After completing an admission assessment on a client who recently experienced a stroke, the nurse should choose which of the following nursing diagnoses as a priority?
Risk for injury
Altered cerebral perfusion
Decreased mobility
Altered thought process
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason: Risk for injury is a potential nursing diagnosis for a client who recently experienced a stroke, but it is not the priority. Risk for injury is related to the possible complications of stroke, such as hemiparesis, hemiplegia, dysphagia, or sensory deficits, that may increase the risk of falls, aspiration, or pressure ulcers. However, these complications are secondary to the primary problem of altered cerebral perfusion, which is the cause of stroke.
Choice B reason: Altered cerebral perfusion is the priority nursing diagnosis for a client who recently experienced a stroke, because it is the most urgent and life-threatening problem. Altered cerebral perfusion is defined as a decrease in blood flow to the brain, which can result in ischemia, infarction, or hemorrhage of the brain tissue. This can lead to irreversible neurological damage, disability, or death. Therefore, the nurse should focus on restoring and maintaining adequate cerebral perfusion as the first priority.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","C","D","E"]
Explanation
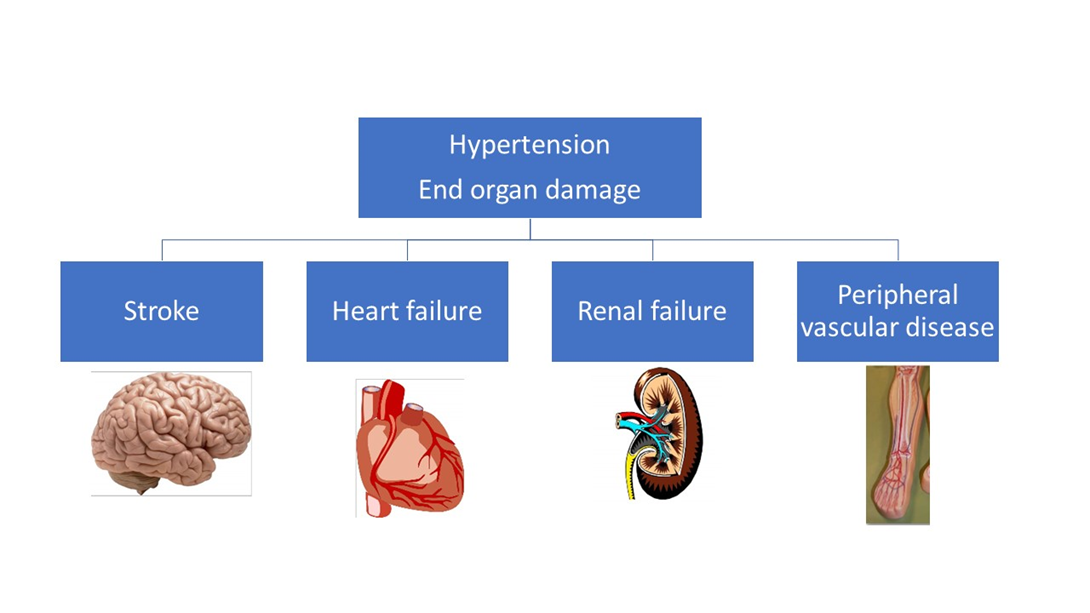
Choice A reason: Isolated systolic hypertension is not a result of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension, but rather a risk factor for it. Isolated systolic hypertension is a condition where the systolic blood pressure is elevated (>140 mmHg) while the diastolic blood pressure is normal (<90 mmHg). It is common in older adults due to the stiffening of the arteries, and can increase the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events.
Choice B reason: Atrial fibrillation is a result of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension. Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and often rapid heart rate that can cause poor blood flow and increase the risk of stroke and heart failure. Chronic hypertension can damage the heart muscle and the electrical system of the heart, leading to atrial fibrillation.
Choice C reason: Renal insufficiency is a result of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension. Renal insufficiency is a condition where the kidneys are unable to filter waste and fluid from the blood adequately. Chronic hypertension can damage the blood vessels and the nephrons of the kidneys, leading to renal insufficiency.
Choice D reason: Stroke is a result of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension. Stroke is a sudden interruption of blood supply to the brain, causing brain cell death and neurological deficits. Chronic hypertension can damage the blood vessels in the brain, making them prone to rupture (hemorrhagic stroke) or blockage (ischemic stroke).
Choice E reason: Cardiac disease is a result of end-organ damage from chronic hypertension. Cardiac disease is a broad term that encompasses various disorders of the heart, such as coronary artery disease, heart attack, heart failure, and cardiomyopathy. Chronic hypertension can damage the heart by increasing the workload and the oxygen demand of the heart, causing the heart to enlarge and weaken over time.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Position the client to achieve their comfort is not the most important intervention, as it does not address the potential risks of opioid analgesics, such as respiratory depression, sedation, and falls. Comfort is important, but not the priority in this situation.
Choice B reason: Offer toileting and a sip of water is not the most important intervention, as it does not address the potential risks of opioid analgesics, such as respiratory depression, sedation, and falls. Toileting and hydration are important, but not the priority in this situation.
Choice C reason: Place side rails up x 4 is not the most important intervention, as it may not prevent the client from getting out of bed and falling. Side rails may also be considered a restraint, which can increase the risk of injury and agitation. Side rails are not a substitute for proper supervision and assistance.
Choice D reason: Instruct the client to ask for help before getting up is the most important intervention, as it can prevent the client from falling and injuring themselves. Opioid analgesics can impair the client's balance, coordination, and judgment, making them more prone to falls. The nurse should educate the client about the effects of opioids and the importance of asking for help before attempting to get out of bed.
Choice E reason: None of the above is not the correct answer, as there is one choice that is the most important intervention for the nurse to implement before leaving the client’s room.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
