A nurse is teaching about nutrition guidelines to a parent of a newborn. Which of the following statements by the parent indicates an understanding of the teaching?
"I should wait to begin fluoride supplements until my baby is 4 months of age."
"I should introduce cow's milk when my baby is 9 months old."
"I should wait to give fruit juice until my baby is 6 months of age."
"I should start solid foods when my baby is 3 months old."
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason:
Introducing fluoride supplements to a newborn is not typically recommended until the age of 6 months, unless advised by a healthcare provider due to specific water supply conditions. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) suggests that fluoride supplementation should begin at 6 months if the water supply is deficient in fluoride.
Choice B reason:
Cow's milk is not recommended for infants under the age of 1 year. Introducing cow's milk before this age can lead to iron deficiency and potentially cause harm to the infant's developing kidneys. It also lacks the proper nutrients that infants require, which are found in breast milk or formula.
Choice C reason:
The AAP recommends that fruit juice should not be introduced to infants before 6 months of age. Before this age, babies should only be fed breast milk or formula. Introducing fruit juice too early can contribute to excessive weight gain and tooth decay.
Choice D reason:
The introduction of solid foods is recommended to start at around 6 months of age. Starting solid foods at 3 months is too early and can increase the risk of choking and may lead to the development of food allergies.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
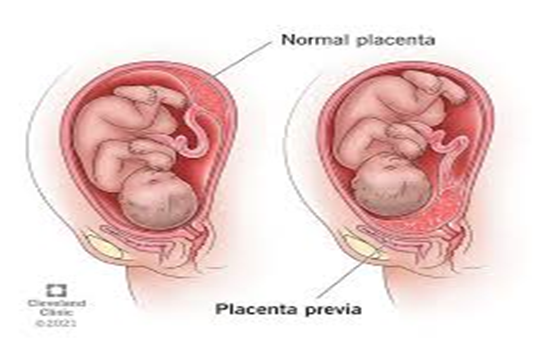
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice a reason:
While there is always a risk of introducing infection with an internal examination, this is not the primary concern with placenta previa. Infections are a risk with any invasive procedure, but the precautions taken during a typical internal examination minimize this risk.
Choice b reason:
Initiating preterm labor is a concern with any manipulation of the cervix or uterus during pregnancy. However, at 37 weeks, the pregnancy is considered early-term, and the risk of preterm labor is not the primary concern in the context of placenta previa.
Choice c reason:
The primary reason for avoiding an internal examination in a client with placenta previa is the risk of profound bleeding. With placenta previa, the placenta covers part or all of the cervix. An internal examination could disturb the placenta and lead to significant hemorrhage, which can be life-threatening for both the mother and the fetus.
Choice d reason:
While there is a risk of rupturing the membranes during an internal examination, this is not the primary concern with placenta previa. The main issue is the potential for causing significant bleeding due to the placenta's location over the cervix.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice a reason:
Mongolian spots are a type of pigmented birthmark commonly found in newborns, often appearing as blue or grayish areas on the skin. They are not related to swelling and do not result from vacuum-assisted deliveries. Mongolian spots are usually located on the buttocks or lower back and are not associated with the type of swelling described by the mother.
Choice b reason:
Caput succedaneum is a condition where the newborn's scalp swells due to pressure during delivery. It is characterized by a soft, spongy mass that crosses suture lines and is most apparent on the part of the skull that was first to enter the birth canal. This condition is common in vacuum-assisted deliveries and is the correct explanation for the swelling observed on the newborn's head.
Choice c reason:
Erythema toxicum is a common and benign skin condition in newborns, presenting as red patches or small, fluid-filled bumps. It is not related to the swelling described and does not result from vacuum-assisted deliveries. Erythema toxicum typically resolves on its own and does not cause the type of swelling that crosses suture lines.
Choice d reason:
Cephalohematoma is a collection of blood between a newborn's scalp and the skull bone that results from ruptured blood vessels, which can be a result of birth trauma or pressure. However, it is typically confined to one area and does not cross suture lines. Since the swelling described by the mother crosses the suture lines, cephalohematoma is less likely to be the correct diagnosis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
