A nurse is providing anticipatory guidance to the parents of a newborn about feeding skills. Place the following feeding skills in the order the newborn should develop them. (Move the steps into the box on the right, placing them in the selected order of performance. Use all of the steps.)
Pushes solid objects from mouth
Eats pieces of soft, cooked food
Drinks from a cup held by another person
Begins experimenting with a spoon
Correct Answer : A,B,C,D
Choice A rationale: Around 10 to 12 months of age, babies develop more advanced oral motor skills and can start to use their tongue to push solid objects out of their mouth. This is a natural reflex that helps prevent choking as they continue to learn how to eat solid foods.
Choice B rationale: Between 8 to 10 months of age, babies start to develop the ability to chew and swallow soft, cooked food. At this stage, they are typically introduced to mashed or finely chopped solid foods to complement their breast milk or formula diet.
Choice C rationale: Newborns typically start with bottle-feeding or breastfeeding. As they grow and develop, they eventually transition to drinking from a cup, which is usually introduced around 6 to 9 months of age. At this stage, the baby is held by another person while they drink from a cup with assistance.
Choice D rationale: Around 6 to 8 months of age, infants start showing an interest in self-feeding and may begin experimenting with a spoon. They may try to scoop food with a spoon but often need assistance and are still primarily dependent on being fed by a caregiver.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
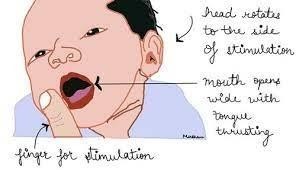
Choice A rationale: The rooting reflex is a natural reflex in newborns that helps them find the nipple for feeding. When the baby's cheek is touched or stroked, they will turn their head in that direction and open their mouth, searching for the breast or bottle.
Choice B rationale: The Babinski reflex is a different reflex, which involves the fanning and curling of the toes when the sole of the foot is stroked. It is not related to sucking or feeding.
Choice C rationale: The Moro reflex, also known as the startle reflex, occurs when a newborn is startled by a sudden noise or movement. The baby reacts by extending their arms and legs and then bringing them back toward the center of their body. It is not related to sucking or feeding.
Choice D rationale: The stepping reflex is observed when a newborn is held upright with their feet touching a solid surface. The baby will make stepping movements, but it is not related to sucking or feeding.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale: An amniocentesis involves inserting a needle through the abdominal wall into the amniotic sac to obtain a sample of amniotic fluid. Emptying the bladder before the procedure reduces the risk of bladder puncture during the process.
Choice B rationale: Fasting is not typically necessary for an amniocentesis. It is generally done on an outpatient basis, and fasting is not required.
Choice C rationale: An enema is not necessary before an amniocentesis and is not part of the standard preparation.
Choice D rationale: While cleanliness is important, this instruction is not specific to an amniocentesis and is not a standard pre-procedure requirement.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
