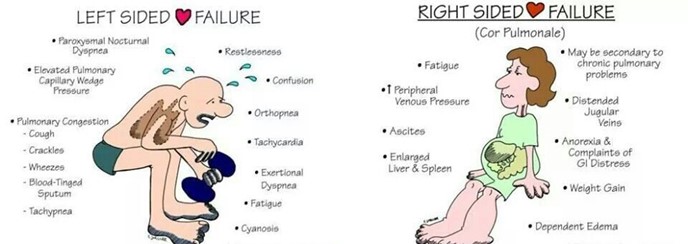
Left heart failure, on the other hand, occurs when the left ventricle of the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, which can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention in the lungs and legs. Causes of left heart failure include coronary artery disease, hypertension, and valvular heart disease.
Low output failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, and can result from a variety of conditions affecting the heart muscle or heart valves. High output failure occurs when the heart is working harder than normal to meet the body's demands, such as in conditions such as hyperthyroidism or severe anemia
Correct Answer is {"dropdown-group-1":"A"}
Explanation
Clubbing is a medical condition characterized by bulbous enlargement of the distal portion of a digit (usually a finger, but sometimes a toe) due to soft tissue proliferation and increased bone deposition. The affected digit takes on a rounded or "club-like" appearance, and the angle between the nail and nail bed (known as the Lovibond angle) increases to greater than 180 degrees.
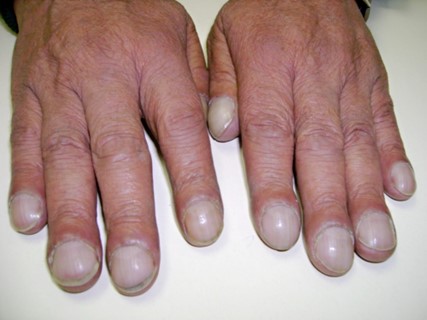
Clubbing is commonly associated with a variety of medical conditions that interfere with oxygenation of the blood, including lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung disease, and bronchiectasis; heart diseases such as congenital heart defects and cyanotic heart disease; and gastrointestinal diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease and cirrhosis.
The exact mechanism underlying clubbing is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of vascular, inflammatory, and neurogenic factors. Hypoxia (low oxygen levels) is believed to play a central role in the development
of clubbing, leading to the release of growth factors and cytokines that promote soft tissue and bone proliferation.
Clubbing is typically diagnosed based on physical examination findings, including the Lovibond angle and the presence of nail bed fluctuation (when the nail bed feels spongy or compressible). It is important to identify and treat any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to clubbing, as these can have significant implications for the patient's health and quality of life.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
