A nursing instructor is evaluating a student caring for a neutropenic client. The instructor concludes that the nursing student demonstrates accurate knowledge of neutropenia based on which of the following interventions?
Monitoring the patient's breathing and reviewing the patients arterial blood gases
Monitoring the patient's temperature and reviewing the patient's complete blood count with differential
Monitoring the patients blood pressure and reviewing the patient's hematocrit
Monitoring the patient's heart rate and reviewing the patient's hemoglobin
The Correct Answer is B
A. Monitoring the patient's breathing and reviewing the patient's arterial blood gases:
Rationale: While respiratory status is crucial in any patient assessment, arterial blood gases primarily evaluate respiratory function. Neutropenia directly affects the immune system, not respiratory function.
Appropriateness: Not directly related to assessing neutropenia.
B. Monitoring the patient's temperature and reviewing the patient's complete blood count with differential:
Rationale: Neutropenia can cause fever due to the increased risk of infection. Monitoring temperature and reviewing the complete blood count (CBC) with differential, specifically the neutrophil count, is essential in evaluating neutropenia and identifying potential infections.
Appropriateness: Correct. Monitoring temperature and reviewing CBC with differential are crucial in assessing neutropenia.
C. Monitoring the patient's blood pressure and reviewing the patient's hematocrit:
Rationale: Blood pressure assessment and hematocrit evaluation are essential aspects of general patient care but are not specific to neutropenia.
Appropriateness: Not directly related to assessing neutropenia.
D. Monitoring the patient's heart rate and reviewing the patient's hemoglobin:
Rationale: Heart rate monitoring and hemoglobin assessment are crucial in various clinical situations but are not specific indicators of neutropenia.
Appropriateness: Not directly related to assessing neutropenia.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Development of a buffalo hump and moon face:
This is associated with Cushing's syndrome, a disorder characterized by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol.
B. Central obesity and purple striations:
Also indicative of Cushing's syndrome, where excess cortisol can lead to the accumulation of fat in the abdominal area (central obesity) and the development of purple stretch marks (striae).
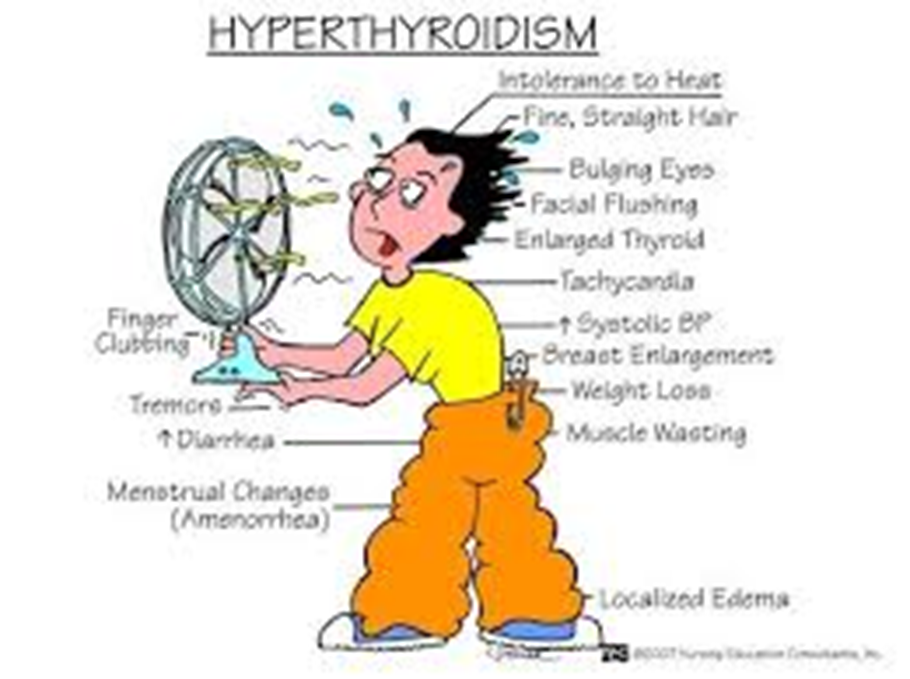
C. Sudden weight loss without dieting:
This is more characteristic of hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid gland is overactive, leading to increased metabolism and unintended weight loss.
D. Positive Trousseau's sign when checking the client's blood pressure:
Trousseau's sign is associated with hypocalcemia and is seen in conditions affecting the parathyroid gland rather than the thyroid. It involves carpal spasm induced by inflating a blood pressure cuff above the systolic pressure for a few minutes.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Flushed skin: Flushed or warm skin is more characteristic of hyperthyroidism, where there is an excess of thyroid hormones.
B. Palpitations: Palpitations or a rapid heartbeat are more characteristic of hyperthyroidism, where there is an excess of thyroid hormones.
C. Bulging eyes: Bulging or protruding eyes, known as exophthalmos, is a characteristic sign of Graves' disease, which is a specific type of hyperthyroidism.
D. Fatigue: This is correct. Fatigue is a common symptom of hypothyroidism, reflecting the overall slowing down of the body's processes.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
