The Correct Answer is {"dropdown-group-1":"A"}
Clubbing is a medical condition characterized by bulbous enlargement of the distal portion of a digit (usually a finger, but sometimes a toe) due to soft tissue proliferation and increased bone deposition. The affected digit takes on a rounded or "club-like" appearance, and the angle between the nail and nail bed (known as the Lovibond angle) increases to greater than 180 degrees.
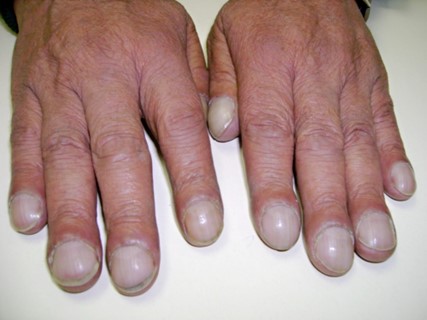
Clubbing is commonly associated with a variety of medical conditions that interfere with oxygenation of the blood, including lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung disease, and bronchiectasis; heart diseases such as congenital heart defects and cyanotic heart disease; and gastrointestinal diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease and cirrhosis.
The exact mechanism underlying clubbing is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of vascular, inflammatory, and neurogenic factors. Hypoxia (low oxygen levels) is believed to play a central role in the development
of clubbing, leading to the release of growth factors and cytokines that promote soft tissue and bone proliferation.
Clubbing is typically diagnosed based on physical examination findings, including the Lovibond angle and the presence of nail bed fluctuation (when the nail bed feels spongy or compressible). It is important to identify and treat any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to clubbing, as these can have significant implications for the patient's health and quality of life.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
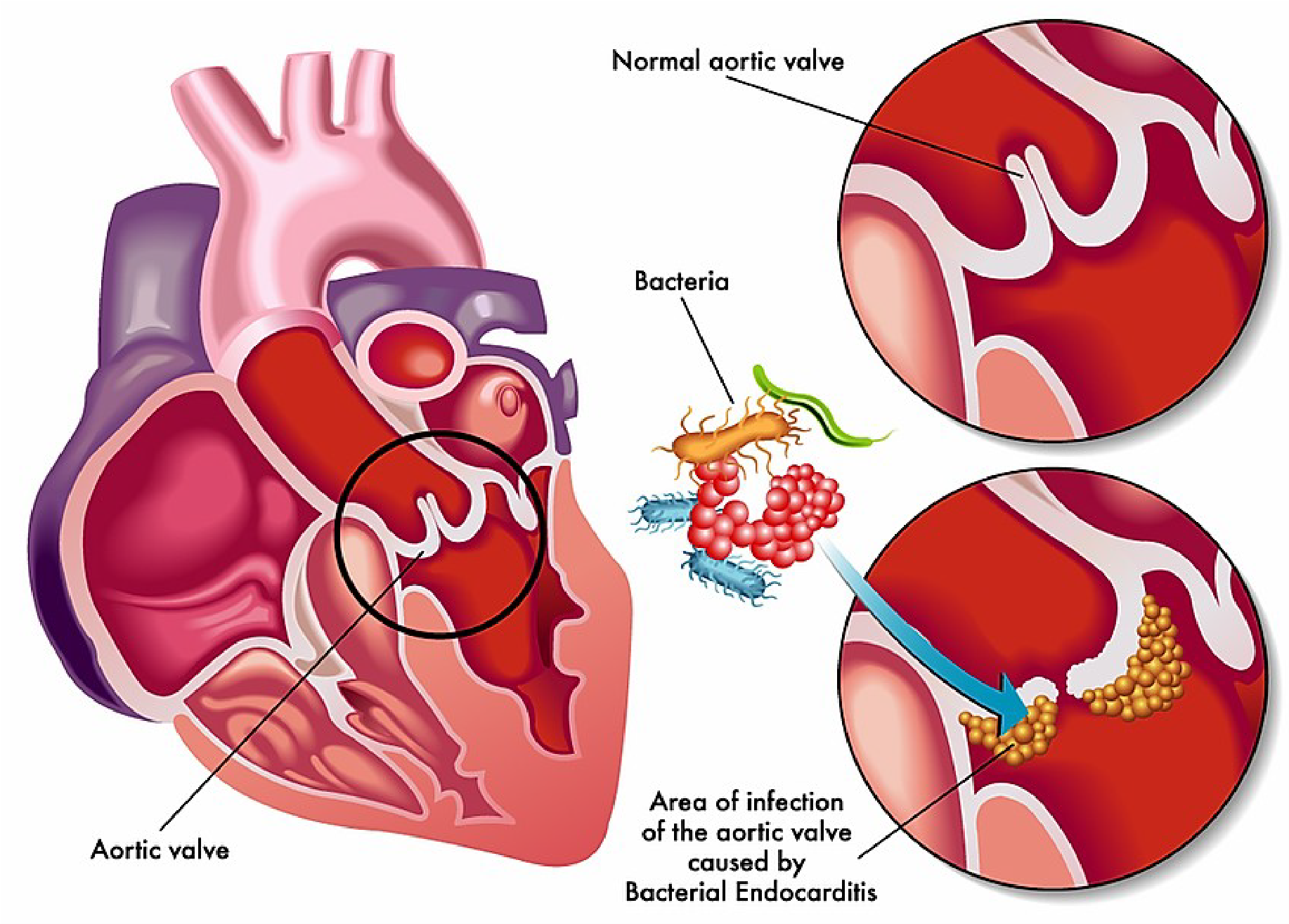 Infective endocarditis is an infection of the endocardium (the inner lining of the heart), which can lead to damage of the heart valves. It is most commonly caused by bacteria, although fungi and other microorganisms can also cause the condition. The bacteria that most commonly cause infective endocarditis are Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species.
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the endocardium (the inner lining of the heart), which can lead to damage of the heart valves. It is most commonly caused by bacteria, although fungi and other microorganisms can also cause the condition. The bacteria that most commonly cause infective endocarditis are Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Orthostatic hypotension is a drop in blood pressure that occurs when a person stands up from a sitting or lying down position. To check for orthostatic hypotension, the nurse typically takes the patient's blood pressure and heart rate while the patient is lying down, then has the patient stand up for a few minutes and takes the blood pressure and heart rate again. If the blood pressure drops significantly (usually a drop of 20 mm Hg or more) and the heart rate increases, it may indicate orthostatic hypotension.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
