Excessive blood loss after childbirth can have several causes; the most common is:
unrepaired lacerations of the vagina or cervix.
retained placental fragments.
vaginal or vulvar hematomas.
failure of the uterine muscle to contract firmly.
The Correct Answer is D
The most common cause of excessive blood loss after childbirth is the failure of the uterine muscle to contract firmly, which is also known as uterine atony. If the uterus does not contract effectively after delivery, it cannot properly close off the blood vessels that were connected to the placenta, leading to heavy bleeding. Uterine atony can occur due to various factors, such as prolonged labor, multiple births, or the use of certain medications during labor.
Other causes of excessive blood loss after childbirth include retained placental fragments, vaginal or vulvar hematomas, or unrepaired lacerations of the vagina or cervix, but these are less common than uterine atony.

Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
In the case of a bioterrorism attack involving anthrax, the main priority for the nurse is to administer antibiotics within 48 hours of exposure using the Strategic National Stockpile. Anthrax is a serious bacterial infection that can be used as a bioterrorism weapon. Antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, and penicillin, can be used to prevent anthrax from developing in people who have been exposed.
There is currently no vaccine available for anthrax exposure. Also, symptom support alone is not enough in cases of anthrax exposure, as anthrax can progress rapidly and lead to serious complications. Placing everyone who was exposed in quarantine may not be necessary in all situations, and should be determined on a case-by-case basis depending on the extent and severity of the exposure.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
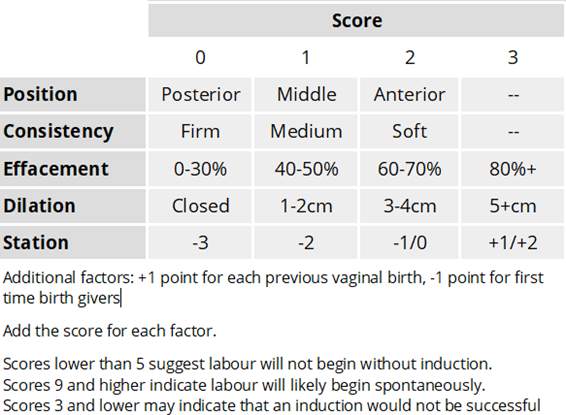
The readiness for induction of labor is assessed by determining the Bishop score. The Bishop score is a system used to evaluate the cervix for induction of labor readiness. It is based on the assessment of five factors: cervical dilation, cervical effacement, cervical consistency, cervical position, and fetal station. Each factor is scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with a maximum possible score of 15.
The higher the Bishop score, the more favorable the cervix is for induction of labor, and the higher the likelihood of a successful vaginal delivery. A Bishop score of 8 or higher is considered favorable for induction of labor. A low Bishop score may indicate that the cervix is not yet ripe and may need further cervical ripening before induction can be attempted.
The Apgar score is a test used to evaluate a newborn's physical condition at birth, based on five factors: appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration.
The biophysical profile is a prenatal ultrasound evaluation that assesses fetal well-being by evaluating fetal breathing, fetal movement, fetal tone, amniotic fluid volume, and fetal heart rate. Fetal position is an important consideration during labor, as it can impact the progression and outcome of labor, but it is not used to assess readiness for induction of labor.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
