A nurse is teaching a client who has a prescription of a nasogastric tube (NG) to treat a pyloric obstruction. Which of the following rationales for the use of the nasogastric tube should the nurse include in the teaching?
Administer medications
Supply nutrients via tube feedings
Decompress the stomach
D. Determine the pH of the gastric secretions
The Correct Answer is C
A. Administer medications:
While nasogastric tubes can be used to administer medications, this is not the primary rationale for their use in pyloric obstruction. The primary goal is often decompression.
B. Supply nutrients via tube feedings:
Providing nutrients via tube feedings is not the primary purpose in the context of a pyloric obstruction. Decompression is more relevant in this scenario.
C. Decompress the stomach:
Decompressing the stomach is a common use of nasogastric tubes in the context of pyloric obstruction. The tube helps to remove excess air and gastric contents, relieving pressure in the stomach.
D. Determine the pH of the gastric secretions:
While determining the pH of gastric secretions is a possible use, it is not the primary rationale for nasogastric tube placement in pyloric obstruction. The primary goal is often to relieve obstruction and decompress the stomach.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Hepatitis A does not infect the kidneys. Hepatitis A is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver, causing inflammation.
B. Manifestations of hepatitis A are indeed similar to flu-like symptoms. Common symptoms include fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
C. The incubation period for hepatitis A is typically 15 to 50 days, not 5 days. The incubation period is the time between exposure to the virus and the onset of symptoms.
D. A family history is not a significant risk factor for acquiring hepatitis A. Hepatitis A is primarily transmitted through the fecal-oral route, often due to contaminated food or water. It is more commonly associated with exposure to the virus through contaminated environments or ingestion of contaminated food or water.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
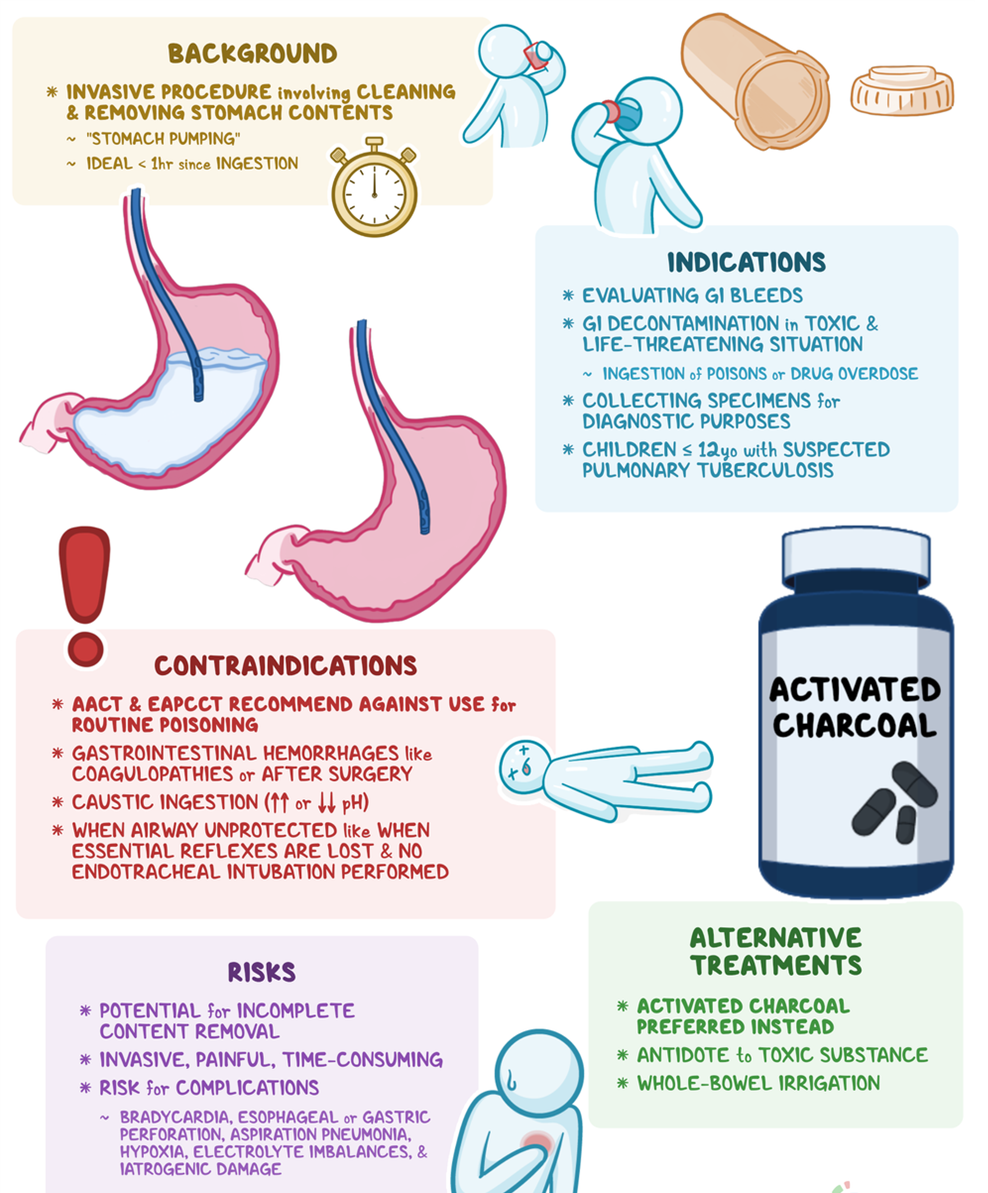
A. Positioning the client on the right side is not a standard recommendation for gastric lavage. The standard position is typically on the left side to facilitate the drainage of gastric contents.
B. Instilling 1000 mL of sterile saline is not a recommended action for gastric lavage. Gastric lavage involves the removal of stomach contents rather than instilling fluids.
C. Withdrawing fluid until it is clear is the correct action. Gastric lavage is a medical procedure used to empty the stomach contents. The process involves introducing small amounts of fluid (such as saline) into the stomach and then aspirating it back, along with gastric contents, until the aspirate is clear.
D. Connecting the NG tube to high continuous suction is not a standard approach for gastric lavage. Gastric lavage involves intermittent instillation and withdrawal of small amounts of fluid to clear the stomach.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
