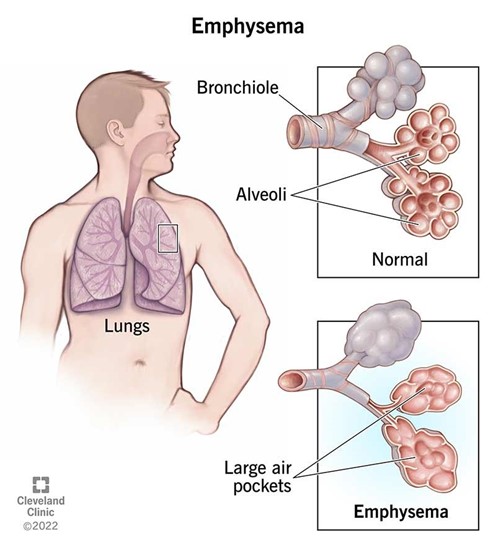
involves an abnormally enlarged gas exchange system and the destruction of alveolar walls
The Correct Answer is {"dropdown-group-1":"B"}
Emphysema is a lung disease that involves damage to the alveoli (tiny air sacs in the lungs), causing them to become stretched out and lose their elasticity. This leads to an abnormally enlarged gas exchange system and the destruction of alveolar walls
Transudative effusion: An effusion is an abnormal buildup of fluid in a body cavity, such as the pleural cavity around the lungs. Transudative effusions occur when fluid leaks out of blood vessels due to changes in pressure or protein levels, rather than from inflammation or injury.
Exudate effusion: This type of effusion occurs when fluid leaks out of blood vessels due to inflammation or injury. The fluid contains high levels of protein and cellular debris, and may be caused by conditions such as pneumonia, cancer, or autoimmune disorders.
D. Abscess: An abscess is a localized collection of pus, usually caused by a bacterial infection. It can occur in various parts of the body, including the lungs.
An abscess in the lung can cause symptoms such as coughing, chest pain, and fever.
.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
associated with chronic heart failure. Activation of the RAAS system occurs as a compensatory mechanism in response to decreased cardiac output and reduced renal perfusion. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system increases blood pressure, maintains blood volume and improves cardiac contractility in the short term, but in the long term it can lead to fluid retention, edema, and worsen cardiac function.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
The correct answer is B. Systolic pressure less than 120 mmHg and diastolic pressure less than 80 mmHg is considered normal blood pressure in adults according to current guidelines. A systolic pressure between 140-150 mmHg (option A) would be classified as stage 1 hypertension, while a systolic pressure greater than 140 mmHg and diastolic pressure of 100 mmHg (option D) would be classified as stage 2 hypertension. A systolic pressure less than 100 mmHg regardless of diastolic pressure (option C) would be considered low blood pressure.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
