A nurse is reviewing the laboratory findings for a client who has idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). Which of the following findings should the nurse expect to be decreased?
RBC
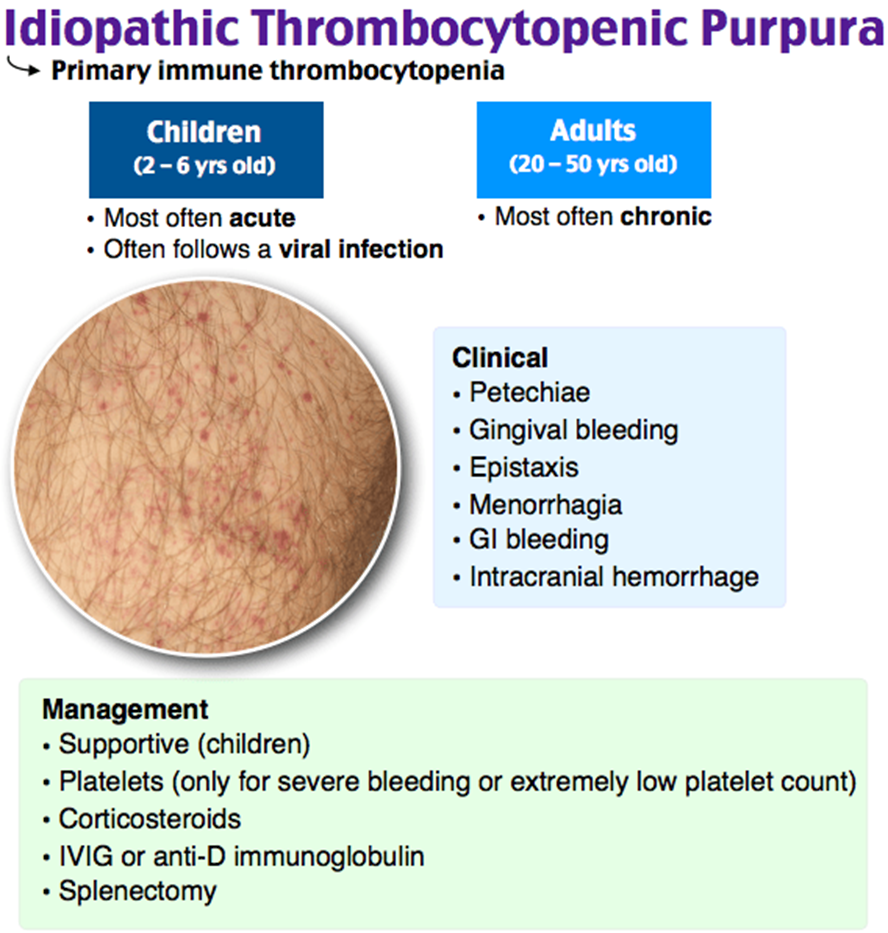
Platelets
Granulocytes
WBC
The Correct Answer is B
A. RBC (Red Blood Cells): ITP primarily affects platelet levels, not red blood cells. Therefore, red blood cell counts are not typically decreased in ITP.
B. Platelets: This is the correct answer. ITP is characterized by a low platelet count due to immune-mediated destruction of platelets. A decreased platelet count can lead to an increased risk of bleeding.
C. Granulocytes: While ITP primarily affects platelets, it does not have a direct impact on granulocyte counts. Granulocytes are a type of white blood cell.
D. WBC (White Blood Cells): ITP primarily affects platelets, not white blood cells. Therefore, white blood cell counts are not typically decreased in ITP.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","C","D","E"]
Explanation
Asthma action plans often use a color-coded system to guide management based on peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) measurements. The zones are typically green (80-100% of personal best), yellow (50-79% of personal best), and red (less than 50% of personal best).
A. The student needs to go to the hospital.
This is not necessarily required when the student is in the yellow zone. The yellow zone indicates caution and the need for intervention, but it does not immediately require hospitalization unless symptoms worsen or do not improve after using the quick-relief inhaler.
B. The nurse should obtain a second expiratory flow rate.
Confirming the peak flow measurement with a second reading ensures accuracy and helps to make informed decisions about the student's asthma management.
C. The student should use his quick-relief inhaler.
In the yellow zone, indicating moderate impairment, the use of a quick-relief (rescue) inhaler is often recommended to relieve symptoms and prevent progression to the red zone.
D. The student's peak flow is 50% to 80% of his best peak flow.
This is the correct range for the yellow zone, indicating moderate impairment. Action is needed to prevent worsening.
E. The student's asthma is not well controlled.
Being in the yellow zone indicates that the asthma is not well controlled and may require adjustments in the long-term management plan, including possible changes to daily controller medications.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. A room that is within view of the nurses' station: While visibility to the nurses' station is advantageous for monitoring the client, it is not the most critical consideration for a client with active tuberculosis. The priority is to prevent the spread of infectious droplets to other clients and healthcare workers.
B. A room in the ICU: Placing a client with active tuberculosis in the ICU may not be necessary unless there are specific medical reasons requiring intensive care. However, the room assignment should prioritize infection control measures.
C. A room with another nonsurgical client: It is not advisable to place a client with active tuberculosis in a room with another nonsurgical client due to the risk of spreading the infection to a potentially vulnerable individual.
D. A room with air exhaust directly to the outdoor environment: This is the correct answer. The preferred room assignment for a client with active tuberculosis is one with proper ventilation that allows air to be exhausted directly to the outdoor environment. Negative pressure rooms with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration are often used to minimize the risk of airborne transmission.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
