Aureissisting a nurse midwife in examining a client who is a primigravida at 42 weeks of gestation and states that she thinks she is in labor. Which of the following findings confirms that the client is in labor?
Fain just above the navel
Cervical dilation
Amniotic fluid in the vaginal vault
Contractions every 3 to 4 min
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A rationale: Pain above the navel is not a specific indicator of labor and may be unrelated to the onset of labor.
Choice B rationale: Cervical dilation is a definitive sign of labor. It indicates that the cervix is opening to allow the baby's passage through the birth canal.
Choice C rationale: The presence of amniotic fluid in the vaginal vault (rupture of membranes) could indicate that the client's water has broken, but it does not confirm active labor. Labor can begin before or after the rupture of membranes.
Choice D rationale: Regular contractions are a typical sign of labor, but their frequency alone does not confirm active labor. Other signs, such as cervical dilation and effacement, are necessary to confirm active labor.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale: While smoking during pregnancy can have adverse effects on both the mother and the baby, it is not the most common risk factor for placental abruption.
Choice B rationale: Maternal battering, or experiencing domestic violence, can have serious consequences for the pregnant woman and her unborn baby, but it is not the most common risk factor for placental abruption.
Choice C rationale: Maternal cocaine use during pregnancy can lead to various complications, but it is not the most common risk factor for placental abruption.
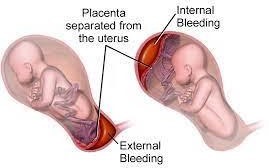
Choice D rationale: Maternal hypertension is the most common risk factor for placental abruption. Placental abruption is a serious condition where the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery, leading to potential complications for both the mother and the baby. Hypertension can cause changes in blood vessels that increase the risk of placental abruption.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A rationale: A breech presentation means that the baby's buttocks or feet are the presenting part, not the shoulder.
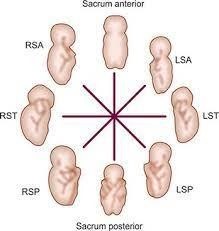
Choice B rationale: Vertex presentation refers to a head-down position of the baby with the occiput (back of the head) as the presenting part. In the RSA position, the baby is in vertex presentation, but the specific part facing the mother's right side is the shoulder.
Choice C rationale: RSA (Right Sacrum Anterior) indicates that the fetus is in a vertex presentation with the head pointing down and the back of the baby's head (occiput) facing the mother's right side. The shoulder is the presenting part of this position.
Choice D rationale; Mentum refers to the chin of the baby. A mentum presentation (also called face presentation) means that the baby's face is the presenting part, not the shoulder.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
