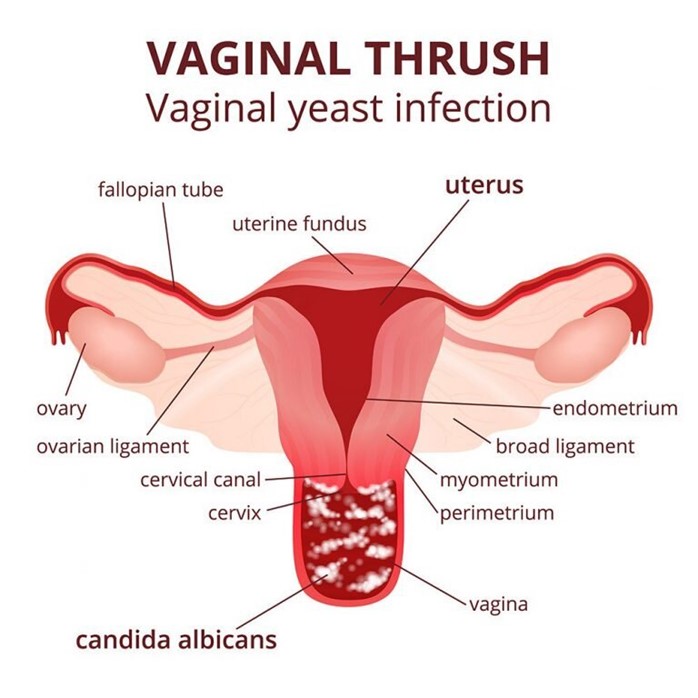
Assessment of a female client reveals a thick, white vaginal discharge. She also reports intense itching and dyspareunia. Based on these findings, the nurse would suspect that the client has:
Trichomoniasis
Genital herpes simplex
Candidiasis
Bacterial vaginosis
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A: Trichomoniasis is not the correct answer because it does not match the findings of the client. Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. It can cause symptoms such as yellow-green or gray frothy vaginal discharge, foul odor, itching, burning, or redness of the vulva or vagina.
Choice B: Genital herpes simplex is not the correct answer because it does not match the findings of the client. Genital herpes simplex is an STI caused by a virus called herpes simplex virus (HSV). It can cause symptoms such as painful blisters or ulcers on or around the genitals, fever, headache, or swollen lymph nodes.
Choice C: Candidiasis is the correct answer because it matches the findings of the client. Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by a yeast called Candida albicans. It can cause symptoms such as thick, white, cottage cheese-like vaginal discharge, intense itching, burning, or soreness of the vulva or vagina, or dyspareunia (painful sexual intercourse).
Choice D: Bacterial vaginosis is not the correct answer because it does not match the findings of the client. Bacterial vaginosis is a condition caused by an imbalance of the normal vaginal flora (the bacteria that live in the vagina). It can cause symptoms such as thin, gray-white or yellow vaginal discharge, fishy odor, itching, or burning of the vulva or vagina.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
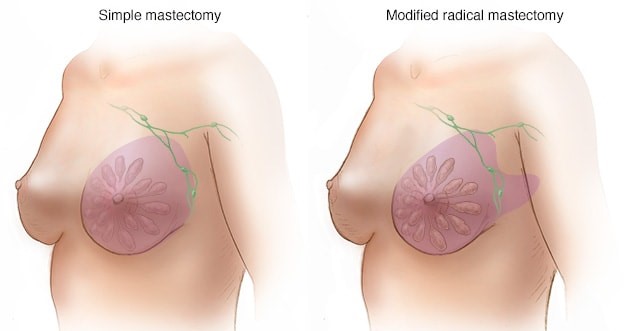
Choice A: Fluid balance is not the most likely priority because it is not directly affected by the mastectomy. Fluid balance is the state of equilibrium between the intake and output of fluids in the body. It can be influenced by various factors such as hydration, nutrition, medication, or illness. It can be monitored by measuring vital signs, weight, urine output, or laboratory values. Fluid balance is important for maintaining homeostasis and preventing dehydration or edema, but it is not a specific concern for a client undergoing a mastectomy.
Choice B: Body image is the most likely priority because it is directly affected by the mastectomy. Body image is the perception and attitude that one has toward one's own physical appearance and function. It can be influenced by various factors such as culture, media, self-esteem, or feedback from others. It can be assessed by observing verbal and nonverbal cues, asking open-ended questions, or using standardized tools. Body image is a major psychosocial issue for a client undergoing a mastectomy, as it can affect one's sense of identity, femininity, sexuality, or attractiveness. The nurse should address body image by providing information, support, and referral to appropriate resources.
Choice C: Urinary elimination is not the most likely priority because it is not directly affected by the mastectomy. Urinary elimination is the process of expelling urine from the bladder through the urethra. It can be influenced by various factors such as fluid intake, kidney function, medication, or infection. It can be assessed by measuring urine volume, color, odor, or specific gravity. Urinary elimination is important for maintaining fluid balance and preventing urinary tract infection or retention, but it is not a specific concern for a client undergoing a mastectomy.
Choice D: Activity is not the most likely priority because it is not directly affected by the mastectomy. Activity is the level of physical movement and exercise that one engages in on a daily basis. It can be influenced by various factors such as age, health status, motivation, or environment. It can be assessed by observing mobility, endurance, strength, or coordination. Activity is important for maintaining muscle tone, joint range of motion, circulation, or metabolism, but it is not a specific concern for a client undergoing a mastectomy.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Brushing teeth does not require much strength or range of motion in the hand, so it should not be very difficult for the client.
Choice B reason: Buttoning a blouse can be done with one hand or with the help of the other hand, so it should not be very difficult for the client.
Choice C reason: Eating breakfast can be done with the left hand or with utensils that are easy to hold, so it should not be very difficult for the client.
Choice D reason: Combing hair requires lifting the arm above the shoulder and moving the hand through the hair, which can be painful and challenging for the client who had a mastectomy and may have impaired lymphatic drainage and nerve damage in the right arm.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
