What is the major effect of calcium channel blockers on cardiac contractions
Increases the rate of cardiac contractions
Decreases the strength of cardiac contractions
Stabilizes the rhythm of cardiac contractions
Stabilizes the vasodilation during cardiac contractions
The Correct Answer is B
Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) are a class of medications that block the influx of calcium ions into cardiac and smooth muscle cells, leading to relaxation of these muscles and dilation of blood vessels.
In the heart, CCBs primarily affect the L-type calcium channels in the cardiac myocytes, which are responsible for the influx of calcium ions during the plateau phase of the cardiac action potential. By blocking these channels, CCBs decrease the amount of calcium that enters the cardiac myocytes, which in turn reduces the strength of cardiac contractions (i.e. contractility). 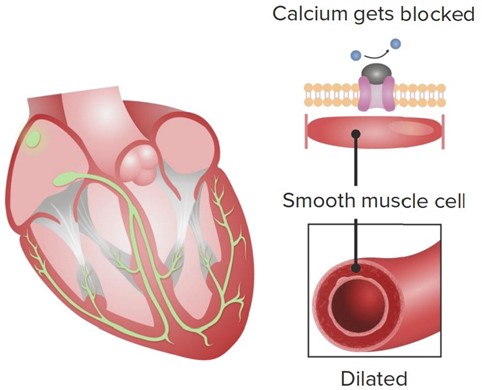
This reduction in contractility can be beneficial in certain conditions where the heart is working too hard or experiencing insufficient blood flow, such as in hypertension, angina, or some forms of arrhythmia. By reducing the workload of the heart, CCBs can help to lower blood pressure, decrease oxygen demand, and improve blood flow to the heart.
While CCBs can also have effects on the rate and rhythm of cardiac contractions, these effects are generally less pronounced than the reduction in contractility. Some CCBs, such as verapamil and diltiazem, can slow the heart rate by blocking the L-type calcium channels in the sinoatrial (SA) and atrioventricular (AV) nodes, while others, such as nifedipine, have little effect on heart rate.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Mitral stenosis refers to a narrowing of the mitral valve, which is located between the left atrium and the left ventricle. This narrowing can cause incomplete emptying of blood from the left atrium into the left ventricle during diastole (relaxation phase) of the cardiac cycle. This can lead to increased pressure in the left atrium and pulmonary circulation, causing symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and pulmonary con
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Atherosclerosis is a condition where plaque buildup occurs inside the arteries, which narrows the arterial lumen and limits blood flow. Aneurysms can occur as a result of atherosclerosis when the plaque formation weakens and damages the arterial wall, making it prone to bulging outwards or rupturing. This weakening of the vessel wall can cause it to lose its elasticity and strength, leading to the formation of an aneurysm. Therefore, the correct answer is C - eroding the vessel wall.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
