An occupational health nurse in the clinic of an industrial plant is developing a guidebook for clinic workers. Which of the following actions should the nurse include as a secondary prevention strategy?
Collaborate with a physical therapist to develop programs for injured employees to return to work
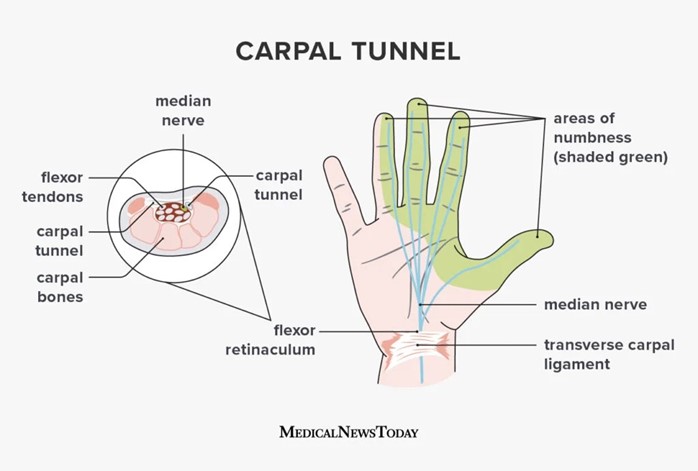
Help plant workers identify signs of carpal tunnel syndrome
Organize an influenza immunization campaign
Teach plant workers about proper lifting techniques
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A: Collaborate with a physical therapist to develop programs for injured employees to return to work. This is incorrect because this is a tertiary prevention strategy, not a secondary prevention strategy. Tertiary prevention aims to restore function and prevent disability or complications after an injury or illness has occurred.
Choice B: Help plant workers identify signs of carpal tunnel syndrome. This is correct because this is a secondary prevention strategy. Secondary prevention aims to detect and treat health problems early before they become more serious or chronic. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common occupational health problem that can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the hand and wrist. Early identification and treatment can prevent permanent nerve damage and disability.
Choice C: Organize an influenza immunization campaign. This is incorrect because this is a primary prevention strategy, not a secondary prevention strategy. Primary prevention aims to prevent disease or injury from occurring in the first place, by reducing exposure or risk factors. Influenza immunization can protect plant workers from getting infected by the flu virus and reduce the spread of the disease.
Choice D: Teach plant workers about proper lifting techniques. This is incorrect because this is also a primary prevention strategy, not a secondary prevention strategy. Proper lifting techniques can prevent musculoskeletal injuries such as sprains, strains, and herniated discs, by avoiding excessive stress on the spine and joints.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: The client's financial resources is not the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Although Meals-on-Wheels is a low-cost or free service that provides nutritious meals to homebound seniors and people with disabilities, it does not require a specific income level or financial status to qualify. The nurse should focus on the client's nutritional and functional needs, rather than their economic situation.
Choice B reason: The client's level of family support is not the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Although having family members who can assist with meal preparation and delivery can be helpful and beneficial for the client, it is not a requirement or a guarantee for receiving Meals-on-Wheels. The nurse should assess the client's individual capabilities and preferences, rather than their family availability or involvement.
Choice C reason: The client's access to transportation is not the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Although having access to transportation can enable the client to obtain food and groceries from other sources, such as stores, markets, or restaurants, it is not a criterion or a barrier for receiving Meals-on-Wheels. The nurse should evaluate the client's dietary and health needs, rather than their mobility or transportation options.
Choice D reason: The client's ability to prepare meals is the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Meals-on-Wheels is designed to serve clients who are unable to cook or shop for themselves due to physical, mental, or social limitations. The nurse should determine if the client has any impairments or challenges that prevent them from preparing their own meals, such as vision loss, arthritis, dementia, or isolation. If the client has difficulty or inability to prepare meals, they may be eligible for Meals-on-Wheels.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Natural history of disease is not an approach that explains the factors that allow the reproduction and spread of infectious disease. Natural history of disease is a concept that describes the progression and outcome of disease in the absence of any intervention. It includes stages such as susceptibility, exposure, incubation, prodrome, clinical, recovery, disability, or death.
Choice B reason: Health promotion is not an approach that explains the factors that allow the reproduction and spread of infectious diseases. Health promotion is a process that enables people to increase control over and improve their health. It involves strategies such as education, advocacy, policy, or community development.
Choice C reason: Levels of prevention is not an approach that explains the factors that allow the reproduction and spread of infectious disease. Levels of prevention is a framework that classifies different types of interventions based on their timing and purpose. It includes primary prevention (before disease occurs), secondary prevention (early detection and treatment), and tertiary prevention (reducing complications and disabilities).
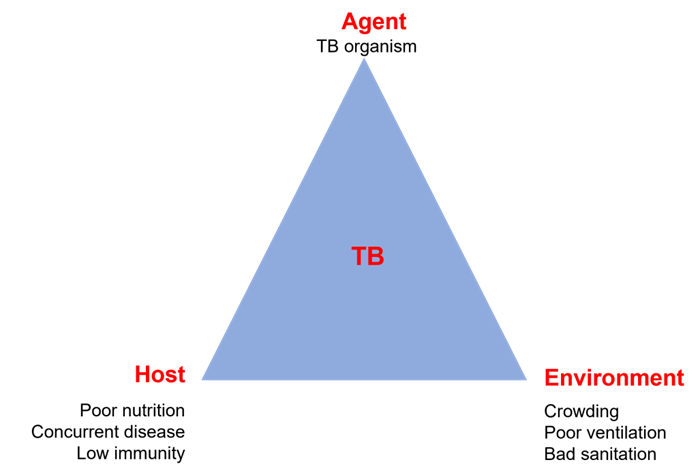
Choice D reason: Epidemiologic triangle is an approach that explains the factors that allow the reproduction and spread of infectious disease. Epidemiologic triangle is a model that identifies three essential components of an infectious disease: agent (the microorganism that causes the disease), host (the person or animal that is infected), and environment (the physical, biological, or social factors that influence the transmission). The interaction and balance among these components determine the occurrence and spread of an infectious disease.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
